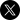The Rise of Android-Specific Malware on the Darknet
2020: the year of the “RAT”
While 2020 has largely become known for the surge in large and small-scale ransomware attacks, which skyrocketed indiscriminately across industries, our analysts have also witnessed an increase in the offers of Android-based Remote Access Trojans/Tools (RATs). These criminally-masterminded digital weapons are used not only to extract information from and spy on Android mobile devices, but are also often the attack vector through which many of the ransomware variants that have been deployed in recent attacks were delivered.
Android-specific malware, especially if deployed alongside a “crypter,” is one of many credible threats to commercial and government organizations that utilize devices with the Android operating system. DarkOwl discovered that threat actors are successfully deploying mobile ransomware such as “Sauron Locker” and RATs such as AhMyth, disguised as a COVID-19 testing app, designed to ‘exfiltrate’ or extract the contents of the mobile device without knowledge of the user, and further ‘extort’ the user locking the device until cryptocurrency ransom is paid.
Android Malware On The Darknet: A Conscious Intention
As discussed in previous reporting, a threat actor that plans offensive operations against a unique range of targets will utilize whatever cyber weapons and tools that are available in their arsenal to destabilize and/or damage their targets. Targets ranging from everyday citizens, government officials, healthcare workers, lawyers, etc. The open-source nature of the Android OS provides an excellent starting point for direct software exploration and ultimate exploitation of vulnerabilities in the technology. This opportunity is not exclusive to nation state actors and their proxies, but amateur cybercrime enthusiasts who are entering the underground malware development community are perfectly capable with the right motivation such as political agenda or social movement to utilize such exploits in their inventory of cyber tools.
The successful implementation of distributing malware and exploiting device vulnerabilities lies in the obscuration and obfuscation methods employed. Deep web and darknet forum users also have the option to purchase DNS hosting services for anonymous port forwarding for their malware, VPNs, RDPs, remote administration tools, ransomware, as well as the specific crypter needed to make the malware fully undetected or undetectable.
RATs on the darknet: Common variants for offer
CERBERUS
Since 2019, one of the most widely discussed RATs has been is Cerberus, particularly in the context of targeting banking applications supported by the Google Play store and Android mobile operating systems.
The Cerberus RAT is capable of deep surveillance within the victim’s device, interfering with the encrypted communications the phone has with its apps, and outside. An update to the RAT appeared in 2020 (v2) that has additional security-evasion functionalities, such as stealing two-step authentication (2FA) codes from apps like Google Authenticator.
Essentially, the Cerberus RAT is capable of intercepting and recording a victim’s mobile phone’s unlock pattern or PIN, Google Authenticator codes, and intercepting SMS messages necessary to perform a two-step authentication. Similarly, this malware can embed itself between the victim and their mobile banking application sitting and waiting to extract any and all the necessary data to perform bank fraud.
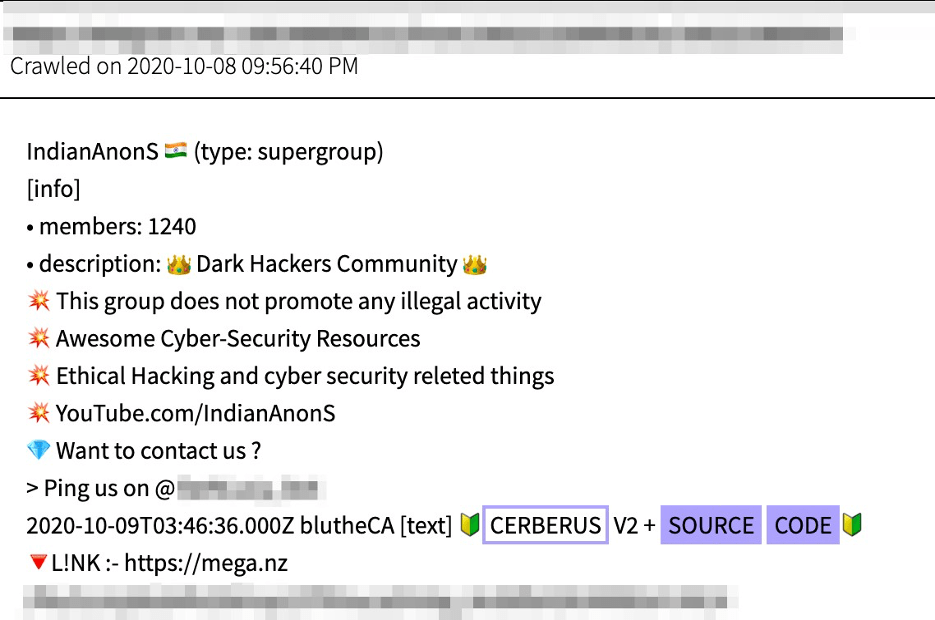
Figure 1: In early October 2020, a Telegram user “blutheCA” posted a link to the Cerberus V2 source code on the IndianAnons supergroup channel. (Source – DarkOwl Vision)
In late July 2020, the developers of Cerberus decided to get out of the banking fraud business, apparently due to internal group conflicts and subsequent fracture, and the main developer offered their entire operation, including the source code and C2 network, for auction. Unfortunately, no one was interested in taking on their criminal operations and the developers instead released the source code of the Cerberus malware into the wild. The auction was marketed on popular darknet malware forum, exploit, with a starting price of $25,000 USD and advertised monthly profit of $10,000 USD. The developers stated they were including “the source code of the apk, the source code of the module, the source code of the admin panel, their servers, the customer base with an active license, the contact list of customers, the contact list of those who wanted to purchase the product, and a lot of additional information.”
