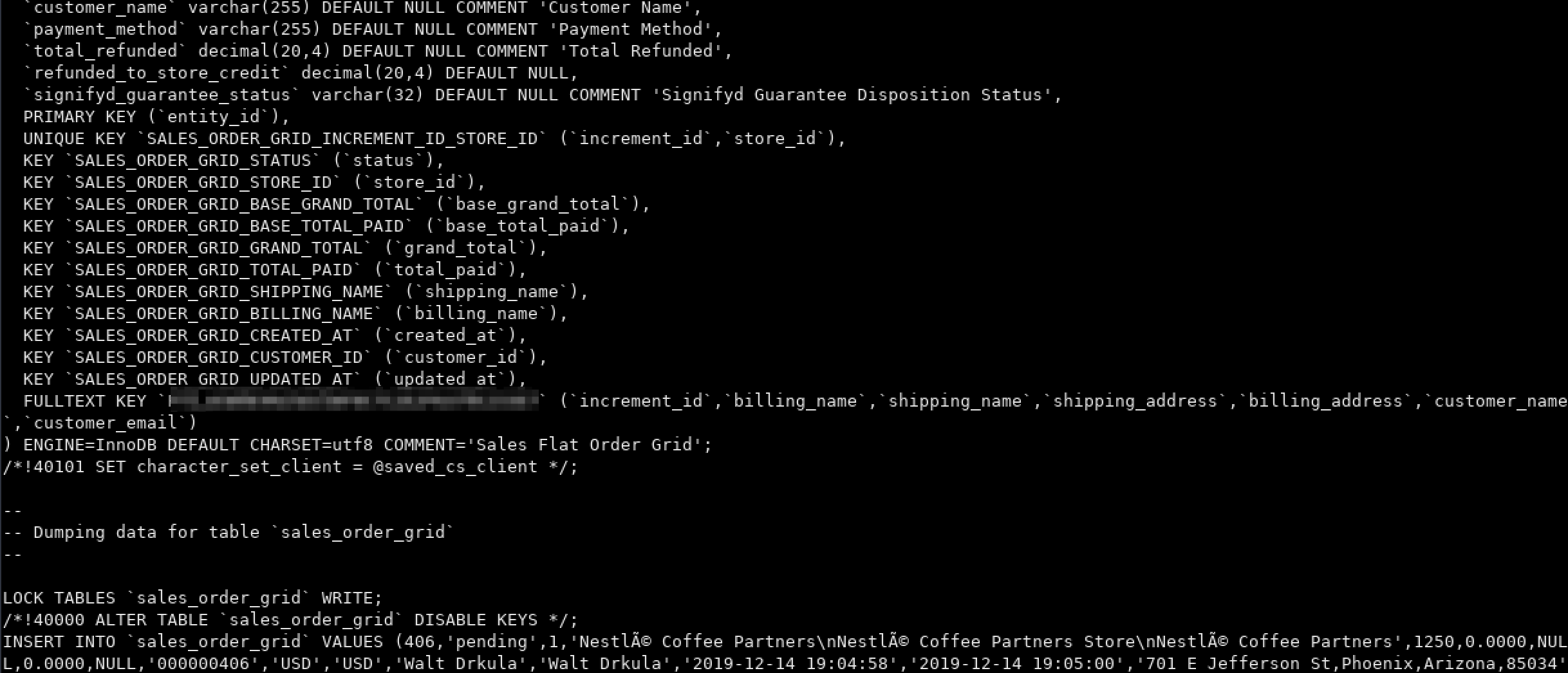
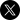[DEVELOPING] Impacts of Ukraine Invasion Felt Across the Darknet
Last updated: April 18 18:30 UTC
The DarkOwl team are actively tracking the fallout from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The effects of the kinetic military operation are causing ripples across the global cyber space including critical underground ecosystems across the deep and darknet.
18 April 2022 – 01:12 UTC
DDoSecrets Leaks 222GB of Data from Gazregion Collected by Anonymous Hacktivists
Three different hacktivist groups (Anonymous, nb65, and DepaixPorteur) submitted archives consisting of emails and sensitive corporate files from Gazregion, a Russian supplier specializing in gas pipelines construction with direct support to Gazprom.
There have been numerous claims of attacks against Gazprom since invasion of Ukraine by Anonymous and other cyber offensive groups. nb65 posted to social media they compromised SSK Gazregion on April 3rd with their version of CONTI ransomware.
18 April 2022 – 01:12 UTC
nb65 Claims Attack Against Russian JSC Bank PSCB with CONTI Ransomware
The Hacktivist group, Network Battalion 65 had claimed they successfully attacked JSC Bank PSCB in Russia and successfully encrypted their network with their version of CONTI ransomware.
The group stated they managed to exfiltrated over 1TB of data including financial statements, tokens, tax forms, client information, and sensitive databases before deleting all backups to prevent data and functionality restoration.
The hacktivists further taunted the bank stating how grateful they were the stored so many credentials in Chrome – a browser for which several emergency security patches have been recently released.
We’re very thankful that you store so many credentials in Chrome. Well done. It’s obvious that incident response has started. Good luck getting your data back without us.
15 April 2022 – 21:59 UTC
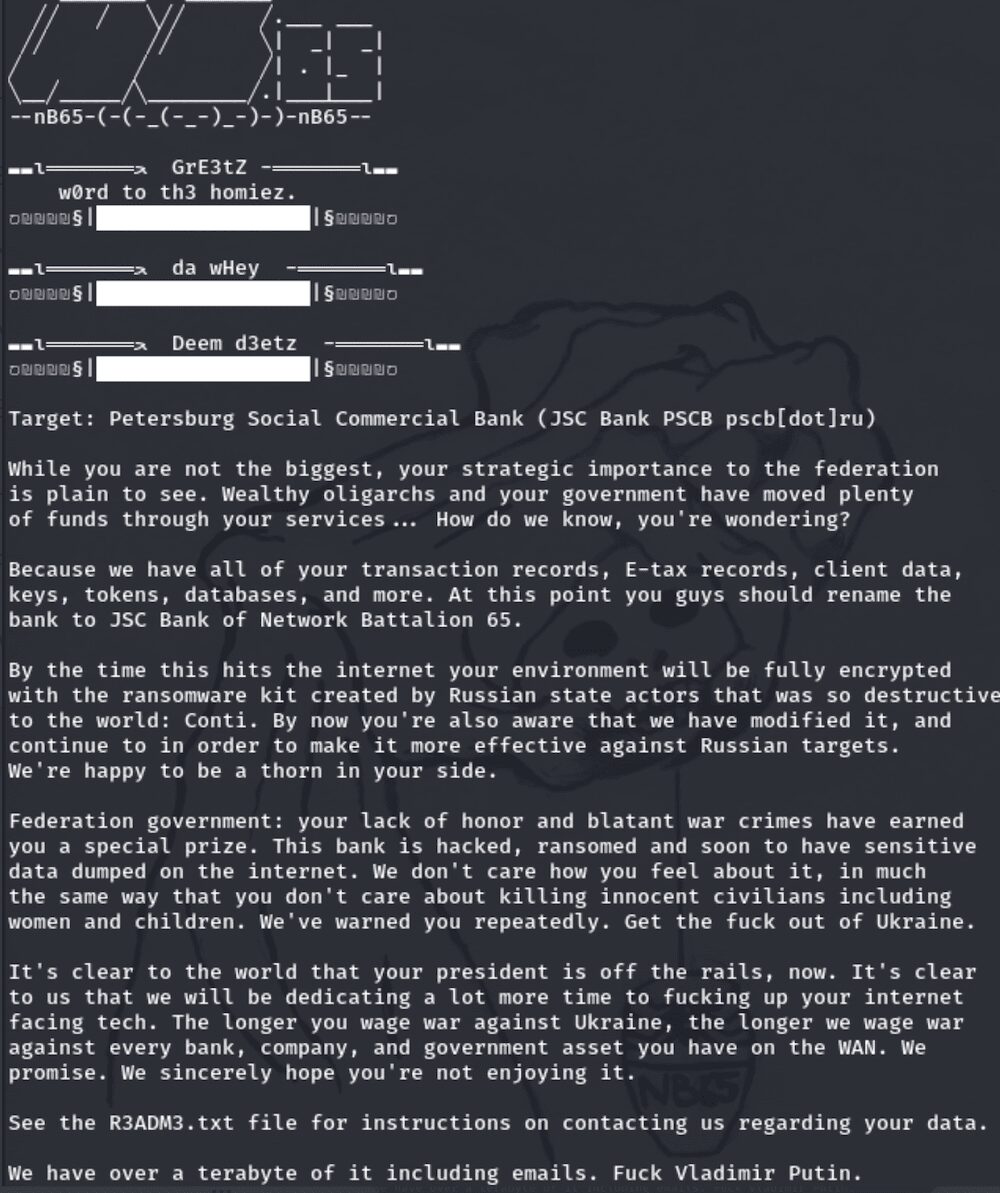
GhostSec Leaks Data from domain[.]ru Hosting Provider
The Hacktivist group, GhostSec claimed to target Russian internet domain registration provider, domain[.]ru in a cyberattack. The group managed to exfiltrate over 100MB of data including screenshots of sensitive files and excel spreadsheet data.
According to the README file in the data leak, during the breach, GhostSec identified over 4TB of SQL databases, but in all the excitement the team’s presence was caught by the company’s intrusion detection systems and kicked off the network before the SQL data could be harvested.
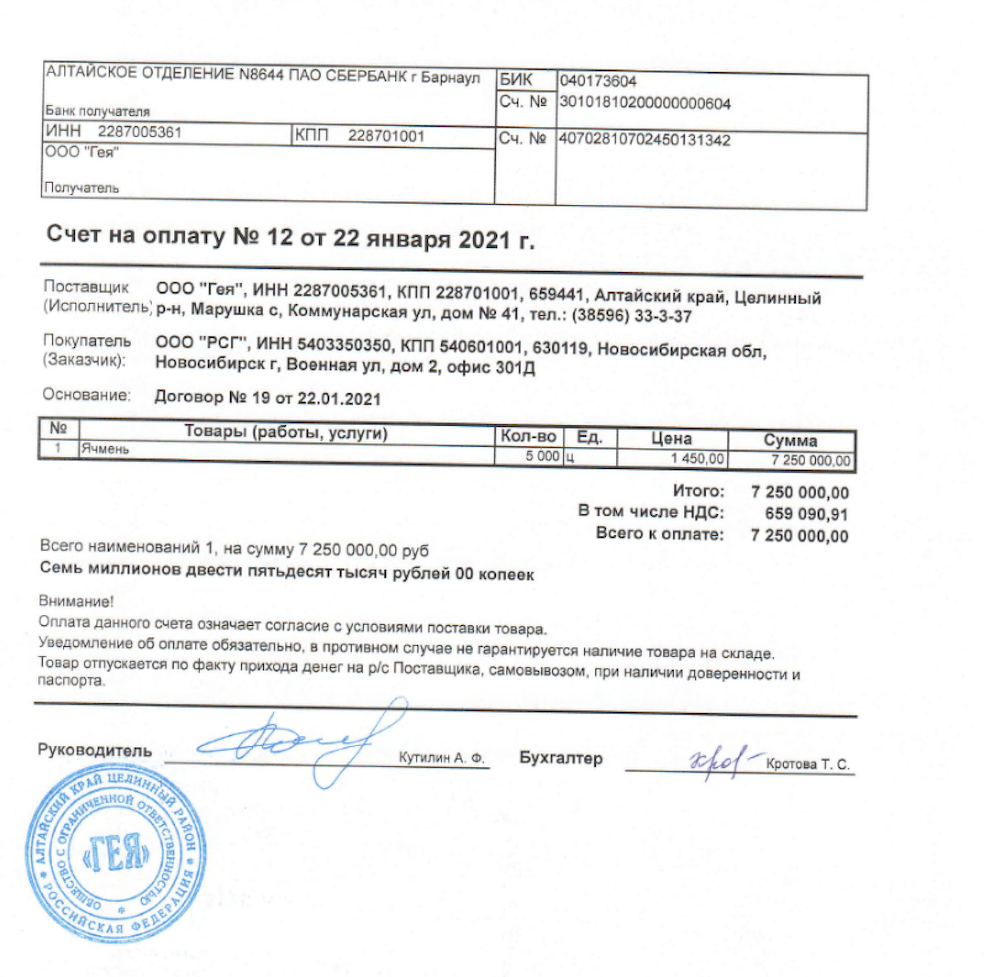
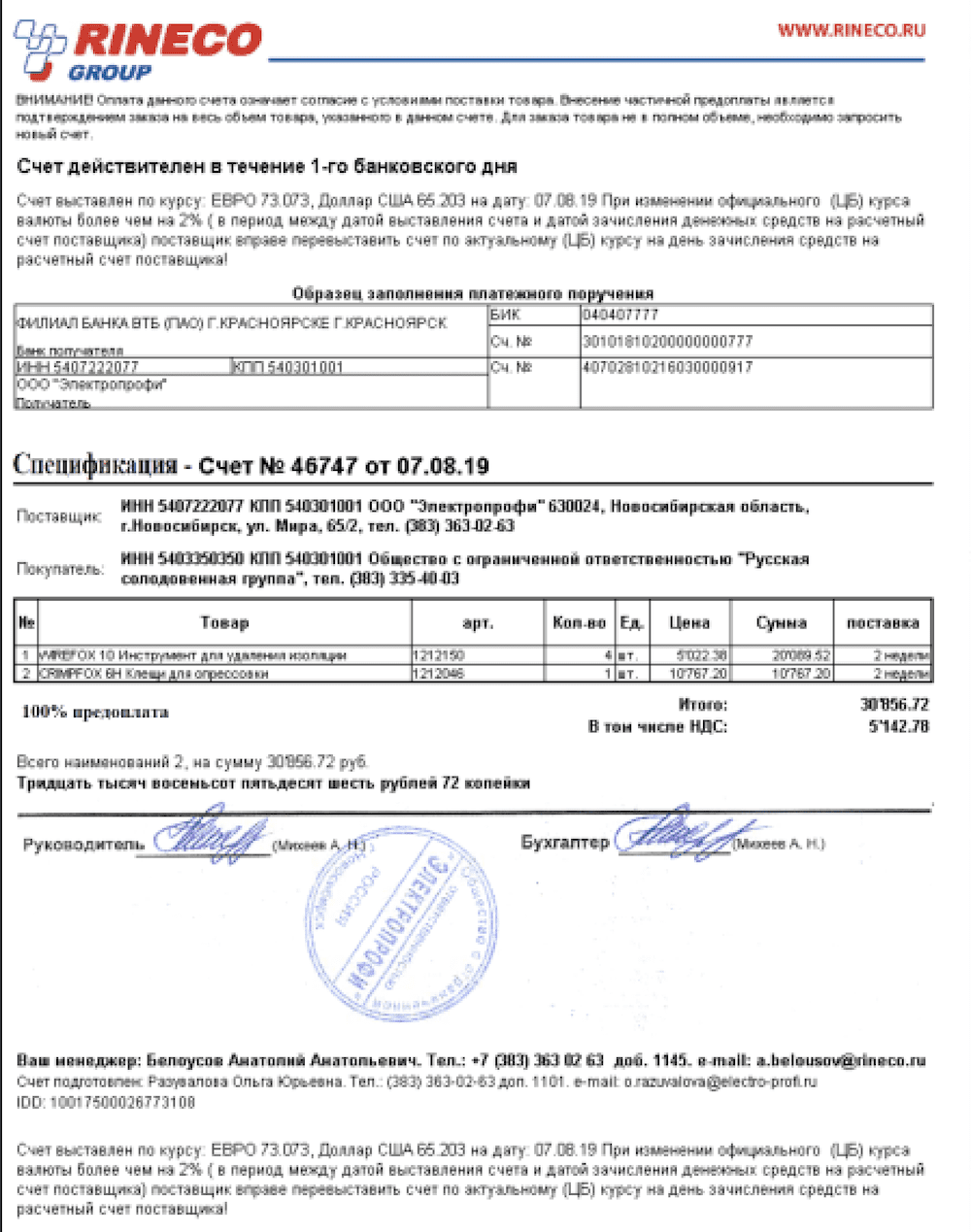
15 April 2022 – 17:52 UTC
nb65 Confirms Attack on Continent Express; DDoSecrets Leaks 400 GB of Russian Travel Agency’s Data
The attack on a Russian travel agency occurred several days ago and was shortly after confirmed by the organization. DDoSecrets assisted nb65 in leaking over 400GB of sensitive files and databases from the travel agency. The details of the leak have not been confirmed.
15 April 2022 – 14:32 UTC
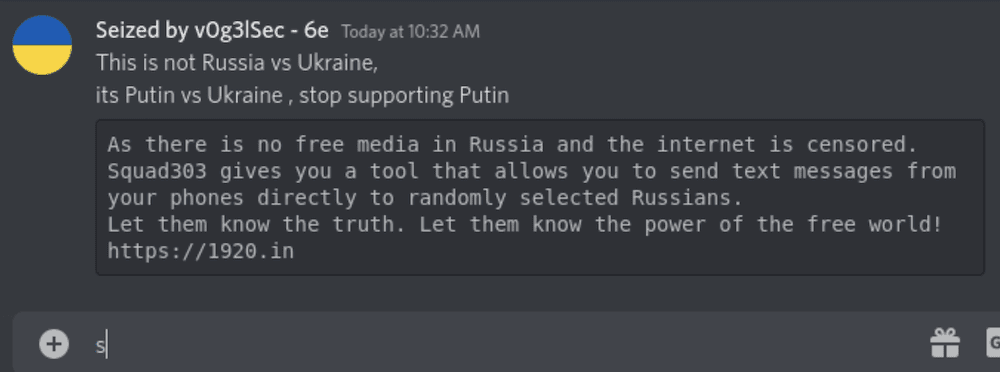
Anonymous Takes Over Pro-Russian Discord Accounts
Hacktivists from the Anonymous Collective have successfully taken control of several pro-Russian accounts on the chat platform, Discord, and are now using these accounts to circulate pro-Ukrainian messaging. An Anonymous member @v0g3lsec – who has been extremely active in the #opRussia campaign – shared an image of a hacked account where they posted links and information about the information operations group, squad303 to share truths about the invasion via SMS, WhatsApp, and email with random Russian citizens.
14 April 2022 – 20:02 UTC
DDoSecrets Leaks Unprecedented Amount of Email Data from Russian Organizations
In the last three days, DDoSecrets uploaded archives for five (5) different organizations across Russia totaling 1.97 Million emails and 2 TBs of data.
- 230,000 emails from the Blagoveshchensk City Administration (Благове́щенск) – 150GB
- 230,000 emails from the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation (Министерство культуры Российской Федерации) responsible for state policy regarding art, cinematography, archives, copyright, cultural heritage, and censorship – 446 GB
- 250,000 emails from the Deptartment of Education of the Strezhevoy (Стрежево́й) City District Administration – 221GB
- 495,000 emails from the Russian firm Technotec, which has provided oil and gas field services along with chemical reagents used in oil production and transportation – 440GB
- 768,000 emails from Gazprom Linde Engineering, which specializes in designing gas and petrochemical processing facilities and oil refineries – 728GB
13 April 2022 – 17:09 UTC
CISA Issues Alert About Destructive Malware Targeting US Critical Infrastructure
A joint advisory issued by the Department of Energy (DOE), the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the National Security Agency (NSA), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) details how nation state actors (likely sponsored by the Russian government) have demonstrated the capability to gain full system access to multiple industrial control system (ICS) and affiliated supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) devices. The critical alert indicated there is an immediate HIGH cybersecurity risk to critical infrastructure around the US. The devices include:
- Schneider Electric programmable logic controllers (PLCs);
- OMRON Sysmac NEX PLCs; and
- Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture (OPC UA) servers.
For more information read the advisory along with recommended security mitigation measures here: https://www.cisa.gov/uscert/ncas/alerts/aa22-103a
12 April 2022 – 15:31 UTC
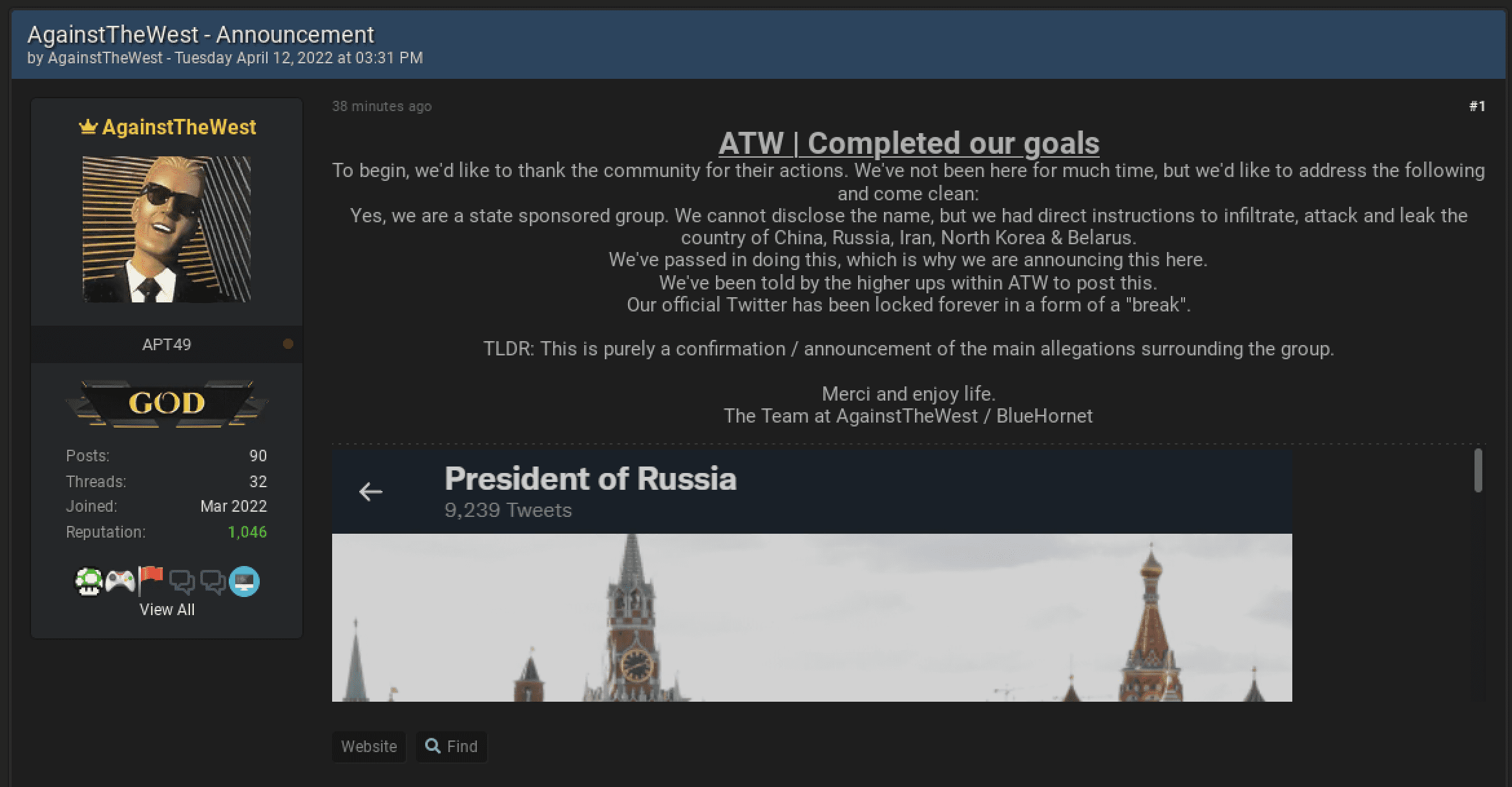
ATW | Blue Hornet Announces That They are a “State-Sponsored” Group
The “GOD” account representing AgainstTheWest (APT49) on the new BreachedForums (with many users from the now officially seized RaidForums) announced moments ago that they are indeed a “state-sponsored” cyber group with “direct instructions to infiltrate, attack and leak the country of China, Russia, Iran, North Korea & Belarus.” The group’s Twitter account was also blocked by Russia’s Kremlin account earlier this week and the notification of this block was included in the post.
There is no way to verify the accuracy of the statement posted and it’s unclear whether or not the group will continue their operations in support of Ukraine.
11 April 2022 – TIME UNKNOWN
CONTI Claims Responsibility for Cyberattack Against German Wind Turbine Company
On the 31st of March, Nordex wind turbine manufacturing company in Germany suffered a significant cyberattack. CONTI has claimed responsibility for the attack (over 10 days later) posting the company’s name to their public-facing Tor service of victims. We anticipate that sensitive corporate data will be leaked by the RaaS gang shortly.

