[Webinar Transcription] Unpacking the Dark Web, How Fraudsters Operate and Why It Matters
August 12, 2025
Or, watch on YouTube
Evan Blicker from DarkOwl explains the three types of internet (Surface Net, Deep Web, Dark Web) and the origins and workings of Tor. The session also covers common misconceptions about the dark web, types of information found there (e.g., PII, banking data, corporate data), and the importance of understanding it for cybersecurity. The speaker emphasizes operational security for investigators and introduces DarkOwl’s role in automating dark web data collection and analysis.
NOTE: Some content has been edited for length and clarity.
Good morning, everybody, and thank you for joining our iTOOsday. Today’s session was made possible by Leslie Cameron, who is the Managing Director of Alert Plus Technologies. Leslie is a seasoned IT professional with a long-standing career in technology, innovation and business solutions. His current focus is on cybersecurity and fraud prevention with a passion for helping individuals stay protected against identity theft as well as online threats. From DarkOwl, we will be joined by Evan Blicker. Evan is a cyber security professional with over a decade of experience in cyber threat intelligence, dark web investigations and digital forensics. He began his career at the Pasco Sheriff’s Office investigating cybercrime and internet crimes against children. He later served as a task force officer with Homeland Security Investigations, where he led transnational investigations focused on the dark web. His unique background bridges law enforcement with corporate security, and he has a deep expertise in OSINT, emerging threats and proactive intelligence strategies. For those of you who are unfamiliar with DarkOwl, they are the industry leading provider of dark net data, offering the world’s largest commercially available database of information collected from the dark net. With that, let’s jump into the conversation.
In today’s session, we are going to explore a side of the internet that very few people truly understand, yet it does impact us all, the dark web. Often sensationalized in media, the dark web is more than just a digital underworld. It’s a thriving ecosystem where stolen data, compromised credentials, cyber attack tools and illicit services are traded like currency. A cybercrime becomes increasingly organized, sophisticated and global, understanding what happens beneath the surface is essential for individuals and businesses looking to stay secure. I’m thrilled to be joined today by our expert, Evan from DarkOwl, which is one of the world’s leading providers in darknet intelligence. Over the next hour, we’ll uncover what’s really happening in the dark web, how it affects you, and as an organization and how you can effectively manage against it.
Evan: I’m a cyber threat investigator with DarkOwl. We’re here today to talk about the dark web, kind of unpacking it so we can get a better understanding of what it is, what type of data we can obtain from the dark web and how can we utilize that to better protect our clients, our organizations, and help make the internet and a little bit safer.
To start, we have a short disclaimer about this presentation being for informational purposes, only accessing the dark web manually can lead to security concerns if proper operational security is not followed. So, we want to make sure that this is understood that our presentation today is for informational purposes only.
We’re gonna cover some very awesome topics. We’re gonna go into how the dark web works, its origin, different things that we can find on there and the communities that operate on the dark web. The dark web very much is a community. Similar to any other community, whether you play sports or in the business community or volunteering. However that works, there’s always subsets, there’s always communities in there. So, we’re going to talk about some of those communities. And then we’re going to also go into a little bit about dark web investigations, right? How to utilize this information, how to take it from raw data to actionable intelligence. We’re going to cover a lot. It should be really fun. So, let’s get started.

What is the dark web? That is a question that gets asked a lot because we see movies, we see TV, it’s dramatized as this really cool person sitting in a basement wearing a hoodie, typing away at a black and green screen. And it’s not as cool as that, but it is still pretty interesting. So, there’s essentially three types of internets. The first one is the surface net – all of us here have used the surface net, right? That’s that sites that have been indexed by Google. So, if you have gone to any website like a news provider or to a you sports site or any of those other things. That’s the surface net, a website anybody can get to and you can find it through Google or one of the other search engines.
Now there’s also the deep web or deep net. We’ve all accessed this whether you’ve known it or not and this is any type of website that can’t be found without doing something else. So, for instance going to your banking site, you have to type in a login to get into your or your bank account information, that’s once you type in that login, you go to your bank account site, that itself is the deep web or the deep net. ‘Cause that’s not something that you would want to show up on Google. Could you imagine the world if you could just Google somebody’s bank account and see, it’d be a wild place.
And then we have the dark web or the darknet, and this is an internet that uses standard internet but requires special software. And this special software typically allows for anonymity. It also provides some level of security through encryption. It allows people to bypass maybe countries restriction on certain websites or whatever the case is. And that’s the dark web, which is what we’re going to be kind of focusing on today.
The dark web. It actually got its start by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. Onion Routing, it was designed to protect sensitive information for government communications. Then in about 2002, it was released as an open-source project to the public, where it remains as an open-source project, where lots of companies and organizations actually donate to keeping the project alive. So, it went away from its government excludability and went into average people, anybody being able to use it for their purposes. Because though when we hear the word dark web, we think cybercrime and criminals, there’s actually some very, very valid uses which we’ll touch into later related to the dark led. It has some good uses in this world. It’s used by a wide range of people seeking anonymity while they’re on the internet. They want some type of encryption for privacy concerns, but it is also involved into such a good complex ecosystem where you have not only people using it for negative purposes, but also people using it for good. The thing that I always kind of fall back on when talking about stuff on the internet is for everything good on the internet, there’s somebody there that’s able to take that good and use it for evil.
There are multiple dark web technologies. The one that we’re going to focus on and talk about today is Tor, because it is the most widely known dark web, but there are several others. So, these are logos from across the different one. The one in the upper left of the screen, that’s the onion routing, that’s TOR. That’s typically the one when somebody’s talking about the dark web, that’s what they’re referring to.
The onion router, TOR. It’s multi-layered encryption, right? It means data is wrapped into multiple layers of encryption and each node that you go through, I’ll explain this a little bit better in the next slide, encrypts only what it needs to, to pass the traffic onto the next thing. So, it typically goes through a minimum of three nodes. You have your entry node, you have your middle node, your exit node. The exit node is what sends your traffic onto your destination. And this allows for your data to be fully encrypted in through its path.