Other users on the forum suggested that Google Play released a security update that is capable of detecting Cerberus’s main module signature and this RAT was no longer viable without software changes.
ALIEN
Within weeks of the Cerberus source code leaks, a fork of the initial variant of Cerberus (v1) called Alien surfaced for sale on the darknet. In addition to all the main capabilities that Cerberus provided, Alien also included a keylogger, device application installs, removals, and service start and stop, 2FA authenticator stealer, and device notification sniffer. The Alien RAT successfully installs and leverages the commercial TeamViewer application in its operation on the victim’s mobile device providing the threat actors full remote control and observation of the device and its owner’s behaviors. (Source)
A longtime user of the darknet forum, exploit, using the pseudonym “megabyte” first offered a three-month license to use the Alien Android RAT on August 14, 2020 for $4,500 USD.
AHMYTH
Over the last three years, AhMyth is another malicious Android RAT that has been actively traded and discussed on the darknet. Its repositories on github.com were updated as recently as three months ago. The RAT includes an electron-framework based server-side desktop application and the APK installers for the client or victim’s Android device. The developer is active on Twitter under the handle @AhMythDev and states their location is Oman.
The AyMyth RAT features:
•A file manager allowing the threat actor to view the contents of the victim’s device including firmware
•Access to victim device’s browser data, cookies and web browsing history
•Remote access to the victim’s device microphone and camera
•Remote access to all device call logs
•SMS access – allows the threat actor to not only read but also send SMS text messages from the victim’s device
•GPS location data – allows for the threat actor to track the geographical location of the victim.

Figure 2: Screenshot of AhMyth repository on GitHub (Source – hxxps://github.com/AhMyth/AhMyth-Android-RAT)
ROGUE

Figure 3: Advertisement for Rogue RAT (Source: DarkOwl Vision)
Earlier this year, open source reporting indicated that the developers of the Rogue RAT had been circulating the malware across darknet forums for rent for as little as $29 USD per calendar month and offering discounts such as $45 for 3 months and lifetime memberships. According to researchers, the Rogue RAT exploits Google’s Firebase development platform to conceal its malevolence and Android’s Accessibility Services to bypass restrictions on tracking user actions and registers its own notification service to view such messages on the infected device; an exploitation technique observed with other Android malware strains.
The seller of the RAT, known as “Triangulum” released version 6.2 of the malware on deep web forums back in April 2020, and its source code emerged too, revealing that the Rogue RAT does not appear to be a unique malware codebase, but instead an update to an earlier variant known as DarkShades.