11 April 2022 – 20:58 UTC
Anonymous Compromises Regional Government of Tver, Russia; Leaks 130,000 Emails from Governor’s Mail Server
Hacktivists from the Anonymous Collective using the monikers DepaixPorteur and wh1t3sh4d0w0x90 have compromised the domain tverreg[.]ru believed to be associated with the Regional Government of Tver, Russia. Tver is located 110 miles (180km) northwest of Moscow on the banks of the Volga River. The archive is over 116GB in size and consists of over 130,000 emails exfiltrated from Governor Igor Rudenya’s email system dating from 2016 through 2022. The governor was appointed by President Putin in 2016.
Anonymous shared a leak consisting of Russian regional governors on the darknet on 23 March 2022.
11 April 2022 – 14:35 UTC
Finland Suffers Cyberattack; Announces They Will Expedite Application for NATO Membership
On April 8th, the Finnish government confirmed many of its military, defense, and foreign affairs webservers experienced unsophisticated, yet concerted DDoS attacks likely originating from Russian threat actors. The cyberattacks coincidentally occurred just as Ukraine President Zelenskyy started to address the Finnish Parliament on the status of the war in Ukraine around 10:30 GMT.
On the same day, the Finnish Minstry of Defense confirmed, hours earlier, Russia state-owned aircraft also breached Finland’s airspace off Porvoo in the Gulf of Finland – the first time in over 2 years. The aircraft, an Ilyushin IL-96-300 cargo transport airplane, was traveling east to west and landed in Berlin.
Both Finland and Sweden have signaled they will be submitting applications to join NATO. According to open-source reporting, Finland will likely finalize their application during the month of May in time for a NATO summit scheduled in Madrid, Spain in June.
Kremlin spokesman, Dmitry Peskov stated that Russia would have to “rebalance the situation ” with its own measures should Sweden and Finland choose to join NATO.
09 April 2022 – 03:39 UTC
ATW | BH Group Leaks Data Stolen from Russian Temporary Work Agency and Recruitment Firm: Rabotut
AgainstTheWest (Blue Hornet) announced on their Telegram channel they have successfully targeted the domain (rabotut[.]ru) for Rabotut, a “federal scale service” supplier in Russia. According to the threat actor, the archive includes the organization’s entire backend and front end source code, API keys, and SSL keys. According to open-sources, Rabotut is a temporary workers agency and provides contract employees to a number of critical government and corporate businesses around the country.
Contents of leak are in the process of verification by Darkowl analysts.
08 April 2022 – 21:41 UTC
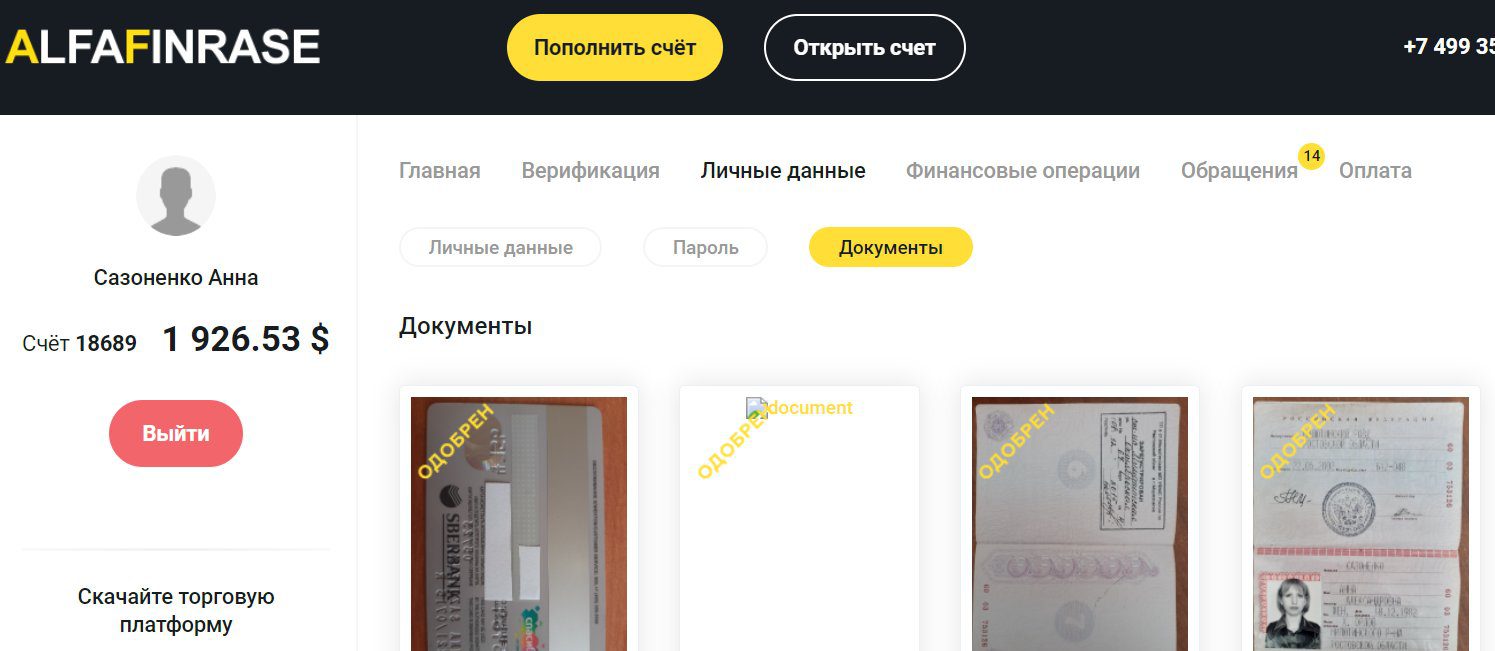
KelvinSecurity Team Targets Russian Cryotcurrency Scam Website: alfa-finrase
KelvinSec released data reportedly from the domain (alfa-finrase[.]com) known for trading in fraud data, e.g. passports, driver’s license, and other sensitve PII. The group claims to have exploited the website, shutdown a cryptocurrency scam, deleted 400GB from the site’s server, and exposed 1.4GB of customer data from the deep web store.
07 April 2022 – 19:30 UTC
DDoSecrets Leaks Over 400,000 Russian Organization Emails Exfiltrated by Anonymous Operations
The leak site, DDoSecrets once again assists Anonymous hactivist collective in distributing sensitive data exfiltrated from companies and organizations in Russia. Three archives were leaked – within minutes of each other – for three organizations: Petrofort, Aerogas, and Forest. The data from these corporate email archives date back over decades of commercial activitiy.
- Petrofort: 244GB archive consisting of over 300,000 emails between employees and clients. Petrofort is one of the largest office spaces and business centers in Saint Petersburg.
- Aerogas: 145GB archive consisting of over 100,000 emails between employees and clients. Aerogas is an engineering company supporting Russia’s critical oil and gas infrastructure and supports such as: Rosneft, NOVATEK, Volgagaz and Purneft.
- Forest (Форест): 35GB archive consisting of over 37,000 emails between employees and clients. Forest is a Russian logging and wood manufacturing company associated with many high-valued construction projects across the company.
A representative from DDoSecrets earlier shared thoughts about the extraordinary volume of leak data coming out of Russia earlier this week in a social media post.
06 April 2022 – 21:42 UTC
Anonymous Claims to Attack Russian MAUK Cinema, Mirkino Belebey
Members of Anonymous using the aliases ShadowS3c and Anonfearless3c have allegedly targeted servers for the Russian cinema and movie theatre, Mirkino Belebey (domain:mirkino-belebey[.]ru). The Mirkino theatre is also known as the MAUK Cinema a.k.a. “World of cinema” in the Belebeevsky District of Russia.
The hacktivists have leaked screenshots with credential data from the breached database containing hundreds of usernames, email adresses, and passwords.
This entry will be updated if/when the leak contents can be confirmed.
06 April 2022 – 20:42 UTC
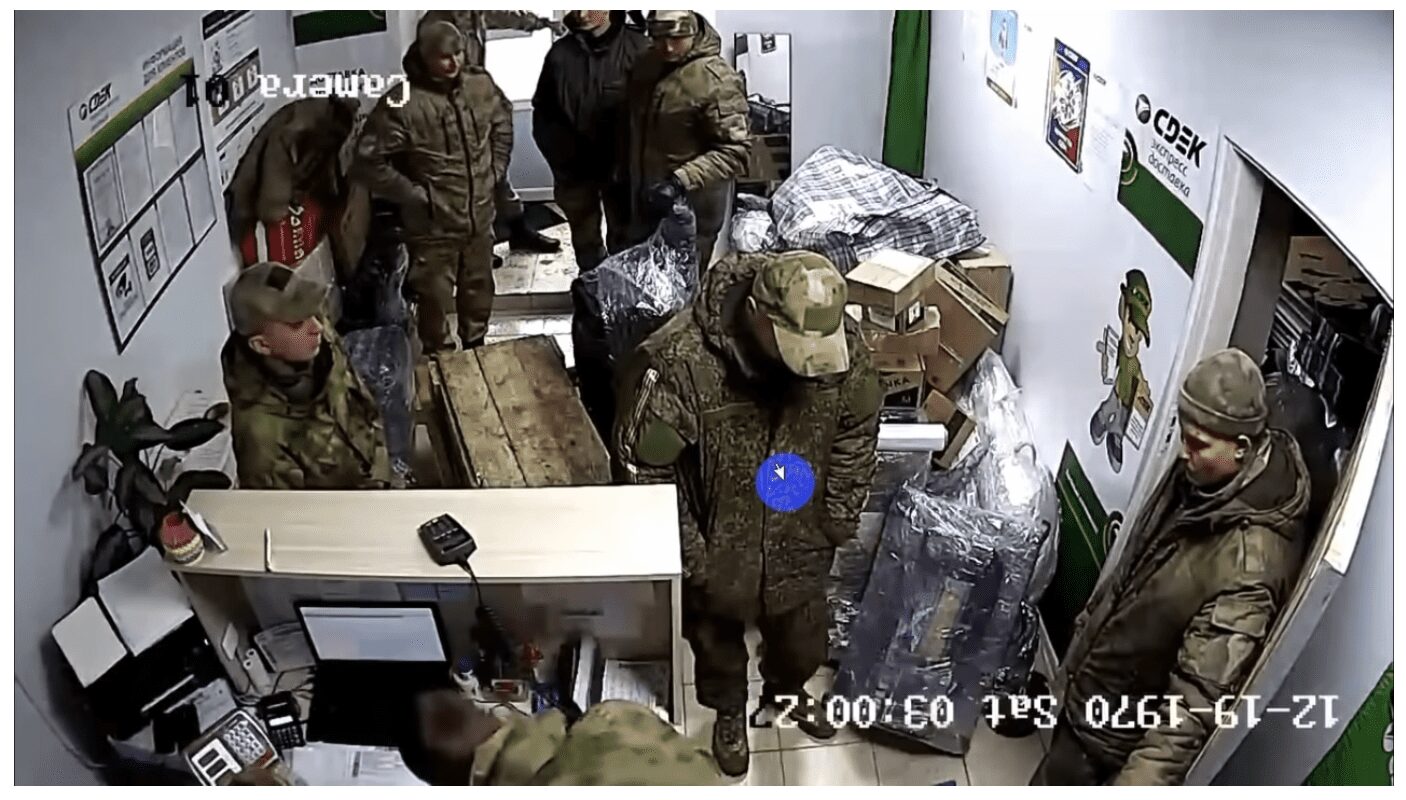
Hajun Project Identifies Russian Soldiers Who Sent Parcels from Belarus Back to Russia
On April 3rd, the Hajun Project published three hours of surveillance camera footage from a CDEK delivery service located in Mazyr, Belarus. The video shows several soldiers from the Russian Armed Forces sending, among other things, items stolen from Ukrainians, during their “special military operation.”
Using leaked personal data available across the darknet and deepweb, the Hajun Project further confirmed the identities of the Russian military consignors and have released the names and phone numbers for at least 50 of the servicemen that sent parcels around the same time as the published camera video.
The Hajun Project maintains a Telegram channel and Twitter account monitoring and tracking the movement of military land and air assets in Belarus.