And this is its path. Now for any of those in the audience that maybe have a little bit more knowledge into the dark web, you don’t have to have a minimum of three notes. You can have seven, eight, nine, adding to your level of protection while using it. But this is typically how it goes standard, right? So, Alice needs to send the information to Bob. Bob’s a server. Alice’s traffic will go through three different nodes in a certain pattern. It’s a randomized pattern. And each one of those nodes, each one of those computers that the traffic passes through only has access to the information it needs to continue that packet onto its final destination. And then at which point it goes to Bob. The only time that that traffic is not encrypted is that final jump from the exit node to the target server. And this allows for that secure communication, right, allowing for that anonymity while using Tor.
Some of those features that we’ve already spoken about, anonymity, right, it gives you access to .onion websites. So, the Tor network doesn’t use .com or .net, they all end in .onion. It’s decentralized. The Tor project is actually really, really successful and really good at making sure one entity does not own too many nodes, right? Because I think it was mathematically calculated that if you owned 40% of the nodes, you can actually track somebody’s traffic across the Tor network. So, they do a really, really good job and so does the community as well as making sure that the people who are registering Tor nodes because anybody can do it, it’s a volunteer basis that they don’t own too many of them, right? Because we want to keep this decentralized. We want to make sure that the anonymity of what Tor provides us is there. And it also allows you to bypass censorship. Some countries censor the news and the media of what’s going on and this allows people and organizations in those countries to get valid news of what’s going on in the world. It allows for privacy and sensitive communications. So, take for instance, a journalist who is getting ready to break a big story with a whistleblower, this allows them to communicate in a manner which will protect the source and the story, right? And it has multi-platform support. So, you can be on your phone, you can be on your computer, whether it’s Mac, Windows, Linux, and still be able to access the Tor network.
It is downloadable at the torproject.org. There is a lot of very, very good information about the Tor project and the dark web on torproject.org. You can actually see all of the different nodes and things that are being used. They do a very, very good job. They also list who donates to them and how they support themselves. And if you are so inclined to believe so, you’re able to do that as well.