COVID-THEMED (DISGUISED) RATS
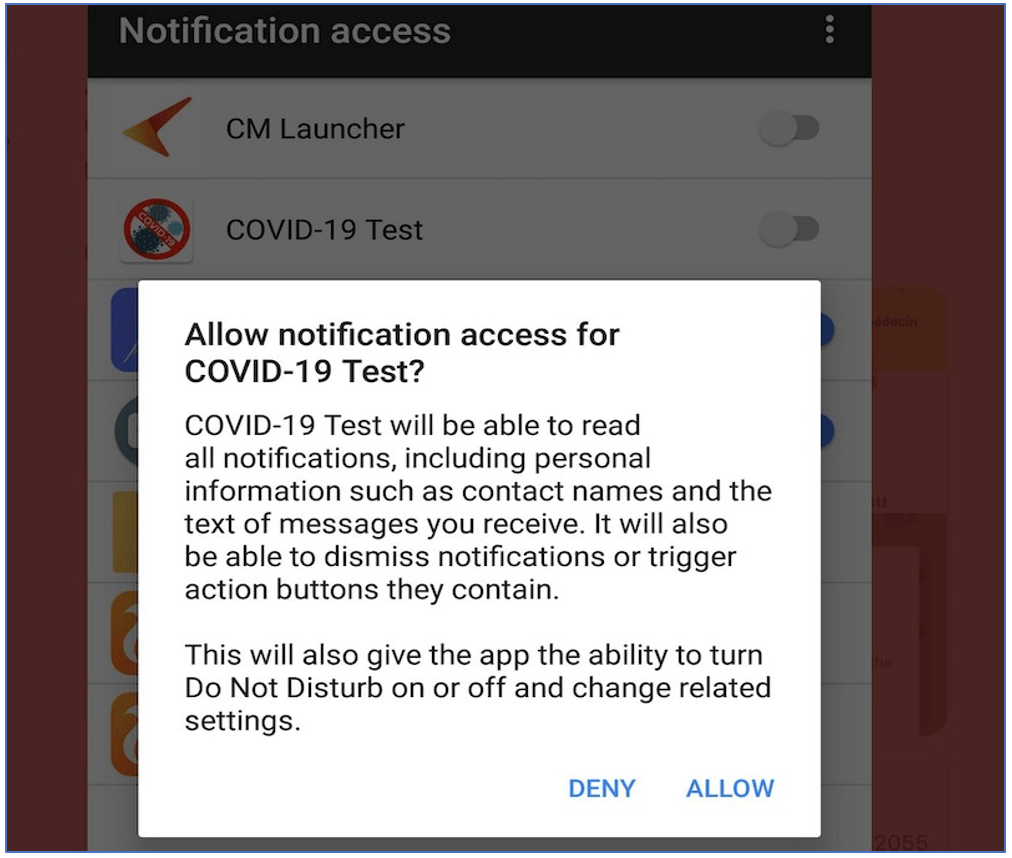
Figure 4: Screenshot from Twitter (Source: https://twitter.com/LukasStefanko/status/1306143556281737217/photo/4)
Given the ‘open-source’ nature of the AhMyth Android RAT, DarkOwl analysts have observed several malicious Android RAT variations based on the AhMyth source code. For example, a malicious fake Indian-based COVID app for Android surfaced in 2020 with remarkable similarities to the AhMyth RAT. The command-and-control (C2) server’s IP address is hard-coded as has been identified as a private IP address: 192.168.1.99:1234 and public IP of: 122.10.114.159. (Source)
Other Twitter users observed the AhMyth RAT disguised as a COVID-19 testing app. Observations came to light in September 2020 in France when a fake website mimicking legitimate services surfaced with a C2 domain identified as hxxp://tweensangoma.servebbs[.]com:22222.
Security researchers assess that Pakistani hacking group, Transparent Tribe, has been actively exploiting COVID-related tracking and monitoring applications for serving up malicious mobile malware. Their targets are often Indian government organizations and persons, explaining why the malware was found alongside Indian-specific COVID tracking apps. The group does not exclusively target Indian organizations as their victims. Multiple darknet sources state the group has successfully attacked more than 1,000 victims in over 27 countries and present as a formidable criminal cyber organization.
Internet security company DomainTools discovered that an Android app called “COVID19 Tracker,” which disguised itself as a coronavirus outbreak geo-tracking tool was actually ransomware that locked the users phone and demanded a payment of $100 in bitcoin within 48 hours, according to reporting.
More recently, a relatively new darknet user named “Shade Me” listed MD5 hashes used as indicators of compromise (IOCs) for twelve COVID-titled Android RATs. Their post, titled, “Most popular Android Threats 2020” was published to a popular deep web forum in September, 2020. Both Covid-Ahmyth and Covid-Cerberus were included in the list. GitHub user sk3ptre shared the same list including the live strains of the malware on their GitHub repository at hxxps://github.com/sk3ptre/AndroidMalware_2020.
Deeper dive: Android-specific ransomware on the darknet
With all the publicity around ransomware attacks of corporate networks around the world in 2020, few realize that mobile devices such as Android and iOS are susceptible to ransomware attack. Law Enforcement indicated they knew of this and warned in their intelligence briefings in the BlueLeaks collection leaked by DDoSecrets in mid-2020.
