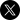Understanding the Difference Between Darknet Adjacent Chat Platforms, Part 1
December 15, 2022
In the early days of the internet, online communities and internet power users relied on web-based technologies like bulletin board systems (BBS), Usenet newsgroups, and internet relay chat (IRC) to communicate with each other near-real-time. Many of these technologies formed some of the earliest communications avenues for cyber criminals using the internet to hack networks and steal information. Even though many of these chat protocols persist and are still in use today by criminal communities, newer chat platforms, especially those that include privacy-enhanced features like end-to-end encryption or anonymity are preferred by many threat actors that collaborate across the dark web.
Many of the chat platforms and networks we will discuss today include channels and communities that are perfectly legitimate and even could be casually considered a form of ‘social media.’ Despite this, DarkOwl refers to chat platforms such as IRC, Telegram, and qTox that have considerable use by darknet cyber criminals as ‘darknet adjacent’ for their role in persisting illicit goods trade, fraudulent activities, and cybercrime.
Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
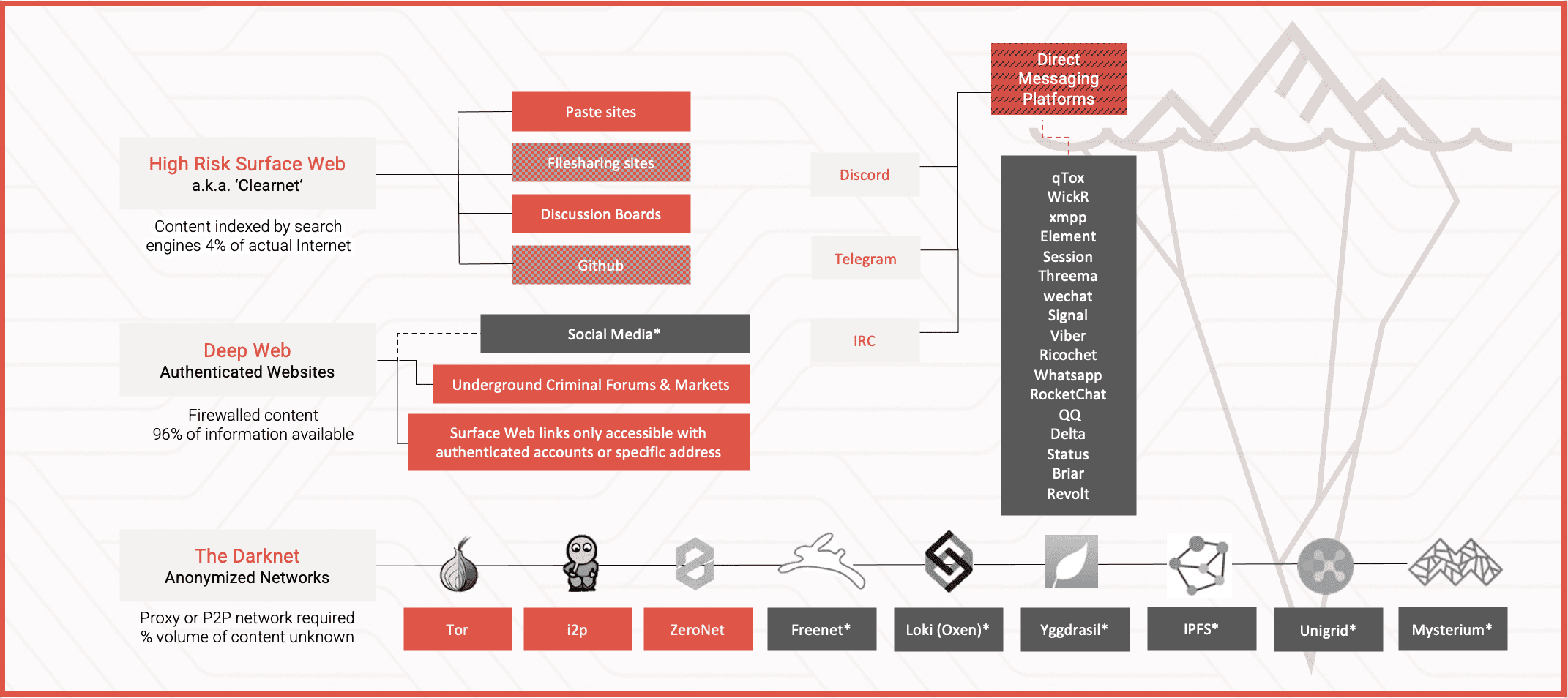
In the late 1980s, IRC was the protocol of choice for communicating real-time with others across the internet. Shortly after, AOL’s instant messenger and their associated chat rooms skyrocketed in popularity as widespread use of the internet spread around the US and abroad. IRC was codified in 1993 as RFC 1459 as an open-source networking protocol, and even though it was originally developed by the Finnish software developer, Jarkko Oikarinen, a.k.a “WiZ”, IRC does not belong to any specific person or group. As use of AOL’s platform diminished in the 2000s, IRC persisted in use, especially amongst technology-savvy and privacy conscious internet users. The size and volume of content distributed via IRC is unknown as there are hundreds of IRC servers and thousands of channels available to connect to at any given time. IRC severs with malicious conversations are often hosted on Tor. Many IRC clients like HexChat support traffic over SOCKS5 proxy for enhanced privacy and security. A virtual private network (VPN) is often recommended to provide additional security protection to IRC server nicks.