There are other types. The Zeronet is another big one. Freenet is one that isn’t really widely used anymore plus you have i2P and then the other ones listed. For the most part, Tor is your primary dark web network that is used today.
We have some common misconceptions, right, because those movies make the dark web look just so utterly fantastic and makes everyone feel like a hacker. We have some misconceptions that come along with the dark web. So, the first one, everyone on the dark web is a criminal and that’s not true. It hosts communities and some of these communities are just privacy focused people. Others are based in free speech. Others are trying to help prevent human trafficking or help, you know, refugees out of countries, whatever the case is. There are some very good uses for it, right? Some governments are extremely restrictive on the news and media that their citizens are allowed to see, and the dark web provides that access, right? And it allows journalists and whistleblowers and human rights activists to communicate in a manner in which they can try to help make the world a better place.
The next misconception is that exploring the dark web is illegal and it is not. Now there may be activities carried out on the dark web, which are illegal. And if you engage in those activities, then yes, now you’re committing a crime and that becomes illegal, but it is not inherently illegal to be on the dark web. There are many legitimate purposes. For instance, the New York Times, which is a very well-known news agency in the United States, they have their own dark web site, where they host their normal site on the dark web for people that are in oppressed countries. So, these are things to keep in mind.
And lastly, the dark web, it’s actually not lastly, but the dark web is completely anonymous, and that’s not 100% sure. There are tools that researchers and law enforcement and methods that can be used and implemented to extract information on threat actors, on people that are using the dark web for malicious purposes, right? Law enforcement also sees this dark web sites and they seize the servers which store information and that information can be used to track and determine who these threat actors are. So those supports extremely strong privacy protections. It’s not infallible because nothing is right. Locks only keep honest people honest, and so there’s always a chink in the armor somewhere.
And lastly, accessing the dark web is super difficult or super easy, and it’s not either or neither. There’s not one specific place to go – the dark web is made up of many hidden services, many different websites, multiple different platforms. Though there are technically dark web search engines, they’re not the same as Google or Bing or any of those other ones. So can accessing the dark web can be complex to find the information that you’re looking for, because you need to know the link. You need to know how to find a specific site. You need to know that that site actually exists, right? So, it’s the same as using the internet back in ’98, ’99 before search engines became really popular, you had to know where you were going in order to get there.
Some dark web concerns. Obviously cybercrime is a concern of dark web and it is used very prevalently by threat actors of many different facets of crime. From financial crime, to hacking, to ransomware, to narcotics trafficking, whatever the case is.
Also, misinformation campaigns happen – the spreading of disinformation and extremist content happens, stuff to try to destabilize public opinion and trust. And so, misinformation can happen. And then there’s also the illegal non-ethical surveillance of the dark web, right? Dark web monitoring needs to have ethics that are involved in it to protect the good people that are on the dark web, using the dark web for valid reasons. So, these are some of our dark web concerns.
We’ve talked about what the dark web is. We’ve talked about its nuts and bolts of where it was created, how it operates, how it keeps us safe. We talked about some of the misconceptions. So, let’s get to a little bit more of the interesting stuff. What is actually on the dark web? What type of information are we able to find that relates to what we’re trying to do? How are we able to protect our clients? How are we able to protect ourselves?
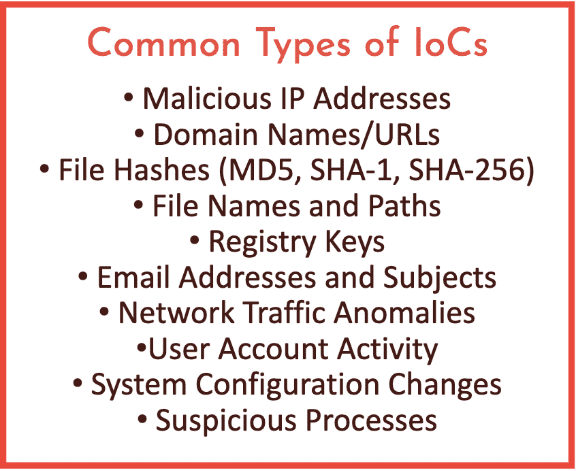
There are several different facets or avenues that we can do to try to find some information. There are Marketplaces where things are bought and sold similar to eBay or any other type of marketplace, Amazon that you go to where you can buy and sell different items in an unmoderated manner. There’s Forums where collaboration between threat actors happens where people ask questions, postings for sale, whatever the case is. Social media related stuff. Obviously, there’s Cryptocurrency information. There’s Leaks from companies. There’s also Leaks from government and then Ransomware related stuff. All of these things are found somewhere in some shape or form on the dark web.
There’s also dark web adjacent stuff. And this is the big thing that a lot of people don’t think about when they investigate the dark web. The dark web, like I said earlier, was a community and we got to look at that community and the community and any one of the communities that you’re a part of, you know, take your work community. So, when you go to work, you’re part of the community with your co-workers and you are talking about work at work. But you also talk about work elsewhere, right? So, a co-worker comes over to your house for dinner and you guys start gossiping about the you know stuff in the office, right? Things happen outside of your office related to what that community is about, which is work. The dark web is the same way. We have messaging apps, we have gaming apps, we even have surface web places. For instance, Reddit is a well-known social media site that has several places on there where they talk about dark web topics and issues and things along those lines. So, monitoring these things is just as important as monitoring the dark web to give you that kind of inclusive photo of what is going on. And a lot of the data on the dark web comes from many different things. So, a lot of the raw data, a lot of the raw data is your PII, your personal identifiable information from leaks. So, data birth, social security numbers, credit card numbers, addresses, things like that. Banking data, stolen bank accounts get sold on the dark web. Corporate data that has been taken maybe from a ransomware organization or from a hacker, whatever the case it is. Credentials and compromised accounts, whether it’s fake accounts to a social media site or accounts that have been taken over, being sold, as well as corporate accounts, personal, whatever the case is, plus there’s malware, there’s hacking tools, there’s ransomware, there’s a lot of different things. And then obviously on your forums, your marketplaces, tactics, ideas, how to do this stuff is there. You can buy guides and forms. And this all leads over to some of the biggest kind of risks that we’re kind of thinking about. So, DDoS attacks, right, data exfiltration inside or threat cyber-attacks, and then just, you know, anything from identity theft down to a much more personal level, right, of like somebody being doxxed on the dark web where their personal information is released.
So, let’s delve a little deeper into that type of data that can be found. That was a more high-level overview. let’s get into a little bit more of the nuts and bolts.