Users on the darknet discussion forum, dread also confirm that sophisticated Android-based ransomware is in development by some of the most prolific ransomware criminal gangs in the underground.
“Android ransomware is hard, I think maze is working on some currently but I’m not sure how far they’ve got.”
After considerable review of the popular Android-specific ransomware payloads available for sale or use on the darknet and deep web, DarkOwl analysts believes Android-based ransomware and device locking will be a noteworthy feature of standalone ransomware payloads, RATs and banking botnets.
There is a plethora of free and pay2play downloads available from notable threat actors and well-respected darknet hidden services, accompanied by instructions on how to use the ransomware. The availability of detailed instructions facilitates the most novice malware fanatic to put such malicious code to action without much effort.
SAURON LOCKER

Figure 5: Offer for Sauron Locker on Deep Web Forum (Source – DarkOwl Vision)
Sauron Locker has been observed distributed to Android devices on a cracked version of the popular mobile game, Clash Royale originally developed by Supercell. The unsuspecting victims hoping to get the free-cracked version on third-party websites are instead delivered the malicious ransomware and their devices locked with ransomware demands displayed. Sauron Locker also includes geographical location detection, allowing it to provide custom ransomware notes and payment demands based on the location of its victims. Researchers have observed the locker demand higher ransoms for victims in the US than in Europe or Russia.
Sauron Locker was most recently advertised on a popular hacking deep web forum by the user, blackhatrussia. DarkOwl analysts have observed blackhatrussia frequently distributing various strains of malware, including Sauron Locker, on hacking forums and their personal website. Sauron Locker is advertised to work on Android devices from 4.4 kit kat to Android 9.0 pie. blackhatrussia accepts payment for the malware exclusively via several cryptocurrencies including: Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Dogecoin. Interestingly, on the threat actor’s personal website, Sauron Locker appears to be available free of charge with three unique download links that may or may not also infect the user in the process of download.
In November 2020, DarkOwl also uncovered another Sauron Locker specific thread on one of the most respected darknet forums, by the user, Cold_Killer. Instead of providing the source code for the ransomware directly. Cold_Killer is requesting $60 USD in cryptocurrency in order to merely use Sauron Locker. The download links are included in the thread, which presumably are password protected, and credentials are handed over once a payment is provided.
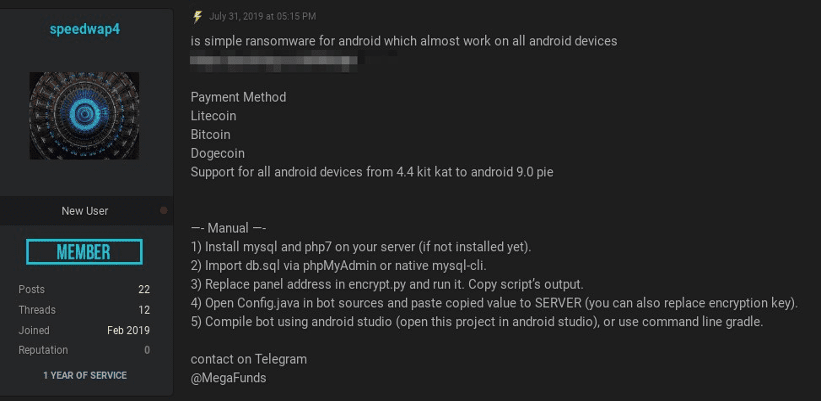
Figure 6: Offer for Sauron Locker on Deep Web Forum (Source – DarkOwl Vision)
Not too surprisingly, DarkOwl also discovered a Sauron Locker thread on additional deep web forums (pictured above), by the user speedwap4. This thread is almost an exact copy of blackhatrussia’s. The user speedwap4 included their Telegram contact information “@MegaFunds” in the advertisement for future discussion. The Telegram handle has been associated with other darknet actors across the darknet carding and hacking communities including Bitcoin stealers.
This association with Bitcoin stealers might explain the origins of observations by some researchers where Sauron Locker is installed alongside a cryptocurrency miner that readily consumes the victim’s device’s resources, data, and bandwidth as it uses these to mine for digital currencies like Bitcoin.
