Israel and Hamas Conflict : A 6 Month Review
April 09, 2024
A new Middle East conflict emerged on October 7, 2023, when Hamas launched an attack on Israel. It rages on to the present day, resulting in physical, digital, and hybrid events that threaten both Israel and Palestine and their borders with multiple surrounding countries. Regional stability is extremely low as actors supporting all sides of the conflict take stances and attack their self-defined opponents on the ground, at sea, and with cyber capabilities. Most recently, Hamas rejected an Israeli offer for a ceasefire on 25 March 2024, ensuring that this conflict continues for an undetermined amount of time.
In the past six months, some of the trending issues the world has witnessed include drastic upticks in maritime and ground-centered activity against Iranian-supported actors, such as the Houthis and Hezbollah. Air attacks and maritime incidents against the Houthis continue all over the Middle East region, impacting civilian vessels in various bodies of water and civilian shipping routes. Telegram remains a vital part of the conflict, with propaganda emerging from Iranian, Arabic, and Israeli Telegram channels, as well as sympathizers and opponents from all sides of the conflict taking a public stance and offering to attack on behalf of their beliefs. A sampling of these activities over the past six months since the start of the conflict is covered in this blog.
Telegram and Choosing Sides
As was previously mentioned and covered extensively in a previous blog, a trend that emerged almost immediately and continues six months later to today, was actors choosing sides in the conflict. No matter what side is supported, whether an entity is pro-Israel or pro-Hamas, supporters publicly emerge and then are targeted by opponents.

Figure 1: Killnet posting their intention to target the Israeli government on Telegram

Figure 2: Anonymous Sudan posting their intention to target the Israeli government on Telegram
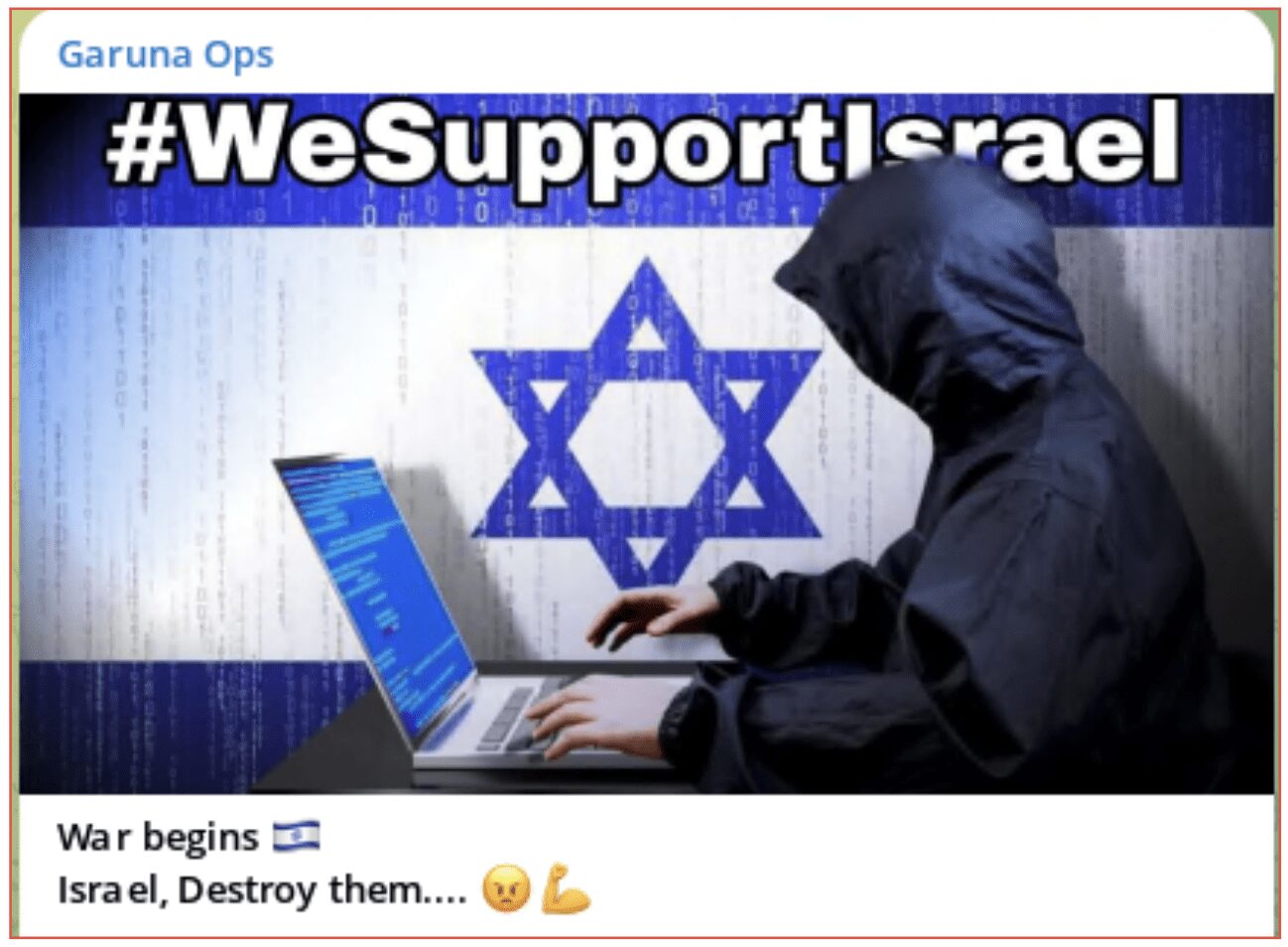
Figure 3: The group Garuna Ops made a number of posts on Telegram in support of Israel and stated as well as attacking Palestine they would attack any other countries that supported them
The end of 2023 witnessed a few key events, ensuring the conflict would continue into the new year of 2024. The list below is not exhaustive, and is only meant to provide high-level examples:
- Navitas Petroleum, based in Israel, was purportedly hit by BlackBasta ransomware (December, 2023)
- However, as of the time of this writing, Navitas had no entry on the BlackBasta ransomware victim blog. It is possible this event was fabricated, or that the impacted entity struck a deal of some kind with the BlackBasta actors to have their data removed from the ransomware website. Either way, the threat of malicious actors coming after an organization because of their country or other allegiance is a continuing trend.
- Predatory Sparrow hacking group attacked 70% of Iranian gas stations (December, 2023):