Ransomware. Most ransomware groups, which new ones are coming out every single day. It is a very successful business model, if you’re a threat actor. They have most of their sites are hosted on the dark web. Also, their chat sites, where you go to negotiate once you have been, once you have been compromised are typically .onion sites because it allows for that level of anonymity. So, some of these screenshots are a little older and the reason for that is that you can’t control necessarily what’s going to happen on a dark web site. So, if we went to it live, there’s a chance that there could be material that we wouldn’t want to see or produce. So, we try to capture screenshots. For instance, LockBit, which is now up to LockBit 3.0, their site is hosted on the dark web, several different ones, we’re constantly in a motion of tracking all of the new sites that are popping up from different ransomware groups.
I guess they like that business model. I don’t like it, though.

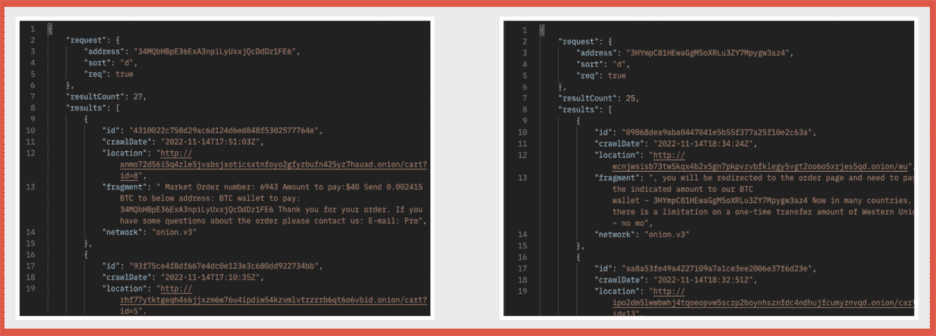
Markets. So, these are what essentially eBay would look like and a lot of them are based off of the same. So, this marketplace, Kerberos, has been taken down. There are several new ones that pop up and they will run until either one of two things happens. Either law enforcement takes down the marketplace or they do what is called an exit scam. And an exit scam is where the owners of the site take all of the money that’s been put into the site for making purchases and then they ride off into the sunset stealing everybody’s, all of their users’ money. Those are typically the only two things, but anything is purchasable through here. There are marketplaces that are specific to firearms. There are marketplaces that cover a wide range of things, from personal identifiable information to credit card numbers, social security numbers between narcotics and drugs, to hacking tools, whatever the case is. Some like to specialize, others like to be a little bit more broad to try to get as many users as possible.
It is kind of crazy some of the things that you can see on a dark web marketplace for sale. There are scam sites and things that pop up. So, for instance, you’re not going to really find a marketplace that’s, you know, human trafficking related. Also, you know, hitman services on the dark web are not real. That’s not how that works. But a lot of people will like to talk about that, especially in movies and TV and things like that. But those types of things are almost always scams. But you can buy just about everything else. You can buy cell phones, skimmer devices, the steel credit cards. The imagination is the limit for what marketplaces may or may not have. But they operate very well and they have better customer service than any company you probably know today because trust is a big part of the dark web. So, one of the things that they do is they hold an escrow service. So, you would actually put your money into the site. The site would hold it. And then once you have made a purchase and you’ve received your product, the site will then release the money. So that way there’s trust between vendor and purchaser. That’s where that exit scan comes in.

Financial crime. Financial crime is a big part of the dark web. You won’t find all of your financial fraudsters on the dark web, some don’t need it, but you will find a lot of information and a lot of stuff being sold because it’s a really easy product to sell on the dark web because you’re not shipping something from point A to point B, it’s a digital good. And we also have a little bit of that dark web adjacent. So, the two photos on the lower right, those are actually taken from telegram. Telegram was a very big hot spot as a dark web adjacent location. It’s since kind of cooled down because Telegram has changed their kind of trust and safety policy, so they’re cracking down on this a little bit more, but for a few years there it was very rampant that every dark web site or marketplace would also have a Telegram channel associated with it. But you can buy anything from credit card numbers as low as 10 cents to bulk credit card information, which will provide the credit card number, the number in the back of the card, the person’s name, address, location, everything that you needed to use that card in a manner to prevent you getting caught by law enforcement as well as information on how to commit fraud. It was a very big thing for the dark web.