XERXES ANDROID BOTNET
In early February, a Telegram post included a link to the Xerxes Android Botnet advertised by a malware developer known as @zEdHacKs. Interestingly, this same name was used as a password to access the software download link shared on a similar hacking-focused Telegram group back in 2019. In addition to a device locker, this botnet is advertised to also include an SMS Stealer, App Downloader, Credit Card Grabber, and Notification Sender. DarkOwl has not confirmed how effective this malware is once deployed on a victim’s device.
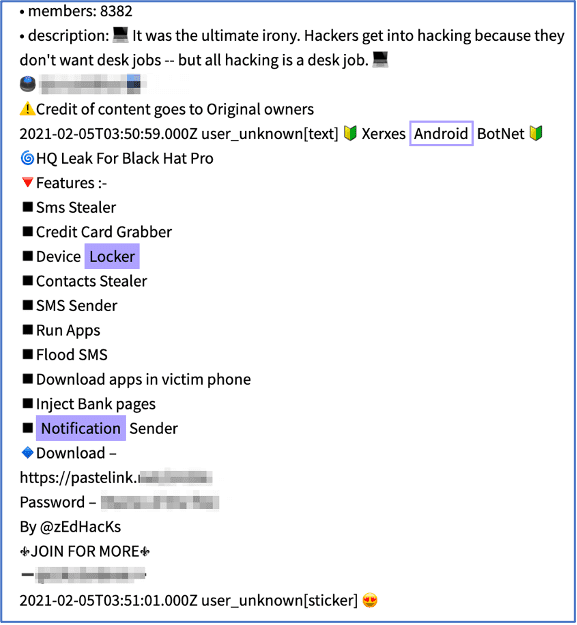
Figure 7: Advertisement posted on Telegram for the Xerxes Android Botnet (Source: DarkOwl Vision)
OXYN-ANDROID-BOT
The Oxyn-Android-Bot is similarly advertised to include the OX-Locker ransomware in addition to exfiltration of banking and personal data of the victim’s Android device. This malware variant also includes harvest of the geolocation data of the device and notification manipulation, a technique discussed in detail in a Microsoft report published late last year, advising on the dangers of a ransomware strain they call MalLocker.B that hijacks the incoming call notification for exploitation. (Source)
The creator of the Oxyn-Android-Bot is active across many of the key darknet communities and like other malware developer, leverages GitHub to distribute information the malware, in addition to darknet and deep web criminal forums and Telegram channels.
The latest price range for this malware was $1200 to $2,000 USD depending on the type of customer support package purchased.
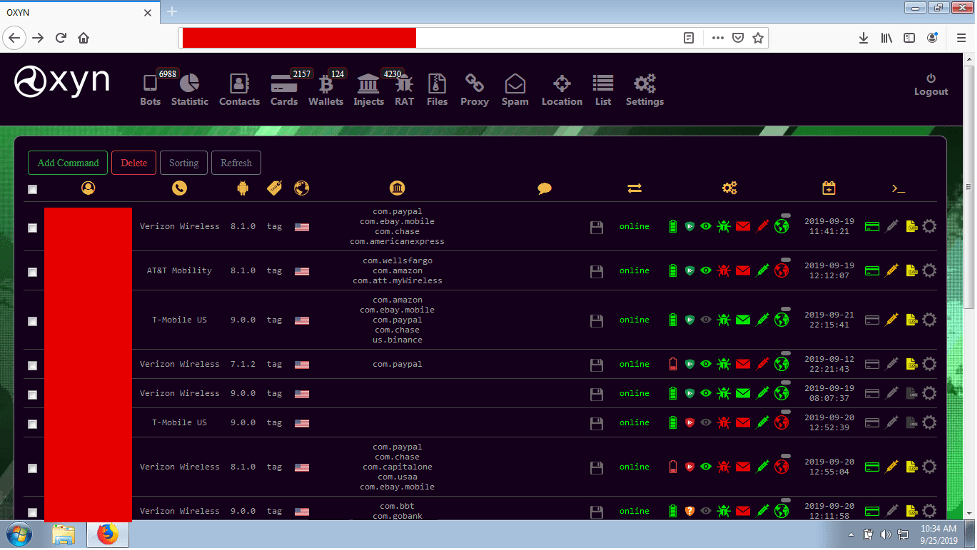
Figure 8: Oxyn-Android-Bot (Source: GitHub)
COVIDLOCKER & WANNALOCKER
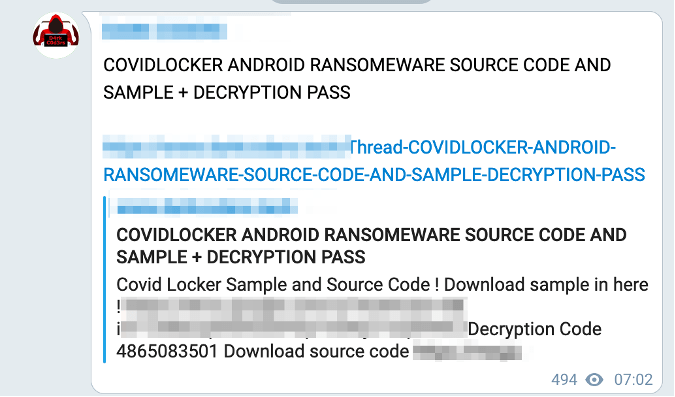
Figure 9: Telegram advertisement for CovidLocker (Source: Telegram)
DarkOwl became aware of these Android Ransomware strains by name after they appeared for download on a hacker Telegram channel last October.