05 April 2022 – 16:22 UTC
Ukraine’s Defense Intelligence Agency (GURMO) Conduct SCADA Attacks on Gazprom
Due to the sensitivities of on-going military operations, there is limited detail available on the nature of the attack, but it appears that offensive cyber units under the direction of Main Director of Intelligence for the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine conducted SCADA cyberattacks against Gazprom pipelines. The attacks began within 48 hours of a fire at an oil depot in Russia’s Belgorod region last Friday, that western media reported was the first time Ukrainian helicopters had been spotted going across the border.
The cyberattacks likely triggered an underground gas leak from a highly pressurized gas pipeline in the village of Verkhnevilyuysk; the leak was reported in Russian open sources. Shortly after this, an explosion occurred in a main gas pipeline “Urengoy-Center-2” that civilians captured on Russian social media platform, VK as a large fire occurred in the Lysvensky district of the Kama region near the village of Matveevo.
Over pressurizing gas lines through disrupting infrastructure industrial control systems (ICS) is a documented method for using cyber to cause kinetic damage to pipeline critical infrastructure. The Congressional Research Services detailed such security risks to ICS in their 2021 report.
05 April 2022 – 14:21 UTC
Anonymous Leaks Data from Russian Rations Supplier, Korolevskiy
The company, Korolevskiy (korolevskiy[.].ru) appears to supply Russian companies and organizations with grain, nuts, and confectionaries in addition to rations for the military. This cyberattack could impact the availability of some food ingredient supplies, such as sugar, which is already in short supply and skyrocketing in price across the country due to sanctions.
The data leak includes an 82GB archive containing thousands of emails exfiltrated from the company’s mail servers.
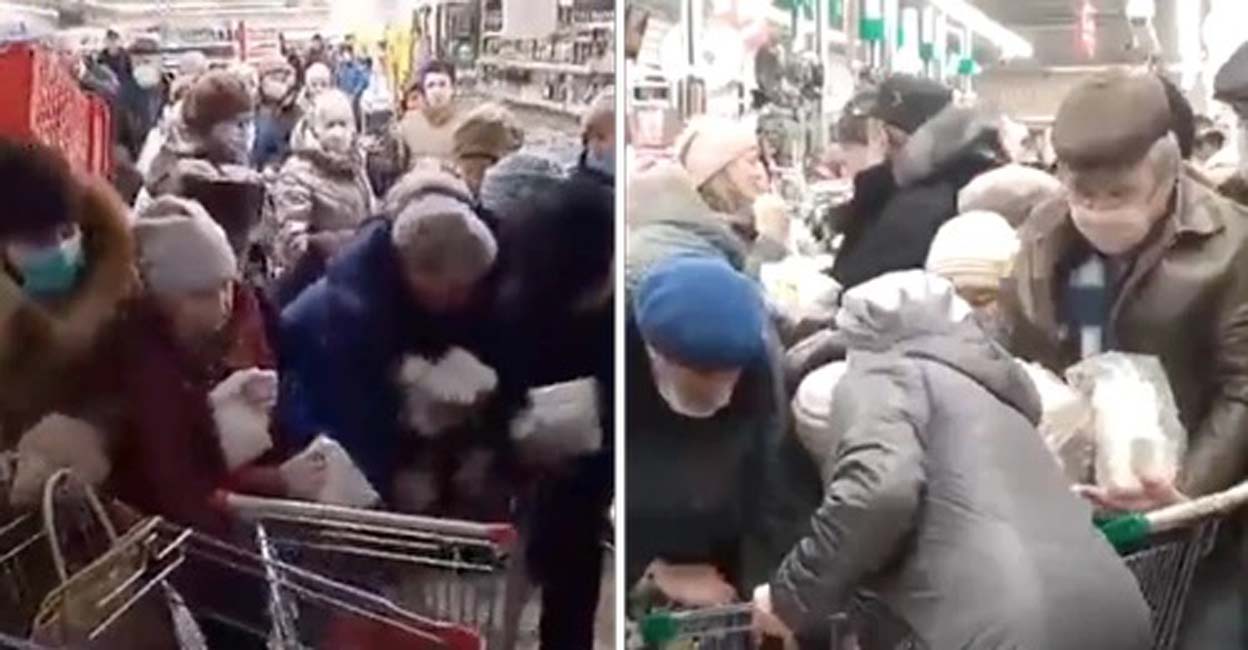


05 April 2022 – 12:29 UTC
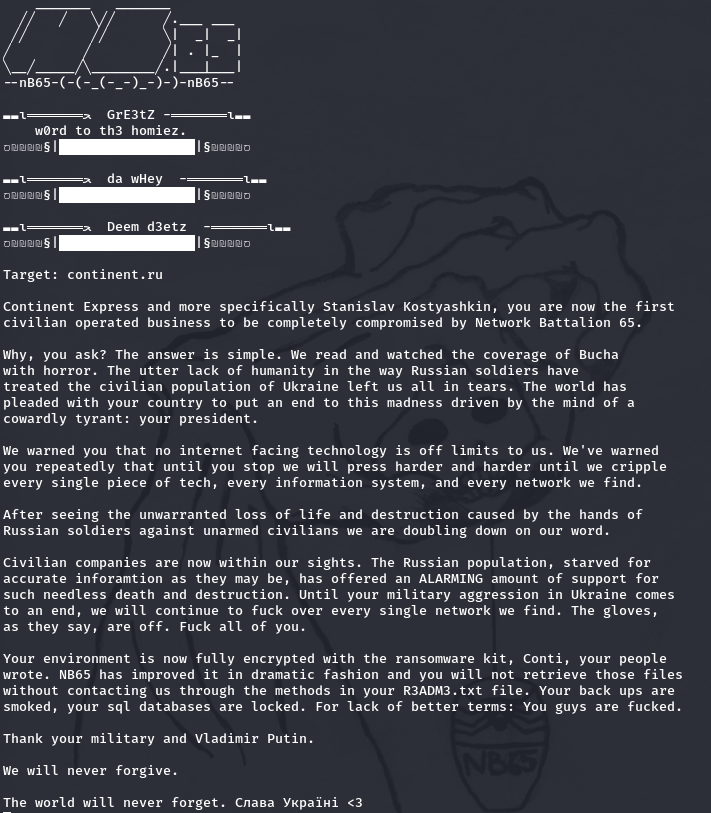
nb65 Claims to Hack Civilian Travel Service in Retaliation for Bucha Massacre
Anonymous and hacktivists around the world step up their offensive against Russia after images of Russian soldiers’ war crimes and atrocities against civlians in Bucha emerged on Monday.
Network Battalion 65 (nb65) reportedly targeted Continent Express (continent[.]ru), a Russia-based travel and supply company, with Conti’s ransomware variant in retaliation for the crimes.
Continent Express is one of the largest agencies for travel in Russia and helps arrange tickets and accomodations. As of time of writing the public facing website for continent[.] is operational.
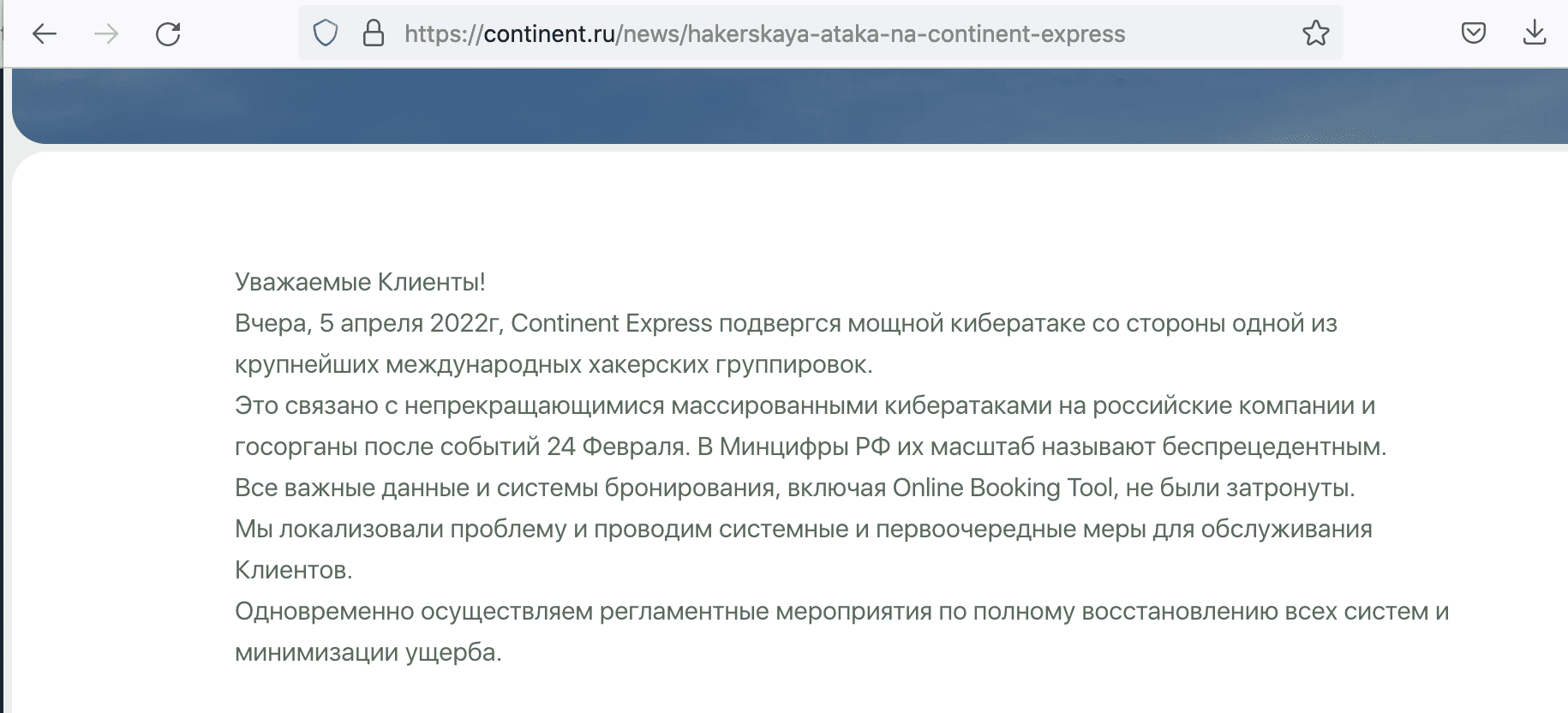
Details of the group’s threatening message posted to social media called out the company’s CEO Stanislav Kostyashkinis in the image below.
“Why, you ask? The answer is simple. We read and watched the coverage of Bucha with horror. The utter lack of humanity in the way Russian soldiers have treated the civilian population of Ukraine left us all in tears. The world has pleased with your country to put an end to this madness drive by the mind of a cowardly tyrant: your president.”
(Update 6 April 2022) Earlier today, Continent Express posted to their news section of the website acknowledging the cyberattack but stated that important data and booking systems were not affected.
04 April 2022 – 12:29 UTC
DDoSecrets Distributes Data Exfiltrated by nb65 From Russian Broadcasting Company
Earlier in the campaign, nb65 leaked a sample of files and emails from All-Russia’s State Television and Broadcasting Company (VGTRK / ВГТРК). The Russian state-owned broadcaster operates five national TV stations, two international networks, five radio stations, and over 80 regional TV and radio networks and has been heralded as essential for the “security of the state.”
According to former VGTRK employees, Kremlin officials have dictated how the news should be covered, and provided incendiary phrases meant to discredit Ukraine. According to the former employees, editors normally have freedom to make decisions, but “where big politics are concerned, war and peace, he has no freedom.”
The 786 GB archive contains over 900,000 emails and 4,000 files spanning 20 years of operations at the broadcaster.
04 April 2022 – 06:24 UTC
Anonymous Leaks List of Russian Soldiers Deployed in Bucha
Anonymous shared a PDF file containing the identities of the members Russia’s 64 Motor Rifle Brigade that was positioned in the Kyiv suburb of Bucha. Since Russia’s withdrawl from the village, the atrocities and war crimes carried out by members of the Brigade have come to light.
The PDF consists of 87 pages detailing the identities of over 1,600 members of the Bridage, including their full name, date of birth, and passport number.
The file most likely originated from the Ukrainian government or intelligence services.
03 April 2022 – 06:16 UTC
Anonymous Shares Data Leaked from Russian Federal Agency for State Property Management
Anonymous shared a single PostGreSQL database, presumably from the domain: rosim.gov.ru, containing over 785MB of logged domain Internet activity available via the domain user: kluser. Much of the data is several years old, including IP addresses, domains, user agents of site vistors. Without further analysis, the value of leaking this data other than psychological operations and information warfare is unclear.
03 April 2022 – 05:07 UTC
nb65 Claims to Compromise Russian Gas Pipeline Supplier: SSK Gazregion
nb65 shared on social media that they have successfully hacked SSK Gazregion LLC (domain: ssk-gaz.ru) – a prominent natural gas pipeline construction company – with an ‘improved’ version of Conti’s ransomware. They taunted the company’s IT department, claiming that they also deleted all backups and restoring services would be an issue for the department.
They also claim to have exfiltrated 110GB of sensitive files, emails, and company data during the operation and trolled the company further stating it took forever to steal the data with the “chincy ass soviet connection” they were using for Internet connectivity.
“Federal Government: This will stop as soon as you cease all activity in Ukraine. Until then, fuck you. Your Preisdent is a coward who sends Russian sons away to die for his own ego. War in Ukraine will gain your country nothing but death and more sanctions. none of your internet facing tech is off limits to us.”
“We won’t stop until you stop.”
03 April 2022 – 04:24 UTC
ATW Release Dox of KILLNET Member
Similar to the personal details shared for various APT cyber groups in China, Russia, and North Korea, ATW targeted the pro-Russian cyber group, KILLNET. They released a dox containing the Russian national’s personal information, his social media, contact information, and familial associations.
KILLNET claimed to launch cyberattacks against Polish government and financial networks in support of Putin’s invasion in Ukraine. Last week, KILLNET also reportedly conducted DDoS attacks against the International Cyber Police agency, CYBERPOL and hacked the ticketing system at Bradley International Airport in Connecticut.
02 April 2022 – 17:28 UTC
Darknet Threat Actor, spectre123 Releases Sensitive Databases for the Indian Government and Military
The threat actor is well-known for targeting governments and defence contractors and has been circulating sensitive government databases for some time. This weekend, they released a “mega leak” of Indian government data for the PM Modi adminsitration’s “turning a blind eye to the humanitarian crisis…. in Ukraine.”
Over 40 GB of data is included in 11 different archived files and includes classified (up to TOP SECRET) and Confidential government documents from the following sectors: ALISDA, DGAQA, MSQAA, DRDO, DDP, Joint Defence Secretary India, BSF, MOD and the Indian Navy.
“The Indian government has a remarkably twisted propensity towards turning a blind eye to the humanitarian crisis in their own nation and now as well in Ukraine. It continues to do business with Russia and refuses to speak on the war, all in an effort to maintain their shallow political interests. These documents have been released to show that there are consequences for taking such foolish decisions.”
02 April 2022 – 06:13 UTC
ATW | BH Claims to Leak Personal Details of Members of Nation State APT Cyber Groups: ATP3, APT40, APT38, & APT28
The AgainstTheWest group continued their offensive against Chinese, North Korean, and Russian nation state cyber groups. Releasing a dox-style text file on Telegram and the deep web forum, breached.co, the ATW group included the names, email addresses, socials and Github accounts, credit card data, front companies, and other identifying information about the group’s participants along with other shocking revelations. Some include:
- APT38: China and North Korea have collaboratively had a mole inside the United States Congress since 2011.
- APT3: Threat actors are closely aligned with employees from Tencent – the Chinese technological giant behind WeChat and QQ.
- APT38/APT3: The alias “ph4nt0m” appears in information for both groups and is believed to be affiliated with APT17 from China.
- APT40: Threat actors are randomly connected to employees of ByteDance, the parent company for TikTok.
We are unfortunately unable to corroberate the veracity of the information shared by ATW (Blue Hornet).
01 April 2022 – 20:13 UTC
Anonymous Attacks Russian S-300 Supplier: Lipetsk Mechanical Plant
Anonymous shared another large archive of data stolen from a prominent Russian defense manufacturing facility. The archive is nearly 27GB total and consists of company emails and sensitive documents.
Russia’s “Lipetsk Mechanical Plant” produces several defense products for the Russian military and industrial defense complex. Today, the plant is one of the leading and main manufacturers of modernized self-propelled tractors for S-300V4 anti-aircraft missile systems in Russia. The S-300 is one of Russia’s premier air-defense platforms.
01 April 2022 – 16:00 UTC
Anonymous Leaks Multiple Data Archives From Critical Moscow-Based Organizations
Coordinating today through DDoSecrets on distribution, Anonymous shared several highly significant archives, consisting of over 500GB total of emails, files, and databases from critical Russian organizations with close ties to the Russian government.
- Department for Church Charity and Social Service of the Russian Orthodox Church: Database containing 57,500 emails from the Russian Orthodox Church’s charitable wing.
- Capital Legal Services: 200,000 emails exfiltrated from a prominent Russian law firm includes an additional 89,000 emails are located in a “Purges” mailbox, consisting largely of bounced email notifications, cron jobs and other server notifications.
- Mosekspertiza: Three archives consisting of a) 150,000 emails b) 8,200 files and c) multiple databases totally over 400GB of data. Mosekspertiza is a state-owned company setup by the Moscow Chamber of Commerce to provide expert services and consultations to Russian businesses.
1 April 2022 – 08:56 UTC
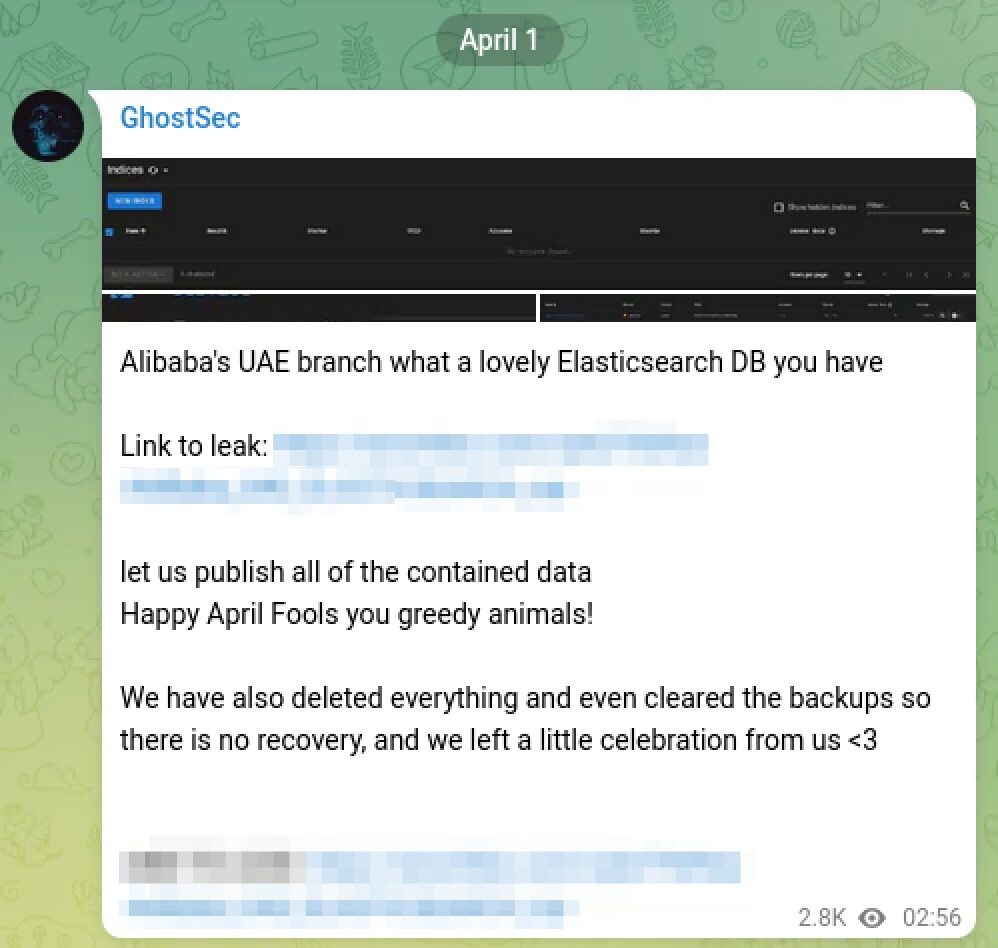
GhostSec Wreaks Additional Havoc on Alibaba
After ATW attacked Alibaba Cloud days before, Ghost Security has allegedly hacked and deleted Alibaba’s UAE branch’s ElasticSearch service database. They included a leak to the database extracted from the company on their Telegram channel.
We have also deleted everything and even cleared the backups so there is no recovery, and we left a little celebration from us <3
31 March 2022 – TIME UNKNOWN
German Wind Turbine Company Impacted by Cyberattack
A German-based wind turbine – Nordex – with over $6 billion dollars in global sales faced a cyberattack that incident responders caught “in the early stages.” It’s likely the attack is retaliation for Germany pausing on the Nord Stream 2 natural gas pipeline deal with Russia.
“Customers, employees, and other stakeholders may be affected by the shutdown of several IT systems. The Nordex Group will provide further updates when more information is available.”
In the early days of the cyberwar, a cyberattack on the satellite communications company Viasat caused 5,800 Enercon wind turbines in Germany to malfunction.