There are drugs and gun sales as well on the dark web. A lot of sites, a lot of marketplaces do try to avoid firearm sales only because that gets a lot of American law enforcement involved. It kind of increases their profile. So, a lot will not allow sale of firearms, but they unfortunately, you know, everything done on the internet has a way to be used for bad and the people that sell these find a way to get their markets, their merchandise posted. And then as well as narcotics. Narcotics are a big sale item on dark web marketplaces and different sites from there. But the nice thing, at least for the good guys related to this type of stuff, is that they have to be shipped from point A to point B, and law enforcement does monitor those shipping avenues, and so do the private companies that do that as well. So, a lot of times, this type of stuff is able to hopefully be stopped before it gets anywhere.

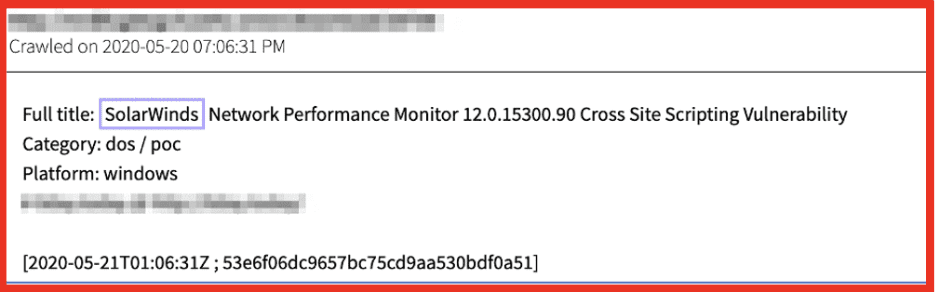
Stolen data. This is going to be something that I’m sure this audience is going to be interested in and about, but stolen data from companies. A lot of organizations have their data stolen. Sometimes they’re not part of ransomware. Sometimes people just steal it to either try to sell it themselves or they post it. They post it for cloud reasons or reputational reasons to give it out to the community. These are screenshots from breach forms, which was recently shut down and potentially working its way on coming back that’s been an interesting saga. But you could go to the site at any point in time, search for a lot of different companies, and find stolen data from those companies. Now that’s obviously bad reputationally for those companies, but it could also be very good for the company’s competitors if they’re not operating in an ethical manner, right? They get that information and if that information contains confidential business secrets to the success of that business, now your competitors have your playbook. As well as the damage that could potentially happen to the clients of those companies if their personal information has been released.

Leaked data. So leaked data is different than stolen data. So leaked data, a lot of times, could involve an insider threat. It could be data that was able to be captured through a tool, for instance, being scraped from a deep website that a company owns, say, for instance, a social media site. You have to log in to access the stuff in the social media site, and then you start running custom tools to pull all of that information down, and then you release it. And then there’s also usernames and passwords that get leaked as well. This is actually a screenshot from our tool, which shows a lot of the leaked content that we are finding out there and are able to catch them. And there is a lot of leaked data that’s out there. It’s actually mind-blowing to understand how easy it is for your personal data to be leaked or your corporate data to be leaked onto the dark web.

Stealer logs. Stealer logs are a very big thing. They can affect corporations, but a lot of times they affect the more individual person. But stealer logs are logs from specific type of malware that when they affect the computer, their job is to pull down all of the usernames and passwords and text files and take a screenshot and get all of the information that they can about that computer. And then these logs are either posted for free or if they’re good logs, they typically get posted for sale. There’s a couple marketplaces on the dark web where one log will cost $10 USD and it will have a person’s entire password history on there, right? All of the passwords that are saved inside browsers, which you should never save your password in a browser due to Stealer Logs because it captures all of that. And then they’re able to access all of your information. And the biggest one that we want to protect is your email, especially if you have used two-factor authentication through email. But Stealer Logs are everywhere. And this is also something else that ends up being dark web adjacent. For instance, Alien Text Base, this one here, they still operate, but they operate mainly on telegram. Even though telegram is very active in trying to shut them down, you will typically find them on telegram releasing this service that they have here. And one month of unlimited amount of stealer logs is only $100, which is crazy. And $1,000 dollars is a lifetime access. So, if you are intentionally trying to hack somebody’s computer to pull down credit card information or to use it for other malicious purposes, that’s relatively a bargain.

And then we have our corporate data. And corporate data involves many different things. It could be our corporate secrets. It could be information related to a tax eminent to that corporation. It could be customer information, whatever the case is, right? And not everybody is immune, right? So, the FBI, federal government, American government agencies have been affected by corporate data issues. CloudStrike, LinkedIn, Facebook, all of your major social media companies at some point in time have had their corporate data leaked, and a lot of that can still be found on the dark web today, even if it’s old data. Just because it’s older data doesn’t mean it’s still not valid and still can’t be put to use. And then also, you know, in here in America, we have the United Healthcare CEO who was assassinated. And you can find corporate, you know, talk about those corporations and the CEO, for instance, this one here, which was posted on an anonymous message board, saying that the healthcare CEO being shot would be a long time coming and for people to stop defending them. So, there’s a lot of information, a lot of things that can break down here, right, from just corporate information to also threats to corporations and businesses. Things to monitor and different avenues to go down.