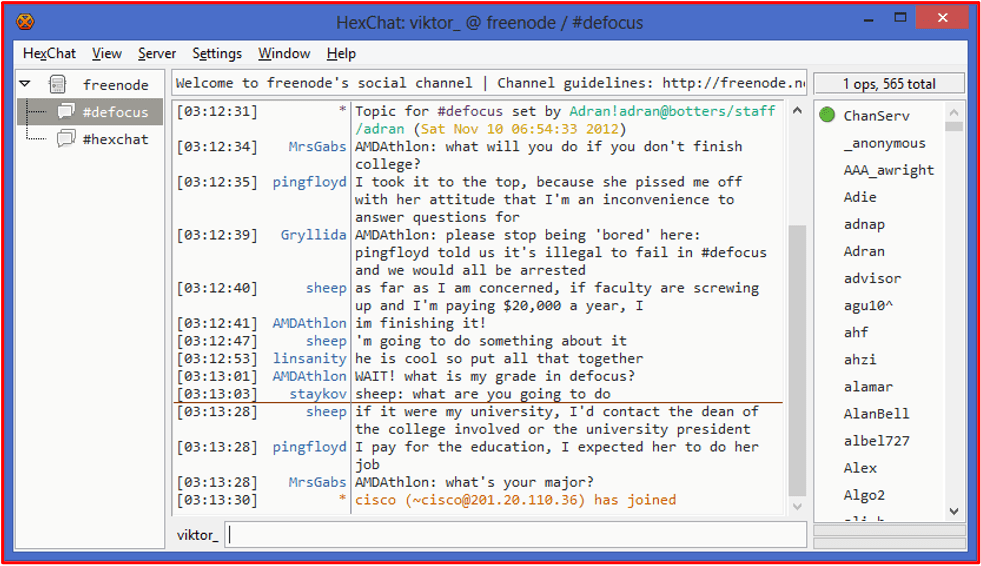
Figure 1: Source – HexChat
Telegram
In 2013, the Russian-born French Emirati entrepreneur, Pavel Durov, launched Telegram messenger. Pavel had established his leadership in Russian-internet technologies, founding the Russian Facebook equivalent social media conglomerate, VKontakte (VK), six years before debuting Telegram. Pavel advocates for personal data privacy in its public advertising of Telegram, stating that selling user data is not a core feature of its software business model nor is user information shared with marketers, advertisers, or third parties — a stark contrast to similar services offered by Facebook’s (Meta’s) Whatsapp and Google Hangouts. Telegram also features a ‘secret chats’ option where all messages are end-to-end encrypted and impossible to screenshot by the chat participants on their device.
Most Telegram channels are public and open for any Telegram user to join. Others are only accessible by invitation. Channels are typically ‘read only’ with the channel owner posting most of the messages and content where Telegram groups allow participants of the groups to start the conversations more akin to a live chat format with dynamic activity from the members of the channel.
In recent years, Telegram channels promoting cybercrime and fraud have surged in volume and usage. The Ukraine-Russia military conflict increased popularity in Telegram considerably with thousands of channels – for both countries – sharing live updates from the battlefield and cyber targets for hacktivism and military cyber campaigns. Information operations campaigns have leveraged right-wing extremism Telegram channels for circulating anti-US and anti-NATO related dis[mis]-information since the war began.
Telegram has historically required a phone number, e.g. SIM or VoIP, to join the application as Telegram levied OTP and multi-factor authentication for the account security. In recent news, Telegram officially announced they would no longer require SIMs for account activation, but users could instead register using ‘blockchain-powered’ phone numbers sold for $16 USD per account by Fragment — another entrepreneurial endeavor by Durov. Conveniently, payments for the anonymous phone numbers are possible through Telegram’s own cryptocurrency token known as The Open Network(TON).
In addition to the no-SIM sign-up, there are several other features in Telegram’s latest release (V9.2) including Topics 2.0, custom emojis and a emoji search feature for iOS, temporary QR codes, and a global auto-delete timer for destroying chat messages for both users.
Discord
While Telegram was created with user’s privacy in mind, Discord was developed with the intent to facilitate open and fast Internet-based communication across online communities, content creators, and friends. Discord developers designed the platform with video gaming communities as its targeted userbase and the application has been publicly available since 2015. Since its growth in popularity, the application hosts servers and channels where private and public users are invited to talk openly about any topic imaginable; many Discord servers support voice and video communications as well. Such deanonymizing features of Discord are a serious red flag for serious darknet users tempted to use the Discord platform although many users suggest simply using a voice changer to obfuscate the sound of one’s voice.