31 March 2022 – 19:43 UTC
Anonymous Leaks 62,000 Emails from Moscow-Based Marathon Group
Anonymous again targets associates of those closest to Putin launching recent cyberattacks against Marathon Group. The Marathon Group is an investment firm owned by Alexander Vinokurov. Vinokurov is the son-in-law of Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Larov and is under heavy sanctions by the EU for providing financial support to Russia. The leaked archive is over 51GB in size and is being distributed via DDoSecrets.
31 March 2022 – 14:31 UTC
Ukraine Government Sets Up Website for Whistleblower Reporting
The Ukrainian Prosecutor General’s Office in coordination with the National Agency on Corruption Prevention and Task Force Ukraine deployed the Whistleblower Portal on the Assets of Persons Involved in the Russian Aggression against Ukraine. The website is setup to provide a secure and anonymous method for the submission of tips and evidence of corruption any activities causing national harm. The website will ideally help in the “tracing, freezing, and confisicating of assets of those involved in Russia’s War Crimes.”
Many OSINT sleuths have identified Russian oligarchs’ and government officials’ assets, like super yachets parked in international ports and submitted photographs via posts on social media. This website could be used to officially report supporting information leading to the seizure of those assets or other correlative intelligence obtained through leaks shared by Anonymous.

30 March 2022 – 22:09 UTC
Database Containing the PII of 56 Million Ukrainian Citizens Leaked on Deep Web
A user on the forum breached.co leaked an arhive containing the personal identification information for over 56 Million citizens of Ukraine. The database includes the full name, dates of birth, and address for the individuals. Its unclear the origins of the data. Members of the forum stated it was the Ukrainian Tax Service and could be dated back to 2018.
30 March 2022 – 21:53 UTC
ATW Continues Offensive Against China, Leaks Alibaba Cloud & Ministry of Justice of PRC Data
The AgainstTheWest/Blue Hornet group have ramped up their attacks against Chinese targets and leaked the largest archive they have exfiltrated to date. ATW successfully breached the e-commerce company Alibaba and have dropped a 30GB archive consisting of Alibaba’s cloud endpoint environment, source code, and customer data. They also released a smaller database obtained from the Ministry of Justice of the People’s Republic of China. Both were shared to the deep web forum, breached.co.

30 March 2022 – 19:49 UTC
Anonymous Continues to Encourage SCADA Attacks; Leaks Default Credentials for COTS Hardware Suppliers
Members of the Anonymous Collective circulate spreadsheets and websites containing the default factory credentials for most commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) vendor hardware. Hardware, that in turn, is often affiliated with and successfully exploited via SCADA-based industrial control system (ICS) cyberattacks.
One list includes 138 unique products including manufacturers such as Emerson, General Electric, Hirshmann, and Schneider Electric accompanied with default factory settings such as username: admin and password:default. Another resource is a surface web website (intentionally not included but available upon request) which lists 531 vendors and over 2,100 passwords deployed with hardware from the factory.
Sadly, most companies will rely on the default passwords upon installaton and do not bother with updating to a more robust credential security standard.
30 March 2022 – 18:19 UTC
Anonymous Leaks 5,500 Emails Stolen from Thozis Corporation
Anonymous successfully attacked Thozis Corporation – a Russian investment firm with links to Zakhar Smushkin of St. Petersburg. According to the Panama Papers, the company is registered in the British Virgin Islands. The firm is allegedly involved in one of the largest development projects in Russia, including a project to build a satellite city within St. Petersburg.
The trove of leaked emails likely include sensitive documents and agreements between the Russian government, its societal elite, and other international entites.
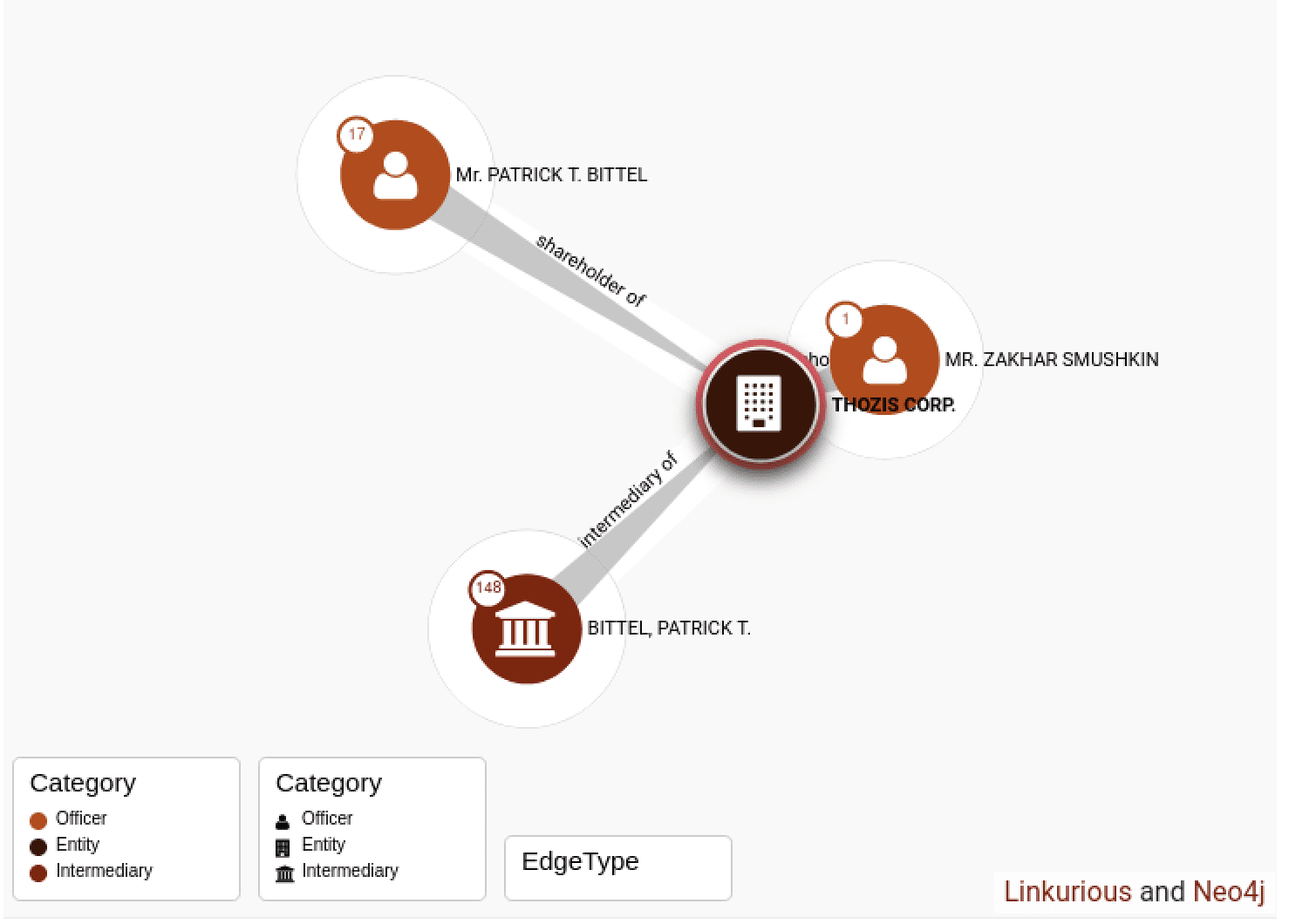
DDoSecrets assisted in the publication of the 5.9GB archive obtained by Anonymous.
30 March 2022 – 17:55 UTC
GhostSec Leaks Shambala Casino Network Data
GhostSec claimed a few days ago they had successfully attacked a prominent casino operator in Russia, known as Shambala.
The hacktivist group targeted the casino as they believed members of the Russian government used Russian casinos to move cash into different currencies besides the Ruble. At least 27 computers were reportedly compromised, data exfiltrated, systems locked, and files erased.

29 March 2022 – 06:12 UTC
Russian Aviation Sector Suffer Additional IT Operational Impacts
A post shared on the Russian Telegram channel, Авиаторщина, indicates that the aviation industry of Russia will have additional impacts to their IT support with the withdrawl of the Swiss-based company, SITA as of 29 March.
According to the Telegram post, SITA shutting down their operations will impact numerous systems utilized by the aviation industry and airlines across Russia.
[translated]
“Products for pilots such as AIRCOM Datalink, AIRCOM FlightMessenger, AIRCOM FlightTracker, and AIRCOM Flight Planning services will no longer be available. Such software is utilized by airlines and flight crews to plan, perform aeronautical calculations and track flights, and more accurately calculate remaining fuel, flight time, etc.”
The company – choosing to withdrawl from operating in Russia due to Putin’s invasion – suffered a significant cyberattack on 24 February, the same day as the invasion of Ukraine, resulting in the compromise of passenger data stored on their SITA Passenger Service System (US) Inc. servers. SITA supports numerous international air carriers.
This annoucement comes within days of the cyberattack against Rosaviatsiya (see below), Russia’s Federal Air Transport Authority.
(Update 30 March – 23:42 UTC) No alias associated with Anonymous has claimed credit for the 28 March cyberattacks against Rosaviatsiya which resulted in 65TB of lost agency data. Interestingly, new Anonymous groups have only recently joined the campaign, including RedCult, increasingly the likelihood that widespread industry sector attacks will continue across Russia.
28 March 2022 – 18:23 UTC
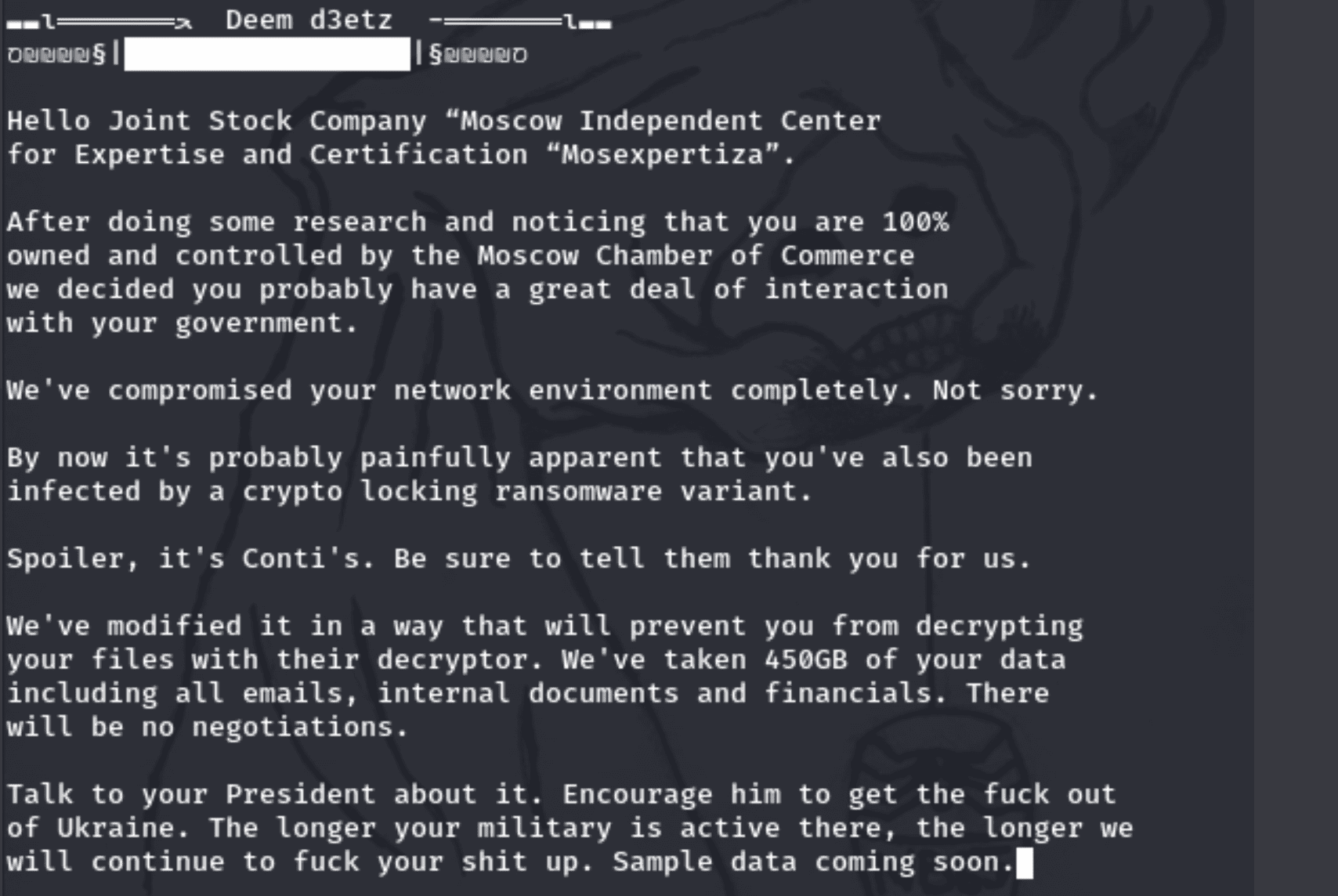
nb65 Claims to Hack JSC Mosexpertiza; Steals 450GB of Sensitive Data
In a social media post, nb65 hacktivist group claims they compromised Joint Stock Company (JSC) Mosexpertiza, Moscow’s independent center for expertise and certifications, via the domain mosekspertiza.ru.
They claim they also infected the domain with, none other than Conti’s “crypto-locking ransomware variant” – released earlier this month in the opRussia campaign. In the process of hacking the network nb65 also exfiltrated 450GB of emails, internal documents, and financial data.
28 March 2022 – 17:07 UTC
Anonymous Leaks 140,000 Emails from Russian Oil & Gas Company, MashOil
Distributed via DDoSecrets, the Anonymous hacktivist collective recently targeted MashOil, releasing over 140,000 sensitive corporate emails from the company.
Moscow-based, MashOil manufacturers equipment for hydraulic fracturing and enhanced oil recovery (EOR); injection, nitrogen and cementing equipment; top drive mobile drilling rigs; directional drilling equipment; and, ejector well clean-up.
Anonymous continues to target companies in Russia and any companies that continue to contribute to economic and financial viability for the Russian Federation.