And the communities that bonds them. I’m very big in saying the dark web is a community, and we have several different communities on the dark web. So, one of the big ones is extremism. You can find a lot of extremist information on the dark web, from everything from terrorism all the way to racially motivated type stuff, to politically motivated things, it’s all on there.

Hacktivist groups. Hacktivists are hackers that claim that they are hacking for the correct reasons because they don’t agree with something, whether it’s a political mind, a political decision, or a business that didn’t do the right thing that they thought was ethically correct. Hacktivists go after them, which was made famous by Anonymous back in the 2000s initially. Hacktivist groups operate on the dark web all the time. They post information, they get together to share ideas, different things like that.

And then we have our ransomware groups. This is a screenshot from our tool showing a lot of the different groups that we are targeting or not targeting but monitoring and pulling information down. This list actually currently has 317 different ransomware groups and threat actors that we’re monitoring and trying to get as much information from it. And the number of ransomware groups that operate on the dark web is growing every single day. And that number never stays static.

And then obviously we have our hackers. What’s interesting about this slide and as we’re talking about hackers is this is how initial access is sold. So, most ransomware groups do not do their own happy. They typically purchase the access from somebody who did the access. And what will happen is in certain dark web forms, a user will post revenue, a companies’ revenue of around 25 million. They’ll say how many hosts the network has. So, in this one in the left by Benjamin Franklin, there’s 500 hosts on this network. They’re looking for $1,500 to purchase this. And then a ransomware group will purchase this access, install their ransomware, and then attempt to export the company when they’re able to. And this is how it gets post. They never necessarily post names. Sometimes they do, but they provide enough information that you can try to disseminate down who the target is in hopes of maybe preventing ransomware. That’s a really big thing for companies to use the dark web is to monitor the initial access side of the ransomware lifecycle. And if they’re able to see that they’re potentially popping up on initial access sale, they can go ahead and start doing extra tests and monitoring and finding where the hole is and hopefully able to plug it before anything bad happens. But hackers do operate on the dark web in many different facets.

And then we have our main APT groups, our advanced persistent threats. For instance, like North Korean groups, different things like that, Chinese groups that are constantly trying to break into things and hack things and gain information, which is another thing that this is a screenshot similar to the ransomware groups from our tool and where we curate information on them.
Why is the dark web important? I’ve touched on this a lot, but it really does allow us the opportunity to learn more from the threat actor to make better decisions as to what we need to do to protect ourselves. So, it gives better insight and allows us to learn from them. There are tools that you can capture and figure out how they work to prevent them from working on your network. There’s also tutorials in fraud, in hacking, in social engineering, whatever the case is, and we can learn directly from the threat actors and monitor that, and it can also give us an early warning sign before anything before anything goes happen.
The early detection of potential emergent threats. It’s a more proactive approach to cyber defense. We’re learning directly from the threat actors, and hopefully it allows us to prevent threats from escalating, which is why it’s important.
So how do we find things on the dark web? One, there are open source tools to help you, but you need to take into consideration the OPSEC considerations, the operational security considerations. There are websites, for instance, ransomlook.io, post information daily on new ransomware groups that are operating on the dark web. There’s also different monitoring stuff and blog posts and things along those lines. But there’s also command line based open-source tools for investigating it. It’s just, you really need to know the operational security side of it.
On the dark web, there are list sites or link sites or directories that will provide links to dark web sites. And they will monitor those links to determine if the site is online or offline. And then we use OSINT. OSINT is our best friend. OSINT, stands for open-source intelligence techniques and it is a way of finding and learning information that’s publicly available. So, whether it’s from the news, it’s from government publications, blogs. At DarkOwl, we post blogs pretty regularly from there. Social media accounts from influencers that specialize in this stuff and then academia and research as well provides good, insight into what is going on.
And then now the operational security concern of investigating the dark web, which our tool does definitely allow to help with this situation, and it is something that very regularly needs to be taken into consideration, right? So, it’s a process to prevent our adversaries from gaining information about us, our capabilities, so that we can identify who they are, right? We’re not trying to become the victim. We’re the investigator or the analyst trying to prevent this.
So, it’s important, right? It’s important for the investigator and the researcher’s safety. We want to make sure that their identity does not get released or known. It also prevents against retaliation and targeting and it ensures that safety during and after dark web investigations, right? We want to make sure that we protect our sensitive information exposure and to avoid data. For instance, downloading certain things off of the dark web because we need them for investigative purposes. If it’s not done correctly in a secure machine that doesn’t have network access, we could potentially be putting malware or ransomware into our own network, you know, and now becoming an actual victim of what is going on. It allows us to maintain that confidentiality and anonymity and does not compromise our investigations. It allows us to reduce detection and tracking by sophisticated adversaries, for instance, some of those APTs that are nation-state groups are very well-trained, have everything that they need, have many people to help them. So, we want to make sure that we reduce detection by them so that we can continue gathering information. And then we want to reduce risks associated with linking affiliate investigations and researchers. We want to try to keep that attribution down to a very low level. And OPSEC is one of the most important things that needs to– and it should be the primary thing that is kept into that mind of dark web investigations.