The offer included links to download the ransomware’s source code and decryption passkeys. The community where this ransomware was discovered offers tutorials and mentorship – along with several “ransomware builder” collections for those in the early-stages of learning how to write and deploy malicious malware for financial gain.
Like Oxyn’s bot, DarkOwl has not verified the degree of severity or specific technical details of this ransomware variants’ features.
Threat Attack Vector for Android OS Attacks
Easy Delivery Method
Android ransomware can be delivered via malicious app download, as observed with Sauron Locker or via SMS message. In 2019, malware developers delivered their ransomware via malicious posts to popular Android-developer focused boards on Reddit and XDA Developers. (Source)
Network-wide deployment against employee devices is not impossible. A successful phishing or vishing attack against users can give threat actors full control of the device. Once inside the device, lateral movement within the network can infect multiple devices at once. Just recently IBM uncovered a phishing attack using a very similar strategy.
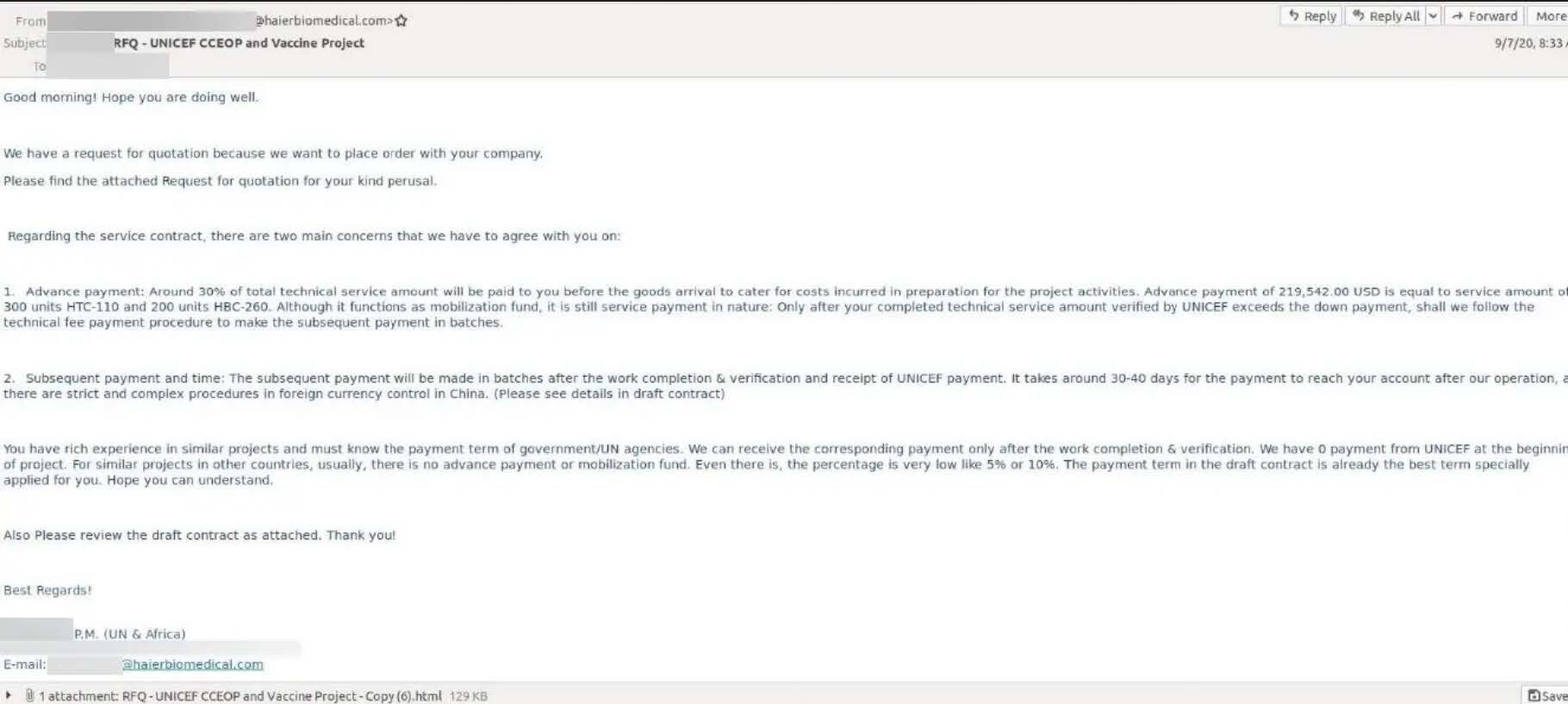
Figure 10: Example of a phishing email, which is a common threat deployment vector for RATs (Source – https://securityintelligence.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/1606993218.jpeg)
“FUD” (no, not that FUD) MALWARE