Figure 4: Predatory Sparrow group publicizes their attack of Iranian fuel stations in December, 2023; Source: DarkOwl Vision
- Iran issued a statement that the October 07 attack against Israel was in retaliation for the January 2020 assassination of IRGC commander Qassem Soleimani (December, 2023)
- Hamas leaders publicly rejected this claim.
In 2024, some incidents included (the list below is not exhaustive, and is only meant to provide high-level examples):
- Anonymous Sudan claims to have hit Israel’s telecom company Pelephone (January, 2024):

Figure 5: Anonymous Sudan uses their Telegram channel to advertise the January 2024 attack against Israeli Telecom Pelephone; Source: DarkOwl Vision
- Lulzsec group targeted Israeli red-rocket alert system:

Figure 6: Lulzsec hacking group advertises their mid-January 2024 efforts against the Israeli rocket alert system on Telegram
- Anonymous Sudan claims to have hit Israel’s Bazan group:

Figure 7: Hacking collective Anonymous Sudan uses their Telegram channel to publicize an attack on Israeli Bazan Group in January, 2024; Source: DarkOwl Vision
- Anonymous Sudan also claimed it conducted a cyberattack targeting “critical parts” of healthcare infrastructure in Israel, and adds “more than a thousand devices are completely disconnected.”
- Terminator Security hacking group claims to have taken down Israeli Air Force servers.
- As of mid-March 2024, Raytheon was again targeted, this time by the Anonymous group due to their supplying weapons to Israel. However, Raytheon and other US defense contractors are frequently targeted by Russian groups, such as this Snatch Ransomware group observation which also came in March 2024:

Figure 8: Snatch ransomware group details attacks against US government contractor Raytheon, which is frequently targeted due to its weapons supplied to Ukraine; Source: DarkOwl Vision
Maritime Activity
Underwater mining conducted by the Houthis and other attacks against maritime vessels continued as recently as mid-March, with this physical element of conflict having cyber implications:
- Underwater sea telecom cables that transit approximately 17% of international data were damaged as maritime conflict continued in the Red Sea. Some media outlets blamed Houthi militants, while other experts state the cables were damaged by ships sinking and hitting them, as they are in shallow waters.
Maritime activity in the Red Sea also involved the United States conducting a cyberattack on an Iranian ship that had been gathering intelligence on cargo vessels in the region. This was intended to prevent the ship from sharing intelligence with Houthi members in Yemen, who have been frequently targeting civilian vessels. DarkOwl analysts have observed multiple platforms, including Discord, onion websites, and 8kun, sharing information regarding the hostile situation in the Red Sea:

Figure 9: Users discuss and share videos of Iranian activity in the Red Sea between January to March 2024; Source: DarkOwl Vision

Figure 10: Users discuss and share videos of Iranian activity in the Red Sea between January to March 2024; Source: DarkOwl Vision

Figure 11: Users discuss and share videos of Iranian activity in the Red Sea between January to March 2024; Source: DarkOwl Vision
Hybrid Incidents
Hybrid events, comprised of both digital and physical efforts to have a real-world impact, have also grown. In mid-February 2024, international media reported on an attempt to reroute an Israeli El Al airliner. The original flight path was from Bangkok, Thailand, and Tel Aviv, Israel. However, during the flight, the crew were provided with instructions that derailed them from their set route. These instructions were discarded, and the crew remained on their original flight path, once they contacted other air traffic controllers and compared flight data, and realized actors were trying to intentionally mislead them.
The incident occurred over Somali airspace, and Israeli sources revealed a certain frequency that was consistently trying to change flight paths, indicating a constant attempt to disrupt air activity. Using technology to attempt to derail a plane or any other means of transportation that carries humans who could be used as leverage in a geopolitical situation, or harmed, brings a new level of urgency towards vetting online information tied to any world event, especially a conflict.
Conclusion
As is confirmed by the events above, conflict these days has a new paradigm using technology to influence and increase physical air, ground, and maritime events, such as using a certain frequency to communicate with planes while trying to pull them from a planned, safe route. Global infrastructure such as underwater cables are either accidentally damaged by water mining or intentionally cut, in some cases, to interfere with regional internet access and connectivity. These physical threats to infrastructure and personnel are separate to the propaganda that is quickly spun and shared among all sides via messaging platforms and social media.
Malicious actors use technology to go after petroleum and water supplies, or even put services for human life, such as healthcare, at risk during geopolitical incidents. Even weapons supplies are in danger, as actors try to prevent weapons delivery or jeopardize the providers of the weapons. The technological component to conflict is here to stay, and actors will undoubtedly use any platform they feel is safe – Telegram, social media, or private messaging, or an online collection of supporters who can contribute to research, and disseminating propaganda to try and influence the public to see issues from a certain perspective.
Don’t miss any research from DarkOwl analysts. Subscribe to email.
Explore the Products
See why DarkOwl is the Leader in Darknet Data
Products
Services
Use Cases