28 March 2022 – 12:41 UTC
Anonymous Leaks Russian Document Ordering Propaganda Video Development
Knowing propaganda is widely circulated by both Ukrainian and Russian affiliated organizations, Anonymous has leaked an official Russian document, titled “On holding informational events on the Internet”, dated 21 March 2022, stating this was an official “order issued” by the Russian government to develop videos to discredit the Ukrainian military and their treatment of prisoners of war (POWs). The order was signed by the “Temporary Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation”, Dmitry Bulgakov and decrees:
- Develop and distribute a series of video materials demonstrating the inhuman behavior of the military personnel of the Armed Forces of Ukraine and nationalist formations on the territory of Ukraine in relatinos to prisoners who showed a voluntary desire to surrender
- Develop and distribute sermographic materials, evidence of the use of briefings by captured military personnel of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation during the filming
- Provide informational support for materials in the comments, the main argument is the violation of the Geneva Convention on the Treatment of Prisoners
- To impose control over the implmtnation of this order on the head of the Information Warfare and Disguise Department of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation

(UPDATE 29 March 2022 – 20:56 UTC) DarkOwl advises that recent open source intelligence research suggests this letter could be fake and disseminated as part of an information operations campaign. Researchers caught signature mismatches of the Russian official, Bulgakov. Such data is a reality in the the fog of asymmetric warfare.
28 March 2022 – 11:58 UTC
Ukrainian Defense Intelligence Doxxes 620 Russian FSB Agents
The Ukrainian Military Intelligence Agency of the Ministry of Defence of Ukraine, known simily as Defence Intelligence of Ukraine or GUR, has leaked the identities of over 600 Russian FSB spies. The database includes the agents’ full names, dates of birth, passport numbers, passport dates of issue, registration addresses as well as other identifying markers for the FSB employees.
Many of these agents may be conducting covert operations around the world and leaking their identities may compromise the success of their operations.
28 March 2022 – 11:05 UTC
ATW (BH) Targets Chinese Companys and Government Organizations
After a brief vacation announced on 23 March, the AgainstTheWest (Blue_Hornet) group returns with concerted attacks against a number of Chinese companies and government organizations. The group claims they successfully attacked the following:
The group also referenced a supply-chain software dependency attack, via a poisoned burgeon-r3 NPM package.
- Fenglian Technology-Digital Ecological Platform Solution
- Bluetopo China security development tool
- China Pat Intellectual Property
- Weipass
- Ministry of Transport China
- Freemud Software (supplier to Starbucks)
- China Joint Convention Committee.
Shortly after the announcement and initial round of leaks, the group also released source code affiliated with China Guangfa Bank, along with associated Maven releases. The group also claims to have breached the Chinese social messaging platform, weChat.
We are still evaluating the data and determining the specific types of data compromised and released.
28 March 2022 – 03:22 UTC
Russian Federal Air Transport Agency, Rosaviatsiya Confirms CyberAttack; 65TB of Data Erased
The civil aviation agency Rosaviatsiyan responsible for air cargo transportation confirmed with a letter shared on the Russian Telegram channel, Авиаторщина that their website domain favt.ru was offline since Saturday due to a significant cyber attack. The attacks had severely impacted their ability to plan and conduct flight operations and the agency had resorted to pen-and-paper-based operations in the interim.
The notice stated that over 65TB of emails, files and critical documents had been allegedly erased along with the registry of aircraft and aviation personnel. There were no systems backups to restore from because according to the agency spokesperson, the Ministry of Finance had not allocated funds to purchase backups.
“All incoming and outgoing emails for 1.5 years have been lost. We don’t know how to work…”
“The attack occurred due to poor-quality performance of contractual obligations on the part of the company LLC ‘InfAvia’, which carries out the operation of the IT infrastructure of the Federal Air Transport Agency.”

27 March 2022 – 20:44 UTC
Anonymous Leaks 2.4GB of Emails from Russian Construction Company, RostProekt
Over the weekend, DDoSecrets helped Anonymous distribute over 2 gigabytes of sensitive company emails exfiltrated by breaching a prominent Russian construction company, RostProekt (in Russian: РостПроект). The company primarily operates in Russia, with the head office in Moscow Oblast. RostProekt is a primary contributor to Russia’s lumber and other construction materials merchant wholesalers sector. The breach may impact construction projects in the country.
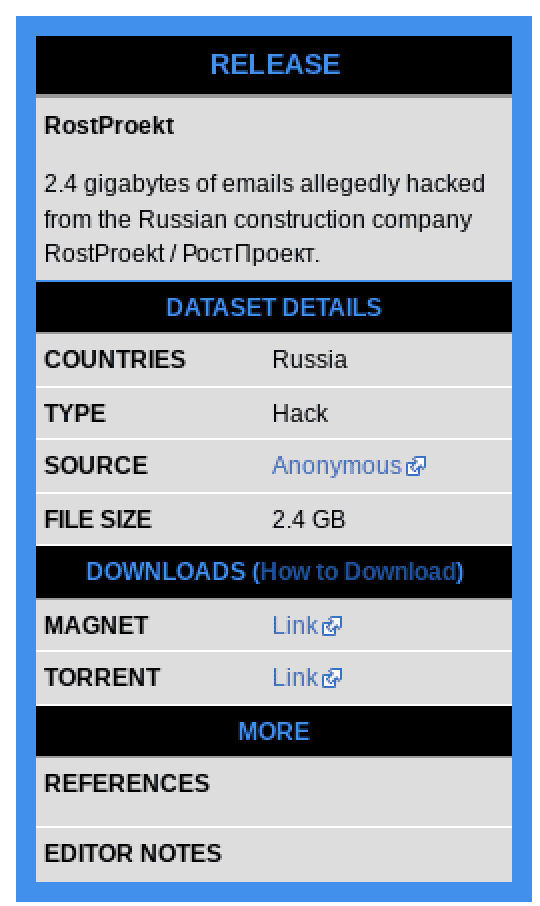

As of time of writing, the website for the company is online.
25 March 2022 – 20:36 UTC
nb65 Leaks Sample Internal Data from the All-Russian State Television and Radio Broadcasting Company (VGTRK)
The nb65 hacktivist team targeted and released data affiliated with a state-sponsored propaganda broadcasting company of the Russian Federation, VGTRK. The All-Russia State Television and Radio Broadcasting Company, also known as Russian Television and Radio (native: Всероссийская государственная телевизионная и радиовещательная компания) owns and operates five national television stations, two international networks, five radio stations, and over 80 regional TV and radio networks. It also runs the information agency Rossiya Segodnya.
nb65 claims they have successfully compromised the organization’s network and exfiltrated over 750GB of data, much of which consists of employee email (.pst) files from the company’s email network. The group claims to be ‘watching’ for their ‘eventual incident response.’
The group continued to troll the organization…
“Your blue team kinda sucks. Hard to find good IT help when all your techies are fleeing the country, eh?”
25 March 2022 – 18:36 UTC
Anonymous Releases Files Exfiltrated from the Central Bank of Russia
Anonymous has released data the hacktivists collected while conducting attacks against the Central Bank of Russia. The archive, broken up into 10 separate parts consists of over 25GB of archived data consisting of over 35,000 files of sensitive bank data. Earlier in the campaign, we observed several posts containing targeting information, e.g. domains, IP addresses, etc for the bank on the deep web.


24 March 2022 – 20:49 UTC
GNG Claims to Hack Russian Mail Server, mail.ru
Georgia’s Society of Hackers (GNG) announced today they successfully attacked Russia’s equivalent to Gmail, mail.ru, including their maps.mail.ru subdomain. The hacktivist group is in process of exfiltrating the data and will provide the detailed data dump in the next few days.
As of time of writing this, the maps.mail.ru website is online and operational.
24 March 2022 – 14:11 UTC
Anonymous Shares Proof of Hacked ATMs in Russia
Earlier today, users at what appears to be a Sberbank ATM reportedly located in Russia experienced technical errors when selecting the Russian language on the screen. Upon selection, the ATM monitor quickly flashes to the Ukrainian flag and the words Glory to Ukraine (Слава Україні!). See the video captured video here.
ATM malware is widely circulated on the darknet and used extensively in the fraud and financial crime communities.


24 March 2022 – 10:43 UTC
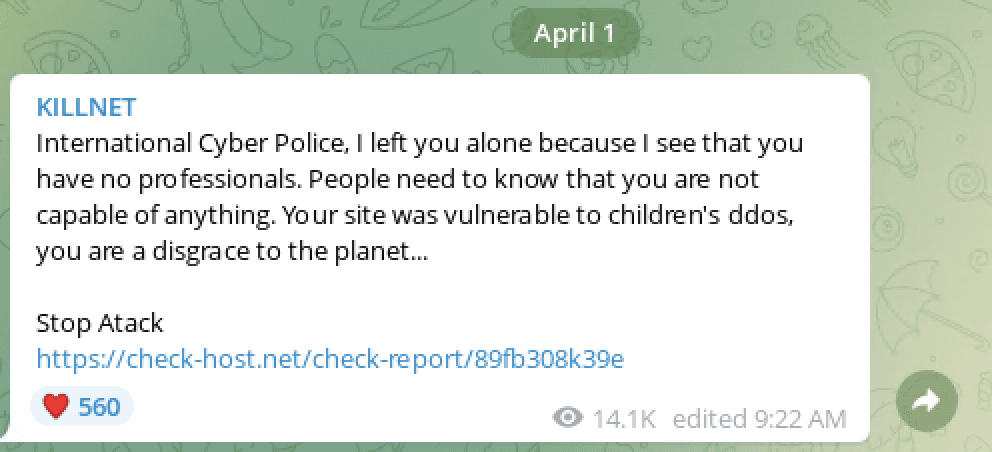
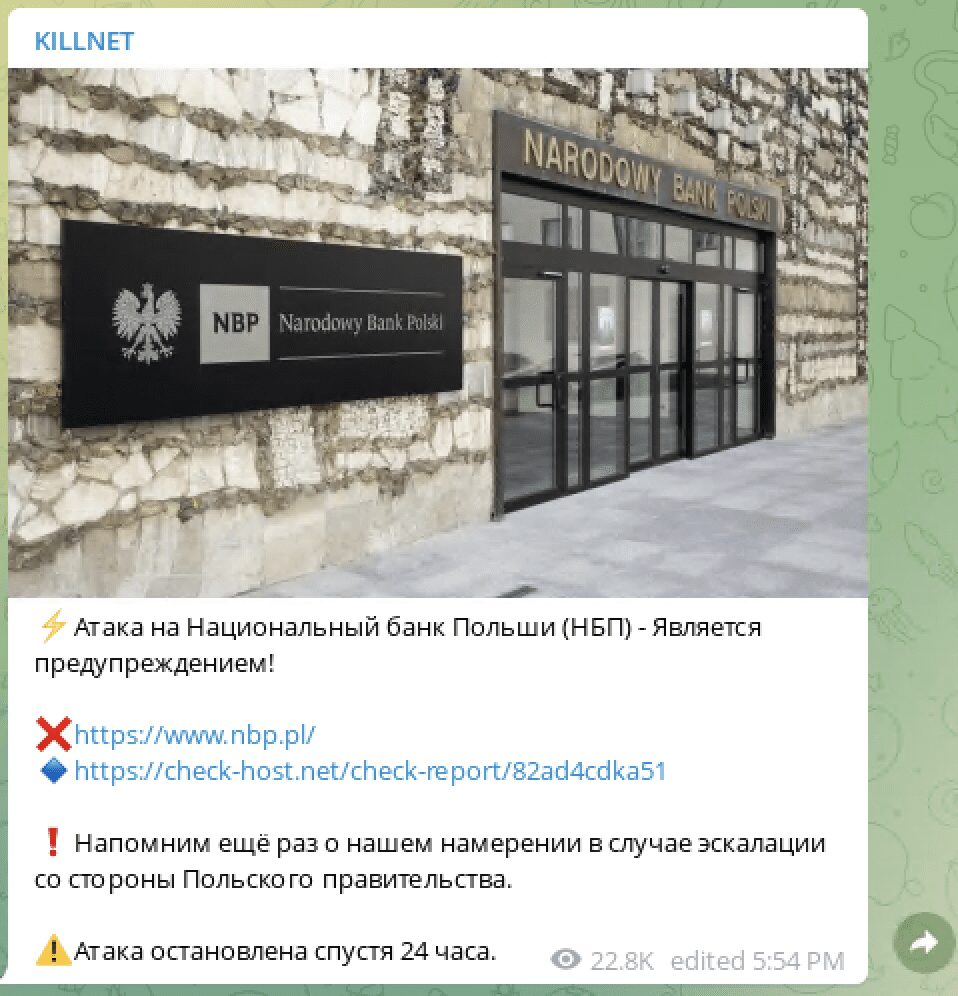
Pro-Russian Killnet Launches Anonymous-Style Campaign Against Ukraine – Targets Poland and NATO
The pro-Russian cyber threat actor group, Killnet have been conducting attacks against Ukraine for several weeks and have stepped up their demands and threats against Ukraine and western Europe. Today, they released a video on social media, mirroring the ominous messaging of an Anonymous-style video with the Russian flag in the background. During the video, the group stated they would attack targets in Poland for their assistance to the Ukrainian government during the invasion. They recently also posted specific targeting information for the National Bank of Poland on their Telegram channel.
“…together with the Russian cyber army, we disabled 57 state websites of the Kiev regime, 19 websites of nationalist parties…”
The group also referred to the Colonial Pipeline attack in the US from May 2021.
[translated] “Let’s remember American gas company attack, which resulted in 40% paralyzed infrastructure of America for few days.”