As previously mentioned, there are a number of readily available “crypters” available for use against Android OS and used in conjunction with Android RATs. DarkOwl analysts discovered users on Telegram sharing an APK crypter that includes an anti-virus bypass coded in Java in 2020, allegedly by DedSec hacking crew (though there is some suspicion that this might be a case of alias hijacking).
They describe this malware variant as “Fud” – which in this case is intended to stand for “fully undetectable.”
![Figure 11: “[Fud]APK Crypter” for sale (Source -DarkOwl Vision)](https://www.darkowl.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/mw11.jpg)
Figure 11: “[Fud]APK Crypter” for sale (Source -DarkOwl Vision)
An Ever-Evolving Threat
At the end of 2020, DarkOwl analysts were informed by darknet sources of a Cyberpunk 2077 related ransomware in circulation across the video gaming community. Shortly after the debut of the popular cyberpunk game, cybercriminals uploaded a “fake” Cyberpunk 2077 Android app to a fake website impersonating the Google Play store that installed BlackKingdom Coderware, developed by Telegram user “@Codersan” that subsequently encrypted all the device’s files, including the embarrassing selfies and displayed a ransom note for $500 USD before files can be recovered.
In early January, DarkOwl detected the source code for this malware with the filename: coderware.ransomware_py, confirming it was developed in Python, posted on a popular darknet hacking forum. The forum user included criticism of the code, stating it was “script kiddie ransomware.”
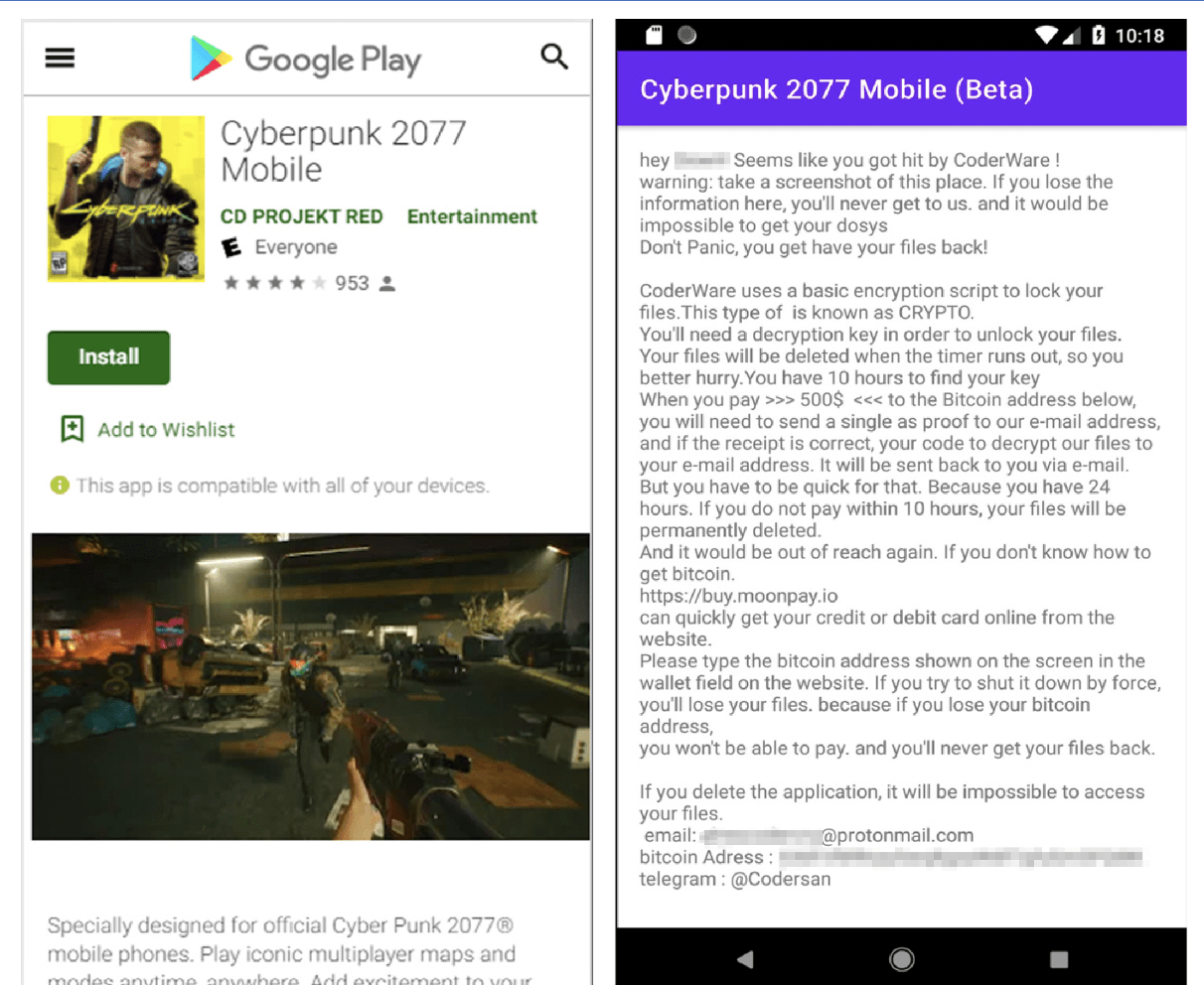
Figures 12 & 13: Screen captures of the Cyberpunk2077 malware offered on Google Play Store.