Six steps to OPSEC. We want to identify the critical information that we need and how we need to keep it secure. We want to analyze the threat. What are our adversaries? What are their capabilities? What are they able to do? We want to look for weaknesses and configurations and behaviors to make sure that we can protect ourselves, evaluate the likelihood and impact of those risks. We want to implement countermeasures, apply security practices. Do we need a machine that’s never connected to the company network, virtual machines, VPNs, things along those lines and we want to constantly reevaluate as we progress in that investigation to make sure that our operation security is providing what we need it to provide. It’s important for protecting investigator safety, securing that sensitive information, maintaining operational integrity for the surveillance and tracking purposes, and then attribution risks, right? We wanna make sure we keep those tools on minimum.
We have gone over a lot. We’ve gone from what the dark web is, to what type of information is on the dark web, to tools for investigating the dark web, open source and ARPS tool and things like that, and operation security. But what are the strategies, right? We have the information, or we need to get the information. What are the strategies to take that investigation and make it fruitful? So, darknet intelligence, right, is involves collecting and analyzing data, like any other investigation would. Going through these specialized tools that we need to get it and determining, right, the complex ecosystems where cyber criminals trade goods and services, right? We need to know is the information that we are looking for on a forum, marketplace, a chat group, whatever the case is.

The intelligence pyramid, everything in intelligence and investigations has some type of diagram or analogy or acronym. This is no different. We start at the bottom with our raw data. That is all of the data that we’ve collected that may be useful for us. We’ll take all of that and turn it into some type of information to figure out kind of the buckets it needs to be in, and then from there we’ll put that into our actual intelligence that we can make decisions on. Kind of weeding out the noise that we don’t need. And you’ll want to do that with dark web data because you will be able to find a lot of things, but not all of those things will matter to your current investigation or needs, right?
So, we’re going to start with the planning and direction through our intelligence life cycle. Once we have — this is what we’re worried about. This is kind of the information that we need to learn. This is our questions. We’ll work on those collections. Once we collect our information, then we’ll move to the analysis phase. Once we analyze all of our data, kind of go through that intelligence pyramid will move into production, write our reports, make our recommendations, and then disseminate that out and get feedback from your cross-functional partners or your clients or whoever the case is. And then we start that all over again for the next question that pops up, the next threat that we have to worry about.
Strategies for monitoring the dark web. You have to know what your intelligence requirement is. You’ve got to know what you want to achieve. Do you need to worry about a client being hacked? Do you need to worry about their data being stolen, whatever the case is. We want to identify the areas that most interest us. For instance, maybe we need to monitor for credit card information. Well, some of the best places to see a specific credit card information pops up are in those marketplaces, right? We want to make sure that we keep a way of monitoring those sources. Once we collect data, we want to analyze that data, see if we need to find more data. Sometimes you need to. There’s always language assessment. If you need to figure out if you need to translate the information that you’re getting, Google Translate Works, AI tools help with that. And then obviously the last thing that we want to do is report our findings to actually have our recommendations matter and help strengthen security posture, prevent cybercrime, and all of those fun things.
Just real quick – to touch on DarkOwl and what we do. DarkOwl is a darknet data technology company headquartered in Denver, Colorado. Our mission was to build automated technology to allow analysts to investigate and monitor the dark web without actually having to go to the dark web. And we have come a long way in producing that tool. We’re led by our CEO, Mark Turnage, and we have a very fantastic team of analysts and engineers to produce that. So, the information in our tool, you don’t ever actually have to go to the dark web to be able to access that information. And it’s all searchable, which is the best thing. So, you don’t actually have to know how to get to a certain forum or have an account on that forum. You’re able to get it yourself.
In our beginning in 2012, we pioneered dark net collection in relevant search, you know, we created our Vision UI tool, which allows you to have a graphical interface to search all of our data. But we also have API access as well. So, we can tie into tools like Maltego has a transform to where you can tie into dark web data. But it gives access to your analysts to have this information, find it, use it and also monitor it through cases or alerts in different things along those lines. So, layers of the surface even dark web that we go after, right? So some of these high-risk surface websites are like pay spin sites or discussion boards, you know, Reddit, social media sites as well. We monitor underground forums and marketplaces as well as Discord, Telegram, IRC. We’re always looking to move into new messaging platforms as we see the community shift, right? And then currently we are in Tor, I2P, and ZeroNet as dark web marketplaces, because those are the main places that threat actors operate, typically now in Tor. There was a little bit that I2P was gaining traction, but that has since lost its momentum. We’ve pull about 2 million documents off of the dark web in about a 24-hour period. And we are constantly pulling in new information every single day. Our information is relatively able to be real-time, depending on the site and how often we crawl it. I was actually just doing research the other day and literally had information that was within the last six hours into the tool. So, it is very successful and really does help in these types of investigations, and it solves your operational security problem. So, you don’t have to worry about that using our tool.