23 March 2022 – 16:45 UTC
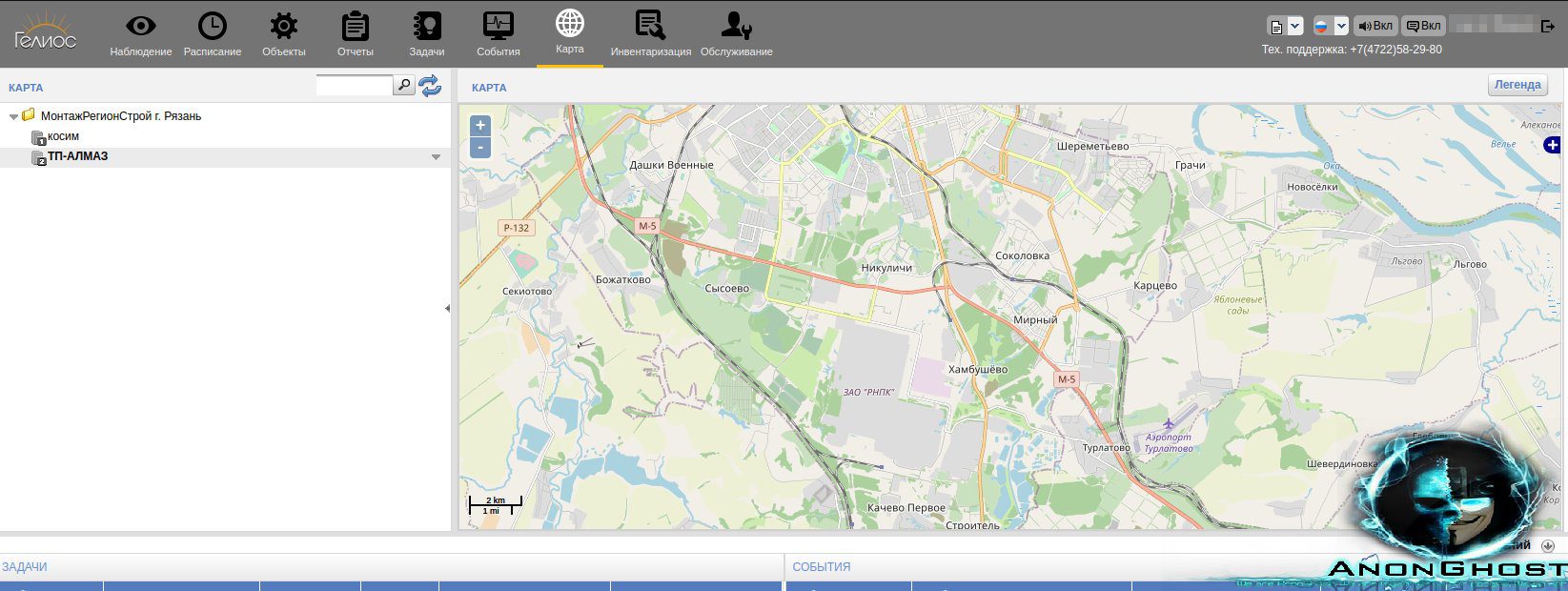
AnonGhost Claims to Hack Russian Street Lighting System and Drops Proofs of Access to Moxa Industrial Wireless Networking Infrastructure
AnonGhost known for their attacks against industrial control systems, continued their campaign against Russia by targeting МонтажРегионСтрой г. Рязань street light control system. They stated they successfully shutoff the street lights at 19:35 Moscow time and it was a “gorgeous show.”
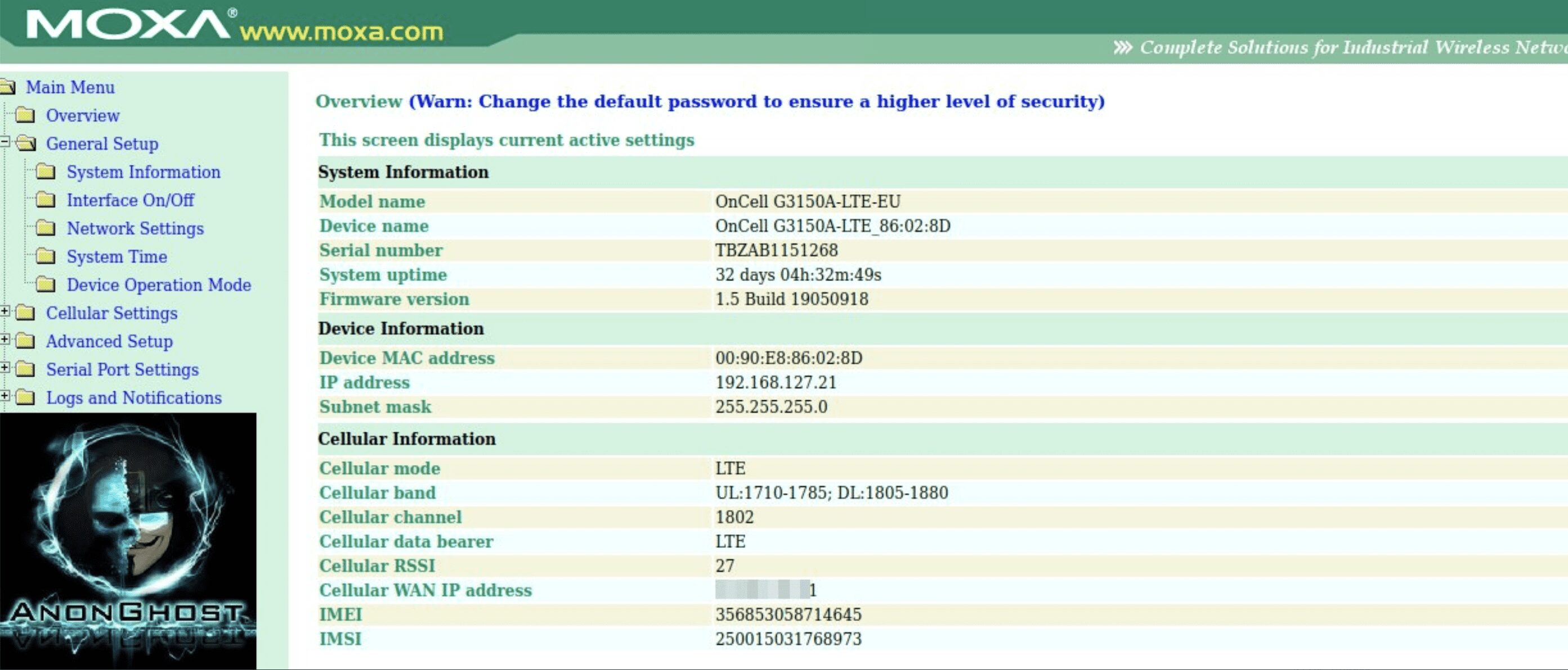
Shortly before announcing the breach of the lighting contol panel, AnonGhost also provided proof of access to Moxa (moxa.com) industrial networking devices. They leaked proof of access to router information for a industrial wireless Moxa device, its associated OnCell specifications, along with defacement of the device’s name, description, and login message.
In addition to the proofs they linked to a pastebin file containing over 100 Russian Moxa IP addresses for additional targeting.
It’s unclear where the Moxa device compromise is physically located or whether the Moxa compromise provides direct access to the streetlight control system.
23 March 2022 – 02:44 UTC
BeeHive Cybersecurity Claims They Are Running Ransomware Campaigns Against Russian Targets
When one thought they only hijacked Discord users and trolled pro-Russian ‘hackers’ like @a_lead_1, BeeHive Cybersecurity claims they have been quiet because they are running ransomware operations against targets across Russia.
Oh, in case you guys were curious why we’ve been so quiet. May or may not have a new #ransomware operation running in Ru right now. Alas, we find allies quicker than Putin finds ways to invade Ukraine. We’ll have more details soon but…consider this the public disclosure.
This would not be the first Russia-specific ransomware variant to emerge. According to Trend Micro, RURansom was detected targeting Russian-specific devices with AES-CBC encryption and hard coded salt. Another ransomware variant recently detected, known as “Antiwar” appends the file extension, “putinwillburninhell” to encrypted files.
22 March 2022 – 19:14 UTC
ATW (Blue Hornet) Compromises Russia’s Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring Service with Bitbucket
The AgainstTheWest / Blue Hornet team has recently leaked several internal documents from Russia’s Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring service (spelled by the threat actors as ROSHYDRO). According to open sources, the monitoring service is hosted on the meteorf.ru domain. The data leaks consists of 45 PDF files containing historical software change descriptions and feature requests from the company’s internal software development tracking system. ATW refers to a superadmin account for the GIS FEB RAS Team on Bitbucket in the leak.
21 March 2022 – 22:44 UTC
ATW Returns to Campaign with Attacks Against Almaz-Antey
After a disruption in the ATW team’s cyber activities due to personal issues, the ATW/Blue Hornet team returns leaking a 9GB archive of data allegedly exfiltrated by breaching Almaz-Antey’s corporate networks. The data leak includes employee login data, multiple documents containing PII, confidential and classified intellectual property, schematics, and SQL database files.
Almaz-Antey (Russian: ОАО “Концерн ВКО “Алмаз-Антей”) is one of Russia’s largest defense and arms enterprises, known for the development of Russian anti-aircraft defense systems, cruise missiles, radar systems, artillery shells, and UAVs.
21 March 2022 – 15:26 UTC
Anonymous Targets Russian Software Developer, naumen.ru
Hacktivists from the Anonymous collective have leaked data exfiltrated from Naumen, a software vendor and cloud services provider in Moscow. The company markets itself as “world class IT solutions fully adapted to the Russian market” and lists several prominent international companies as partners. The leaked data consists of an SQL database containing thousands of usernames, email addresses, hashed passwords, and associated PII. The specific purpose and origins of the database from inside Naumen is unclear, but partner companies could experience supply chain / vendor risk issues.

21 March 2022 – 03:27 UTC
KelvinSec Targets Nestle for Continued Commercial Operations in Russia
The KelvinSec ‘hacking’ team have reportedly compromised Nestle in retaliation for continuing to operate and distribute their products in Russia. The group leaked multiple databases from Nestle consisting of customer entity data, orders, payment information, and passwords (10GB total). The group insisted its a “partial” database leak and more data may be released in the future.
Nestle defended its business decision after President Zelenskyy called the company out to protestors on Saturday night in Bern, Switzerland.
(Update 3/22 – 01:48 UTC) Anonymous issues warning and gives a number of US companies 48 hours notice to pull out of Russia or become targets of the #opRussia cyber offensive campaign. Example corporations include: Subway, Chevron, General Mills, Burger King, citrix, and CloudFlare.
20 March 2022 – 23:33 UTC
Anonymous Compromises Russian Social Media VK to Send Message to Millions
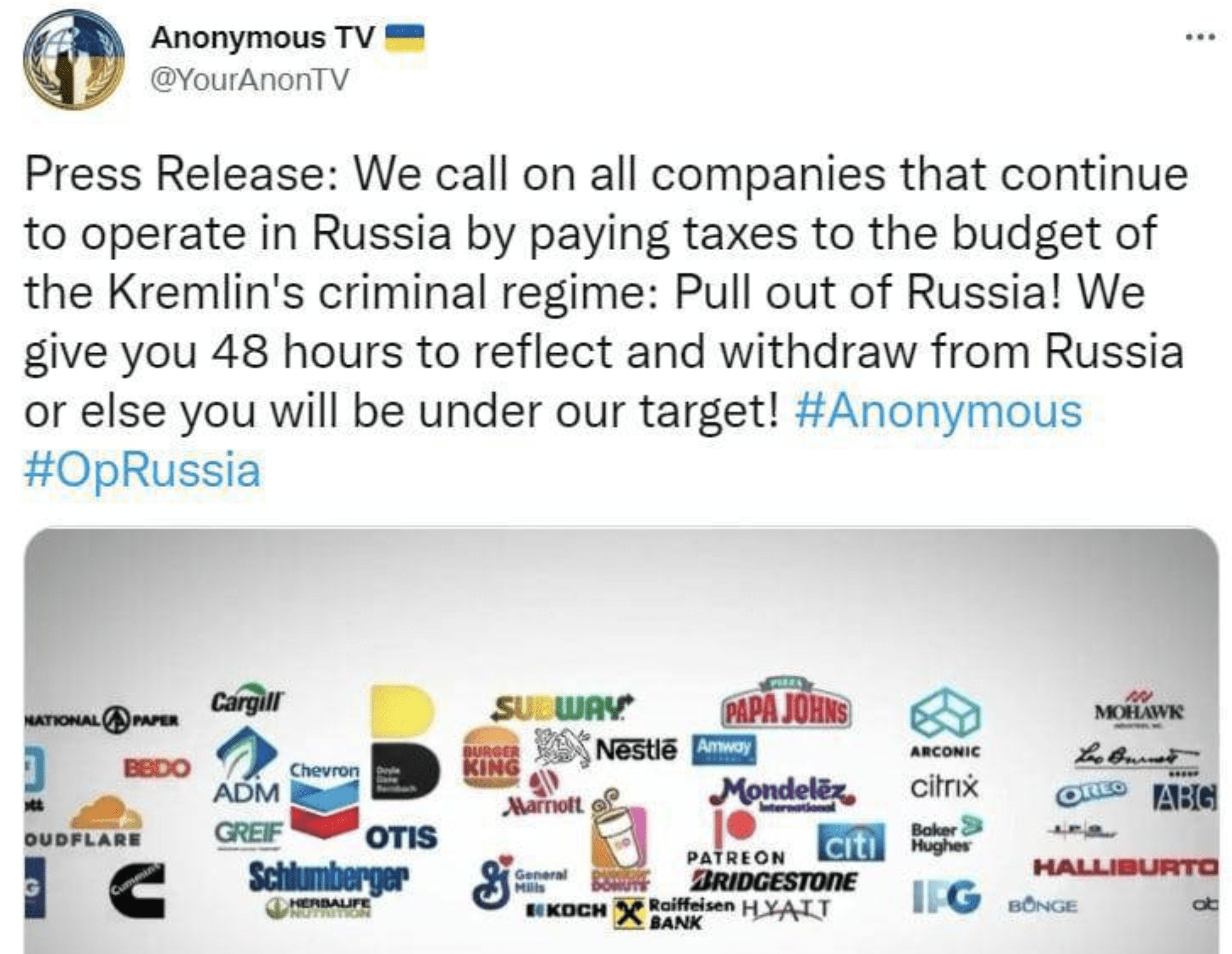
Anonymous accesses VK’s messaging platform and sends direct messages to over 12 million Russian users of the social media app. The message, written in Russian, speaks to the realities of the war in Ukraine, the demise of the Russian economy, and threatens that users using the Russian “Z” insignia on as their profile avatar will be targeted by international authorities.
VK users have shared proofs of the message received to confirm the campaign in VK occurred.
20 March 2022 – 15:32 UTC
GhostSec Leaks Military Asset Monitoring System and More from Russian Networks
The leak includes data exfiltrated from a military operational readiness monitoring website (orf-monitor.com), including inventory tracking of key Russian military assets; a leak of a Russian investment company that includes recent Chinese contract data; and lastly, technical data leaks from Russian Defense Contractor Kronshtadt, that includes computational specifications related to their UAVs, along with military operational doctrine, etc.

GhostSec teased on their Telegram channel they had more data coming and this archive they were sharing was a sample of a much bigger dataset.
20 March 2022 – 13:40 UTC
Honest Railworkers in Belarus Help Stop Lines Going to Ukraine
According to open source reporting and the hacktivist group known as Cyber Partisans, the railways going out of Belarus into Ukraine have stopped. Earlier in the campaign, Cyber Partisans disrupted rail operations in Belarus using cyber attacks against ticketing systems and switching systems; however, others report that the rails are inoperable due to “honest railworkers” who do not want to see Belarus military equipment transported into Ukraine for use in this war. (Source)
“I recently appealed to Belarusian railway workers not to carry out criminal orders and not transport Russian military forces in the direction of Ukraine. At the present moment, I can say that there is no railway connection between Ukraine and Belarus. I cannot discuss details, but I am grateful to Belarus’s railway workers for what they are doing” – Oleksandr Kamyshin, director of the Ukrzaliznytsya state railroad
20 March 2022 – 10:28 UTC
Arvin Club Takes Down STORMOUS Ransomware’s Tor Onion Service
Shortly after STORMOUS ransomware gang setup a Tor onion service, the Arvin Club ransomware group compromised their site and leaked SQL databases, information, and performance schemas. It’s unclear whether or not this attack occurred out of STORMOUS’s Russian allegiance or if Arvin merely wanted to teach the cyber criminals a lesson in setting up secure sites on the darknet.
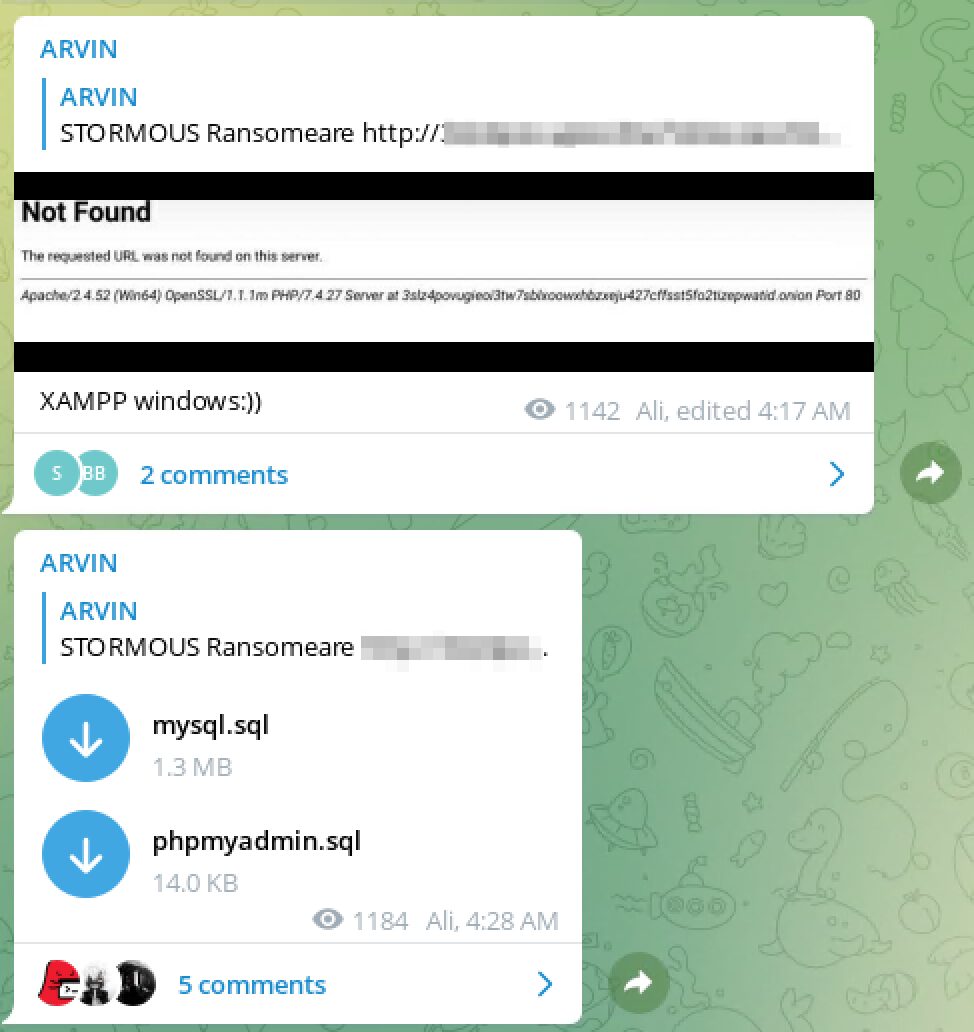
The STORMOUS ransomware group had previously operated only on Telegram.
(UPDATE) As of 3/22 the Tor service is still offline.
20 March 2022 – 02:18 UTC
Anonymous Leaks Database from Russian Aerospace Company Utair
Hacktivists from the Anonymous collective have released the customer database for Russia’s Utair airlines. (Russian: ОАО «Авиакомпания «ЮТэйр»). The JSON database appears to have been collected long before the 2022 #opRussia campaign, as the MongoDB is dated 2019. There are records containing personal data for over 530,000 clients using Utair’s services.
18 March 2022 – 21:29 UTC
nB65 Leaks Data from Russian Space Agency
After a disappointing trolling exercise against Kaspersky, the nb65 hacktivist group returns with data leaks from Russia’s Space Agency, Roscosmos. The group claims they still have persistent access to the agency’s vehicle management system and leaked the IP of the compromised network to prove their access. The leaked data archive consists of over 360MB of user and operations manual, along with solar observatory logs.
Hours earlier, the group also claims to have compromised tensor.ru and leaked 1.6GB of compromised emails for a corporate mailbox for the Russian digital signature company.
18 March 2022 – 15:39 UTC
Russia Targets Ukraine Red Cross Website in Cyber Attack
The Ukrainian Red Cross reported their Internet web servers have been hacked, likely by Pro-Russian cyber threat actors. The website domain – redcross.org.ua – is currently offline with the statement “account disabled by administrator.”
The social media account for the Ukrainian Red Cross stated that no personal data of beneficiaries stored on the website were compromised by the cyber attack.
The Ukrainian Red Cross staff and volunteers are busy and actively providing medical aid and support to vulnerable and wounded Ukrainian civilians across the country as Russian military continue their barrage of cruise missile strikes.
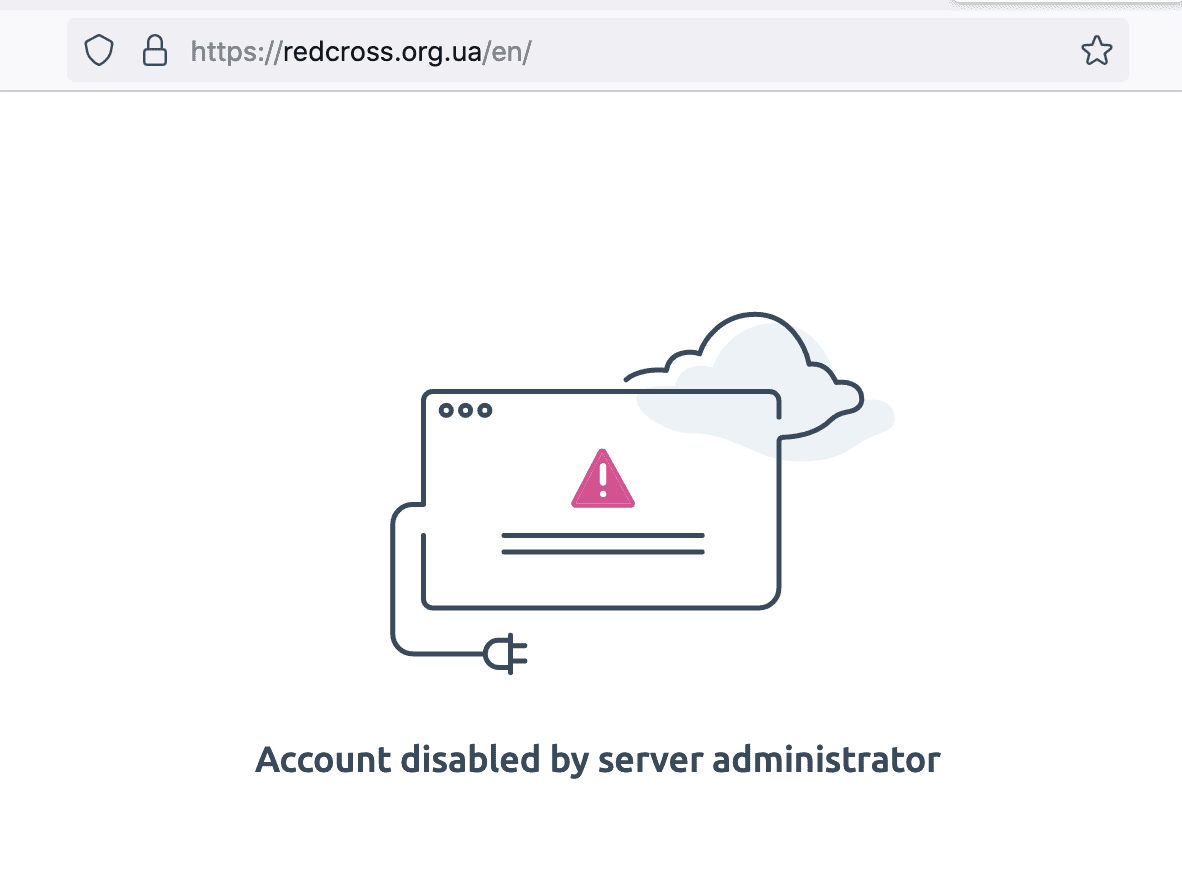