Researchers at Kapersky first detected the ransomware in the wild and noted that the files can be easily decrypted using any RC4 decryptor. Luckily, there are a number of decrpyters readily available on GitHub along with the apk file and malware sample: hxxps://github.com/dot-sec/Cyberpunk2077-android-malware.
This Cyberpunk 2077 fake ransomware delivery app is completely unrelated to the ransomware attack that the developers of the Witchers series have been battling since February 9th, earlier this month. The CD PROJEKT RED Twitter account (@CDPROJEKTRED) shared an update including the ransom note which included threats to release the source code of their popular game series.
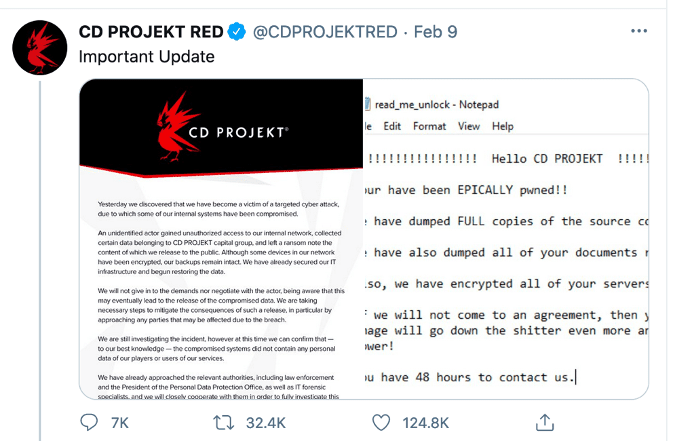
Figure 14: Screenshot from Twitter (Source: https://twitter.com/CDPROJEKTRED/status/1359048125403590660?s=19)
As DarkOwl has observed and historically reported, the darknet and deep web are home to an extensive malware economy, with marketplaces and forums that offer a wide range of malware, threats, and viruses. Sellers not only offer a variety RATs as described above, but also VPN services, exploits, crypters and ransomware, along with all the educational materials and personalized support: private guides, tutorials, and mentors for hire – ready to educate those newly entering the underground cyber-criminal industry.
Curious about something you’ve read, or want to learn more? Subscribe to our blog to get the latest.
Explore the Products
See why DarkOwl is the Leader in Darknet Data
Products
Services
Use Cases