In 2017, Discord allowed for publishers and developers to have their servers verified using social media or other verification methods to receive a Discord badge – like the Twitter blue checkmark – to designate them as official communities. Each server can host hundreds of channels that users utilize to instantly message or share files between channel members. In 2021, Discord launched a new feature called ‘Threads’ which are temporary text-only based channels that have an auto-destruction feature, like Signal’s self-destruct message feature. In late 2022, Discord debuted “Forum Channels” which mirror the format used across Tor or deep web criminal forums where discussions are organized by a topic with an original post and subsequent posts/comments on the original poster’s message are listed sequentially below in a thread like format. This feature was clearly designed to keep users on platform to facilitate the demand for highly structured, and organized discussions instead of freestyle chat.
Figure 2: Source – discord.com
qTox
Another privacy-first focused darknet adjacent chat platform is qTox. Also simply called “Tox” this chat platform is built by and for the users, meaning the source code is a free and open source (FOSS) project without any centralized servers or protocols that could be compromised. The platform forces perfect forward secrecy (PFS) as default – meaning a unique session key is generated with every chat. qTox also employs curve25519 for its key exchanges, xsalsa20 for symmetric encryption, and poly1305 for MACs.
Instead of registering with a phone number or an email address, qTox are assigned a unique 76-character Tox ID. The Tor onion routing protocol is used to store and locate Tox IDs increasing the security of linking users to their other OSINT personas or accounts. Deanonymization of Tox IDs and qTox users without using direct, advanced social engineering methods is impossible.qTox developers have recently formalized the TokTok project with Tox protocol documentation where they clearly state their mission – to promote universal freedom of expression and to preserve unrestricted information exchange – which in addition to the privacy-conscious nation state actors and cybercriminals also benefit from.
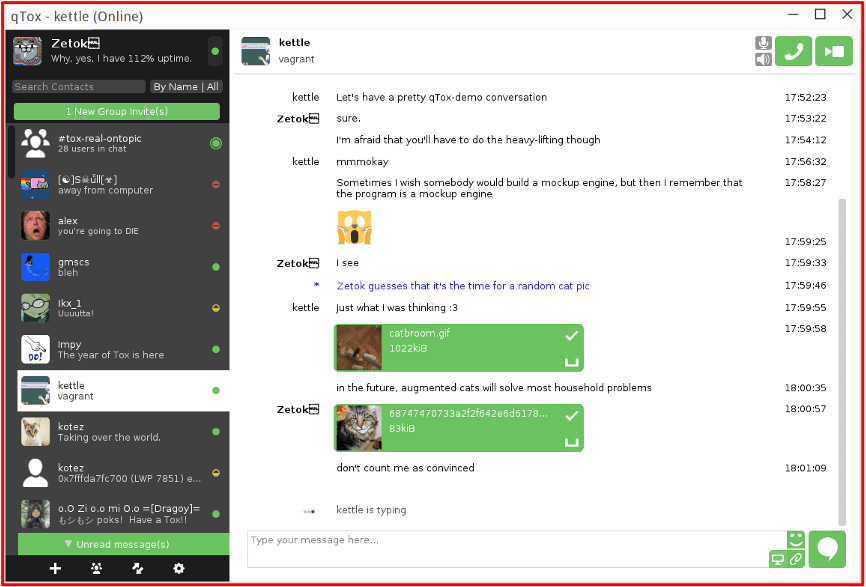
Figure 3: Source – tax.chat
One of the most predominant social applications in China is WeChat, also known as Weixin (微信). WeChat is often confused with its sibling microblogging site, Sina Weibo which is also widely used across the country. Where Weibo features content for mass distribution and behaves more like a social media platform like Twitter, WeChat is designed as a ‘semi-closed’ platform facilitating more direct 1-1 communications and smaller group conversations, which is why it has increased in popularly across Mandarin-speaking cybercriminals. Similar to Discord, WeChat offers instant messaging, voice, and video calls over the internet. Open source information detailing the technical specifications of WeChat is limited since the platform is owned by Tencent and use of the application is restricted to users located in mainland China. The app is leveraged heavily by the Chinese government for digital surveillance of their citizens’ online behavior and the app’s user’s device data.
Both WeChat and Weibo are considered social media so any data collected from WeChat, should be targeted to those specifically linked or referenced by darknet forum and marketplace users.
Interested in reading more content like this? Stay tuned for Part 2 where we will dive into even more Darknet adjacent platforms. Sign up to our newsletter below to be the first to know when it goes live.
Explore the Products
See why DarkOwl is the Leader in Darknet Data
Products
Services
Use Cases