17 March 2022 – 11:43 UTC
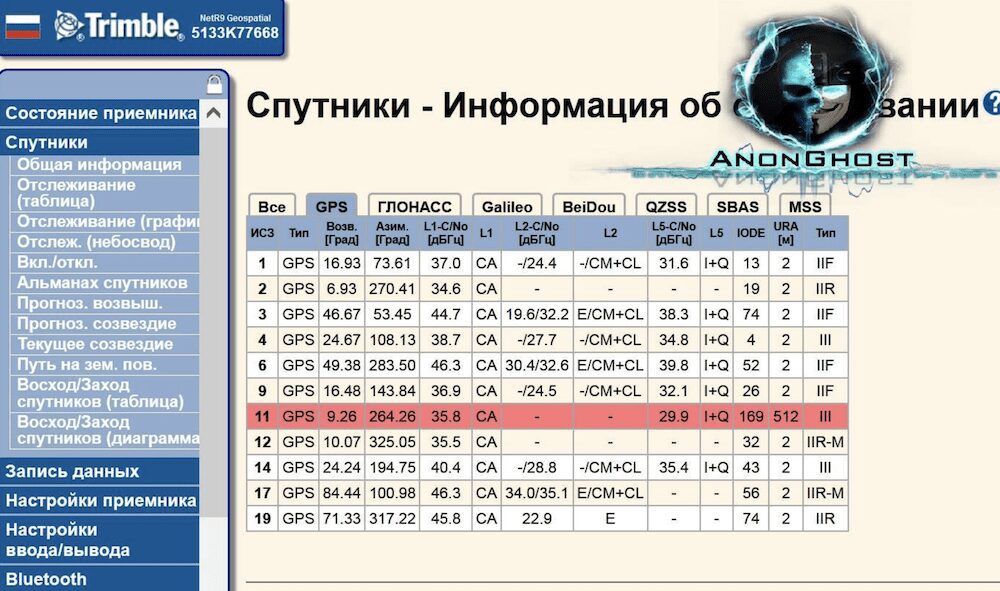
AnonGhost Leaks Screenshots of GNSS Satellite Hacks Along with IP Addresses
AnonGhost shared several screenshots as proof of attacks they conducted against Russia’s Trimble GNSS satellite interface. They claimed on social media that other “fake Anonymous” accounts had taken credit for the operation. They also leaked 48 unique IP addresses associated with the GNSS satellite systems. The group did not specify the nature of the attacks against the Russian assets.
17 March 2022 – 09:23 UTC
Anonymous Claims to Have Located Putin’s Bunker
Using OSINT analysis involving satellite imagery and topography and landmark comparisons like rivers and powerplants, the Anonymous community claims they have detected President Putin’s bunker. There no means to verify the accuracy of these assertions.
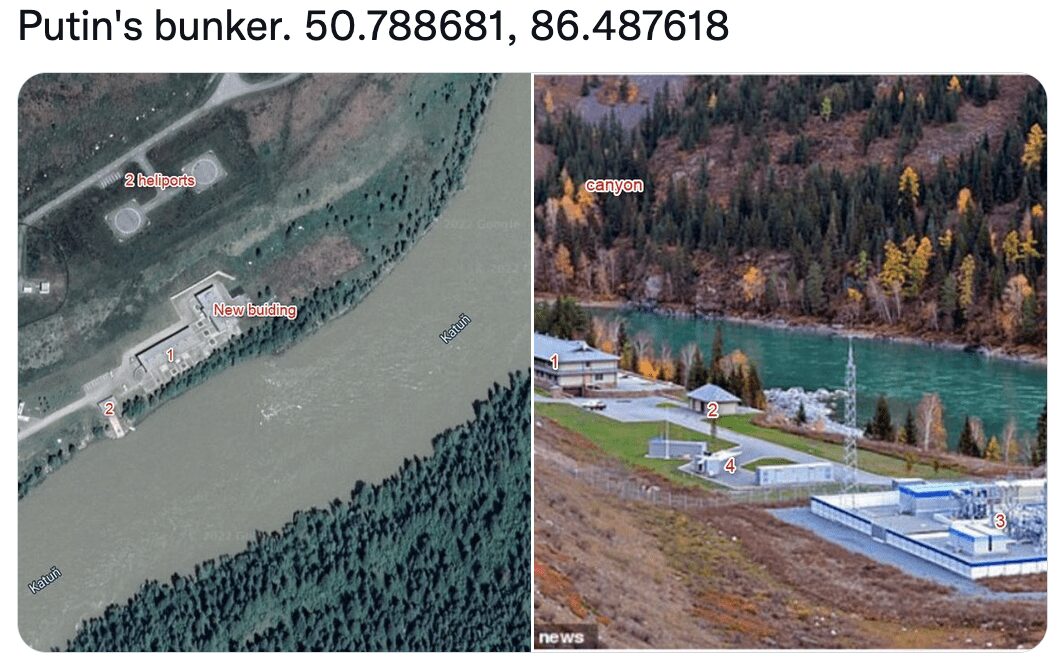

17 March 2022 – 03:58 UTC
Anonymous Leaks 79 GBs of Emails from R&D Department of Transneft – OMEGA
DDoSecrets released the data on behalf of Anonymous hackers operating in cyber campaigns against Russia. Anonymous compromised email inboxes of OMEGA Company, the R&D arm of Russia’s state-controlled pipeline company known as Transneft [Транснефть]. Transneft is the world’s largest oil pipeline company with over 70,000 kilometres (43,000 miles) of trunk pipelines and transports an estimated 80% of oil and 30% of oil products produced in Russia. The emails cover the accounts’ most recent activity, including after the introduction of US sanctions on February 25, 2022. Some of the emails reflect some of the effects of those sanctions.