And then our ecosystem – we have the Vision UI, which has pretty much everything an analyst would need, but then we also have different things. And in our Vision UI, what’s really nice about it is that you can have exposures for us. So, we have an algorithm that we created to where you can put in some information and we can monitor a company’s exposure off of our algorithm inside of the tool. And then this is our contact information. I do have some questions that was brought up. I’m gonna touch on that real quick and then we can go ahead and end. So, one of the questions that was asked was what kind of data are most commonly traded or exposed on the dark web and how has that changed over the past few years? Which is a fantastic question. So, starting with the past few years and how that’s changed. So initially, you saw a lot of financial and drug-related stuff on the dark web, especially around the time where a former marketplace called Silk Road, which was one of the first law enforcement takedowns of the marketplace, there was a lot of financial-related and drug trafficking that was happening through the dark web. And as the years have progressed, we now see a lot more technologically based crimes. Ransomware, leaks, data being sold, personal information being sold. This has grown because more companies from five, six, ten, fifteen years ago, are putting anything and everything on technology and with this come budget cuts at times where security teams diminish. So, cybercrime goes up, hacking goes up, as well as we’re in a time where everything involves ground technology. This has become a very big topic on the dark web. A lot of that information is now available.
Question number two that we got: Are there specific industries or sectors that are more heavily targeted or discussed on the dark web? And there is. And it’s hard to quantify. Healthcare is one that is on it. That personal information, medical records, that type of information, because if a ransomware organization is able to a healthcare organization, they’re typically going to get paid. And most ransomware groups aren’t the most trustworthy people, so they still release the information after being paid. Financial services, bank access fraud opportunities, selling crypto accounts that have already bypassed KYC. So, a threat actor can purchase that account sell it so now or use it to where they can’t be attributed back to them and then your government and defense contractors are always something that pops up as well on the dark web but anybody can be a target. It just depends on if it’s your day or not. Critical infrastructure, that is another thing that can pop up if there’s talk related to that because those are things that typically the payments go through.
The next question we have is, “What are the early warning signs that a company’s data or credentials might be circulating on the dark web?” And that’s actually a very interesting topic and could probably warrant its own webinar in itself. But some of the quick things that we want to do is company credentials, appealing and of their logs in combo lists. So those numbers, if for instance, an employee of a company access their company’s portal from their personal computer, which isn’t monitored by the company’s IT, and it did get captured in stealer logs, that popping up is a definitely strong sign you may be attacked, ’cause it just takes one person to understand, hey, I have a company login. Let me go login and figure out what I want to do. Mention of the company’s domain or brand on dark web forms as that starts increasing, concerns should start populating. That’s more like your medium concerns. Leaked internal documents obviously are an issue. And then that initial access, if you start to see initial access postings that appear to match your organization, that is something that you want to take seriously. Even though it has the potential to be a false positive, we still want to take that seriously. And then, of course, ransomware sites announcing that they hacked you. That is a clear indication that there’s trouble ahead and that we need to monitor that. Because ransomware sites, a lot of times, will post that something is happening before it happens because they’ve already initialized what they were going to start with.
And then the last question I have is: “With the growing use of encrypted messaging platforms and private marketplaces, is the traditional dark web still the biggest threat or is the landscape evolving?” That’s a fantastic question. And yes, the dark web is still a very, very big threat, but we have to make sure that we monitor the adjacent. The thing with the dark web where encrypted messaging platforms won’t ever be able to overtake it is the ability for somebody to find that information, to be able to start the conversations or purchase whatever they need to be. For instance, Telegram was very, very big a few years ago. And even some marketplaces shutting down on the dark web to be in Telegram. Because it was still very easy to find those marketplaces by just using the search bar. There’s no real messaging application that takes that over. So, a lot of times what you’ll see is that things will start on the dark web. And then from there they may move conversations into encrypted messages or channels. That doesn’t mean that that information still can’t be obtained and used for intelligence purposes. But I don’t think messaging will ever be able to take away from the dark web. It’s just another adjacent place that needs to be monitored as the investigation and intelligence needs to develop.
Thank you so much for your time, everybody.