16 March 2022 – 10:47 UTC
Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR) Requests Information via Tor
Russia’s external intelligence agency has issued instructions on how to establish secure communcations via their Virutal Reception System (VRS) to relay any threats to the Russian Federation. The call for leads, found on svr.gov.ru, details how to install the Tor anonymous network, details the v3 .onion address of their secure communications system, and advises the informant using PGP in order to further encrypt the details of any messages provided.
“If you are outside Russia and have important information regarding urgent threats to the security of the Russian Federation, you can safely and anonymously share it with us via the virtual reception system (VRS) of the SVR over the TOR network.”
If you are in hostile environment and/or have reasons to worry about your security, do not use a device (smartphone, computer) registered to you or associated in any way with you or people from your personal settings for network access. Relate the importance of information you want to send us with the security measures you are taking to protect yourself!
15 March 2022 – 11:48 UTC
Pro-Russian Group Xaknet Threatens to Attack Critical Infrastructure Information Centers
“We cannot endlessly give you ‘lessons of politeness.’ We demand the cessation of hacker attacks against Russian infrastructures, we demand the cessation of the activities of information centers for the dissemination of fakes.
In case of refusal, we will be forced to use the most sophisticated methods, and reserve the right to act as the enemy does. Critical information infrastructure facilities will become a priority target for the group. All work will be aimed at the complete destablization of the activities of the aforementioned CIIs.”
It’s unclear from the threats what specific websites or services the cyber threat group considers critical infrastructure information services. The IT Army of Ukraine’s extensive information operations spread across most all social media platforms and information communication mediums across Russia.
15 March 2022 – 07:19 UTC
User on Telegram Leaks New Letter from FSB
A user on pro-Ukrainian Telegram channel (name redacted) has released a new letter, reportedly from an FSB agent, translated into English.
The temperature has really risen here, it’s hot and uncomfortable. I won’t be able to communicate for some time here in the future. I hope we can chat normally again in a few days. There are a lot of things that I have to share with you…
The questions are raised by the FSO (Federal Protective Service of the Russian Federation, aka Putin’s Praetorian Guard) and the DKVR (Russian Military Counterintelligence Department). It is precisely the DKVR that is mounted on horseback and is looking for “moles” and traitors here (FSB) and in the Genstaff (General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation) regarding leaks of Russian column movements in Ukraine. Now the task of each structure is to transfer the fault to others and to make the guilt of others more visible. Almost all members of the FSB are busy with this task at the moment.
The focus is on us more than others at the moment, due to the hellish circumstances regarding the intra-political situation in Ukraine: We (the FSB) have released reports that at least 2,000 trained civilians in every major city of Ukraine were ready to overthrow Zelensky (President of Ukraine). And that at least 5,000 civilians were ready to come out with flags against Zelensky at the call of Russia. You want to laugh ? We (FSB) were supposed to be the judges to crown Ukrainian politicians who were supposed to start tearing each other apart arguing for the right to be called “Russia’s allies.” We even set criteria on how to select the brightest of the most competent (among Ukrainian politicians). Of course, some concerns have been raised about the possibility that we may not be able to attract a large number of people (Ukrainian politicians) to Western Ukraine, to small towns and to Lvov itself. What do we actually have? Berdyansk, Kherson, Mariupol, Kharkiv are the most populated pro-Russian areas (and there is no support for Russia even there). A plan can fall apart, a plan can be wrong. A plan can give a result of 90%, even 50%, or 10%. And that would be a total failure. Here it is 0.0%.
There is also a question: “How did this happen?” This question is actually a (misleading) trap. Because 0.0% is an estimate derived from many years of work by very serious (high-ranking) officials.
And now it turns out that they are either agents of the enemy or simply incomprehensible (according to the FSO / DKVR who are now looking for “moles” within the FSB).
But the question does not end there. If they are so bad, then who appointed them and who controlled their work? It turns out that they are people of the same quality but of a higher rank. And where does this pyramid of responsibilities stop? At the boss (Putin).
And this is where the evil games begin: Our dear Александр Васильевич (Alexander Vasilyevich Bortnikov – Director of the whole FSB) cannot fail to understand how badly he got caught. (Bortnikov realizes the deep mess he is in now)
And our evil spirits from the GRU (Main Intelligence Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation) and the SVR (Foreign Intelligence Service – equivalent to the CIA) understand everything [and not only from these two organizations]. The situation is so bad that there are no limits to the possible variations (of events that will happen), but something extraordinary is going to happen.”
Shortly after a first letter from an FSB whistleblower surfaced around 5 March, Putin quietly placed his FSB chief, Sergei Beseda and his deputy on house arrest last Sunday. While telling the public he arrested them for embezzlement charges, according to open-source reports, the “real reason is unreliable, incomplete, and partially false information about the political situation in Ukraine” and Putin is holding them responsible for the Ukrainians’ success in the invasion thus far.
14 March 2022 – 12:00 UTC
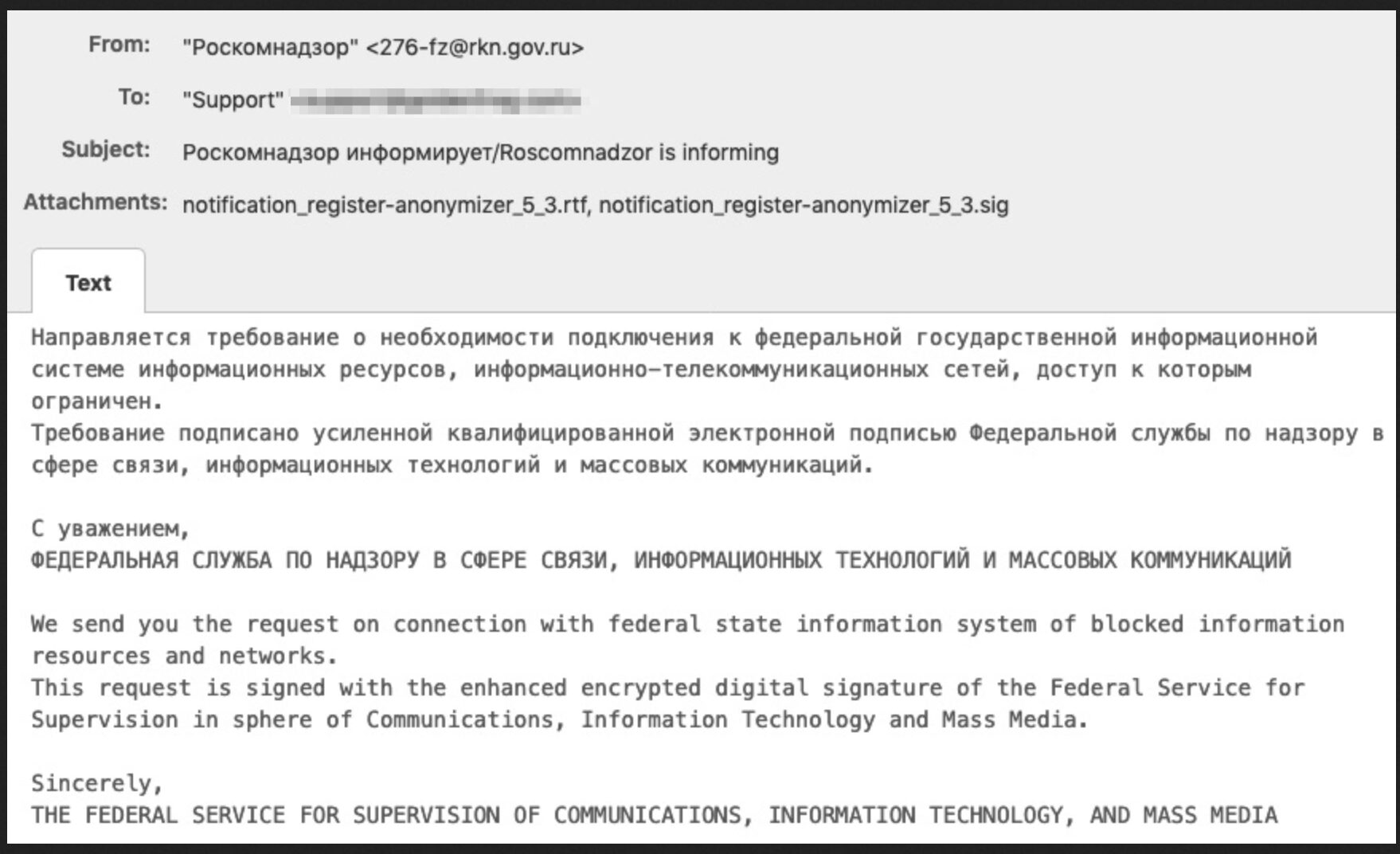
Russian State Duma of the Federal Assembly Confirms Censorship of VPNs
Citing it was “a difficult task” Alexander Khinshtein, chairman of the State Duma Committee on Information Policy, commented that Russia’s media and propaganda agency, Roskomnadzor has been tasked with blocking over two dozen VPNs [virtual private networks] across Russia. (Source)
We anticipate that number to increase as Putin continues to crack down on Russian citizens’ media consumption.
VPNs have been targeted by Russian authorities since 2017, when an initial VPN law was passed. In 2019 many of the VPN providers across Russia received compliance demands from Roskomnadzor representatives via email – captured in the image below.
The demand for VPNs in the country has reportedly increased by over 2,000% in the last month. Users on Telegram encourage widespread use of anonymity tools like VPNs and Tor, and share links to VPN services still in operation and accessible in the region. Many of the VPNs are available via Telegram directly and offer free trial subscriptions to Russian users.
14 March 2022
Russian Cyber Actors Setup IT Army of Russia Group
The collective of cyber threat actors self identifies as the “IT Army of Russia”, mirroring the IT Army of Ukraine Telegram initiative, and claims it has targeted critical Ukrainian cyber services with DDoS attacks. The group has less than a 100 subscribers and many of the members are affiliated with the Killnet forum.
The group recently posted a detailed dox containing personal information for President Volodymyr Zelenskyy [in Ukrainian: Володимир Олександрович Зеленський]. The dossier contains specific information such as his date of birth, passport number, car registration details, and familial associations.
13 March 2022 – 09:31 UTC
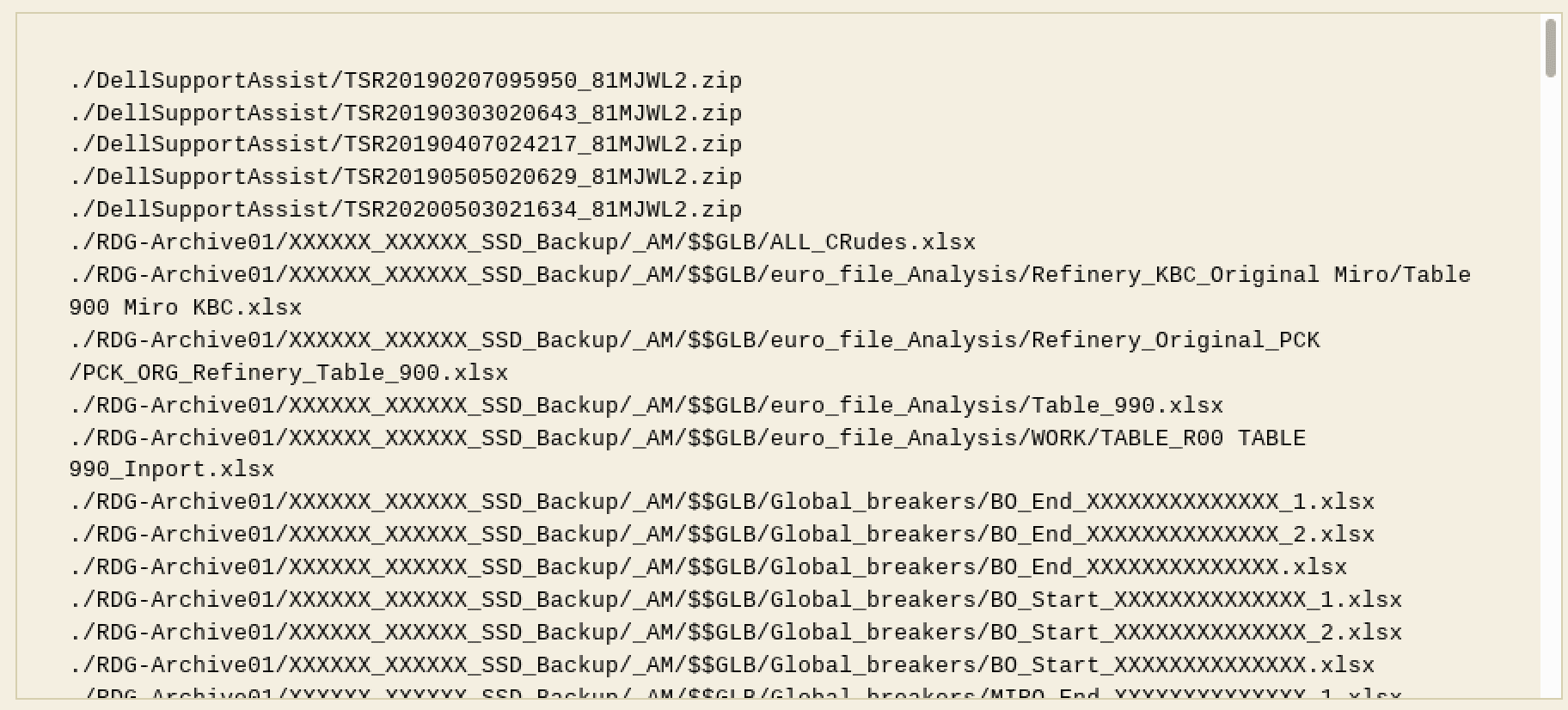
Anonymous Germany Exfiltrates Data from Russian Rosneft Operations in Germany
An Anonymous hacktivist group from Germany, referring to themselves as “AnonLeaks” had access to the networks of Russia’s Rosneft subsidiary in Deutchland for almost two weeks and exfiltrated over 20 terrabytes of corporate data. According to a preliminary review, the data consists of laptop backups, virtual disk images, excel files, work instructions, and other operational information for the refinery.
Anonymous Germany emphasizes they did not have access to critical infrastructure in Germany, nor was the intent of their operation to access critical infrastructure for the refinery or compromise it in any way.
Rosneft is Germany’s third largest petroleum refinery company, processing roughly 12.5 million tons of crude oil per year.
(Update) Details of the leaked data has appeared on a dedicated Tor darknet service setup by the hacktivists.
13 March 2022 – 07:19 UTC
nB65 Claims to Be Jonathan Scott, a US-based Malware Researcher
Since the invasion, a social media account reportedly affiliated with the group nB65 was extremely active in sharing their leaks and targets across Russian networks – including claims of accessing Roscomos Space Agency. Most recently, they stated they had access to Kaspersky’s source code, with many teasers in the hours leading up to a what amassed to a disappointing dump of publicly available code from the Russian antivirus software developer. The group essentially trolled Kaspersky and received heavy criticism from members of the information security research community.
The owner of the group’s Twitter account claimed today they were in real life, Jonathan Scott, a US-based Computer Science PhD student researching mobile spyware and IoT malware. Shortly after, the Twitter account for the group was deleted.
11 March 2022 – 06:25 UTC
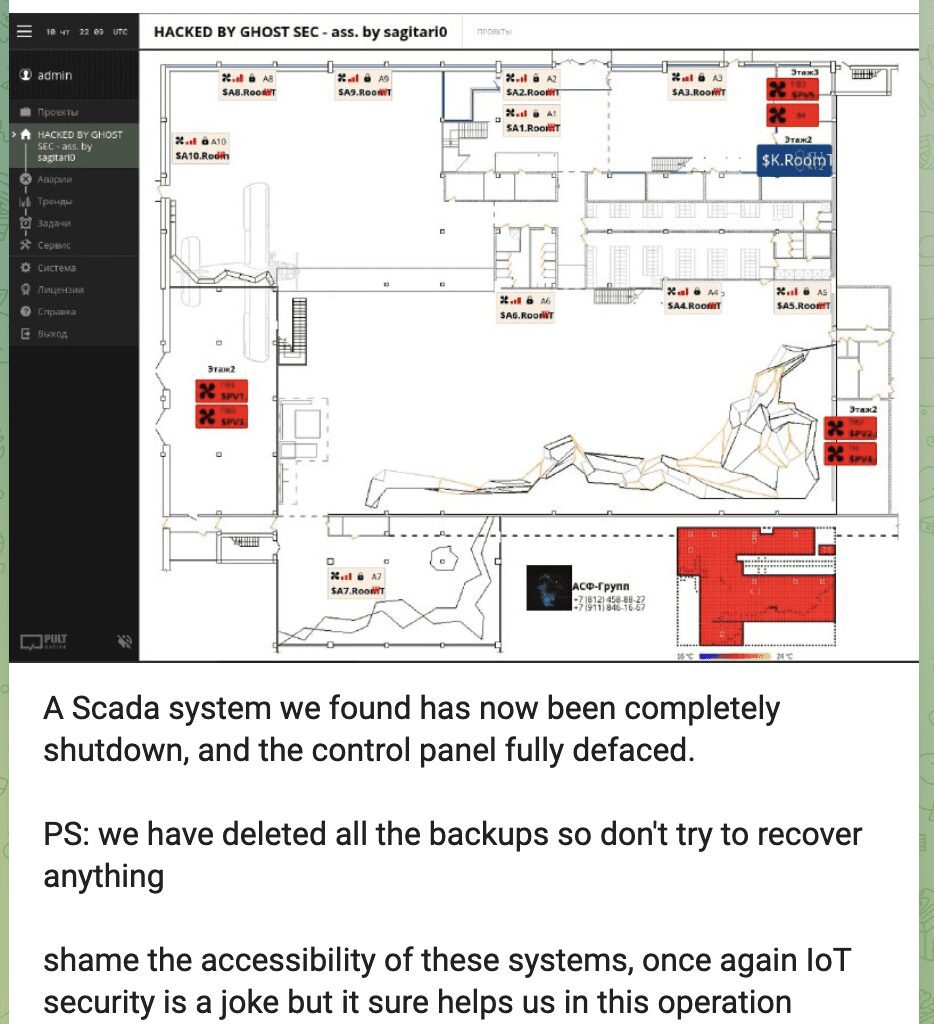
GhostSec Claims to Access, Shutdown, and Deface Control Panel of Russian ICS via SCADA Attack
GhostSec continues their offensive against Russian critical infrastructure with attacks affecting industrial controls systems. Today, they claimed they successfully accessed an unknown Russian industrial control system, deface the control panel, and shut the system down. They also stated they deleted the backups to make restoring services more challenging.
They included the screenshot below which appears to correlate to a typical ICS system. The name or location of the network was not identified.
11 March 2022 – 01:34 UTC
BeeHive Cybersecurity Enters Campaign and Targets Pro-Russian Discord Users
A pro-Ukrainian group, known as “BeeHive Cybersecurity” claims to have attacked over 2,700 pro-Russian Discord users, compromising their accounts and defacing their profiles with statements about the realities in Ukraine posted in English, Ukrainian, and Russian.
The group insinuates that they “CnC [command and control] the platforms of the ignorant” and use compromised devices to help combat disinformation.
10 March 2022 – 12:30 UTC
KelvinSec Leaks Private Chats from Darknet Tor Service: Database Market
KelvinSec, a pro-Ukrainian cyber threat actor on the darknet, has leaked 3,178 files containing the private chats from DATABASE Market. DATABSE is a relatively newly-launched service on Tor, where carding and fraud cyber-criminals congregate and transact.
The service is allegedly hosted by IT Resheniya on the IP address 45.155.204.178. KelvinSec reported they infilitrated the market via an insecure direct object reference vulnerability, commonly called “IDOR” which gives an attacker access to the website’s hidden information.
The compromised Tor service is still active as of time of writing.
10 March 2022 – 11:24 UTC
DDoSecrets Leaks Over 800GB of Data from Russian Media Censor, Roskomnadzor
The whistleblower leak site, DDoSecrets has obtained 360,000 files from Роскомнадзор (Roskomnadzor) via hacktivists from the Anonymous campaign against Russia. Roskomnadzor is a Russian state-controlled agency responsible for monitoring, controlling and censoring Russian mass media. The agency is responsible for the recent crackdowns on digital bans of Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. The two part dataset totals over 800 GB including files, emails, and information critical about their operations.

10 March 2022 – 08:35 UTC
GhostSec Hits Hundreds of Printers Across Russia
GhostSec reportedly hacks hundreds of printers across Russia to spread the message about realities in Ukraine. They tagged on to the announcement an obscure 4chan meme, “Hey Russia do you liek mudkipz?” on their Telegram channel. The stated they are targeting Russian government and military networks for the printer exploit.

9 March 2022 – 20:05 UTC
Pro-Russian Group, devilix-EU Joins Campaign Against Ukraine and the US
Late last week, a new Pro-Russian persona appeared on social media and began sharing pro-Russia propaganda, Pro-Trump rhetoric, and counter #opRussia Anonymous content. Over the last five days, they’ve ramped up their attacks claiming to have compromised AWS instances, Microsoft IIS sysstems, and performed BGP hijacking with mentions of several US-based IP addresses.
The group makes further claims that they’re named after their own custom ransomware, “DEVILIX shark.”
DEVILIX named as me is one of the strongest viruses on the world DEVILIX shark is ransomware which can do anything we can create BotNet. where we want. Just a Simple but it’s not.
They most recently shared their thoughts about the cyber war in Russian, declaring that this was not about Ukraine and Russia, but the US and NATO and their intent to keep Russia and Ukraine divided.
Я вижу, что речь идет о двух сторонах, России и Украине. Почему мы разделены из-за политики? Разве вы не видите, что здесь делает Запад и хочет, чтобы мы были разделены. НАТО избежало конфликтов, и теперь привет! Слава России
[Google Translate]
I see that we are talking about two sides, Russia and Ukraine. Why are we divided because of politics? Don’t you see what the West is doing here and wants us to be divided. NATO has avoided conflicts, and now hello! Glory to Russia
8 March 2022 – 21:05 UTC
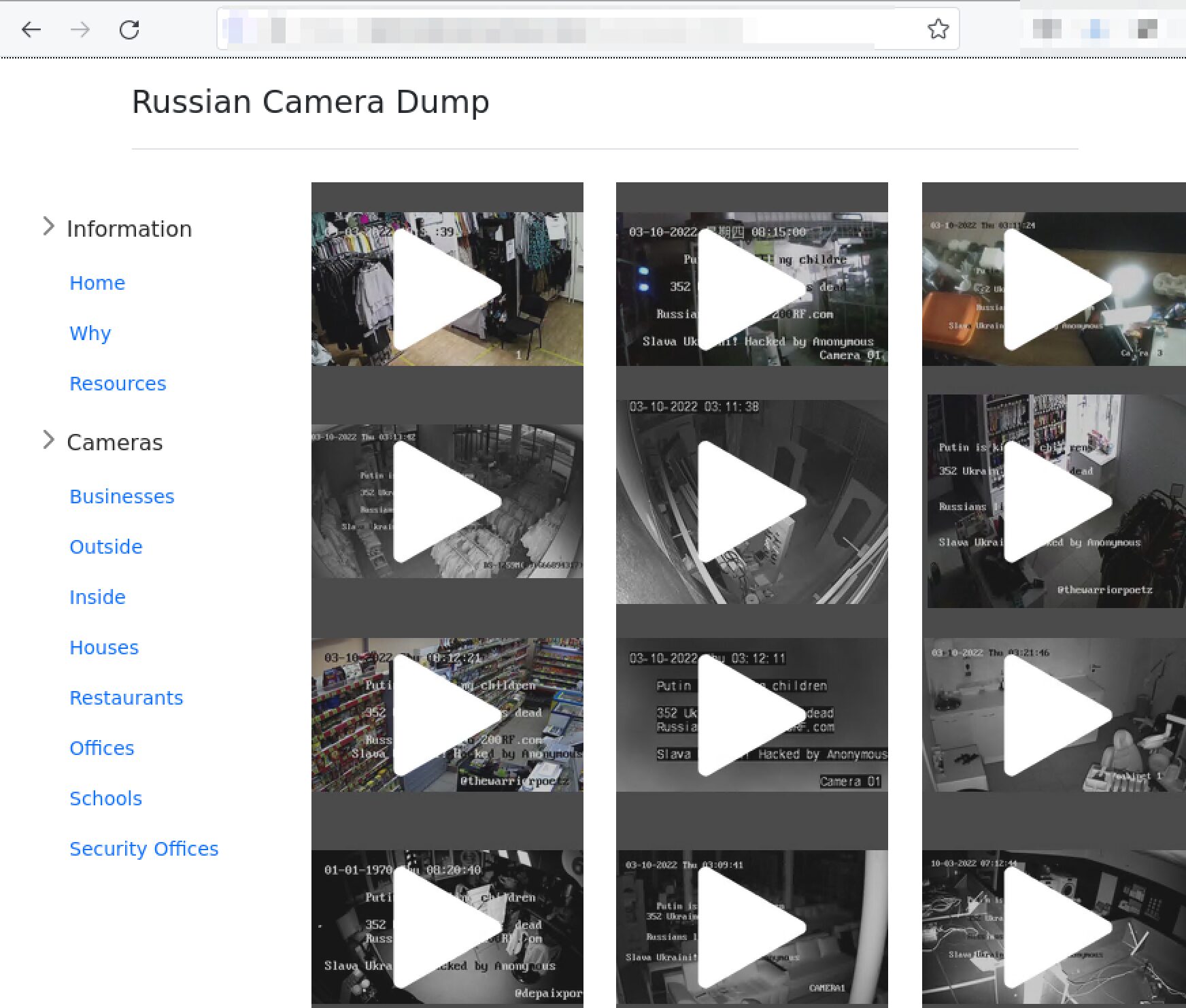
Anonymous Hacks Hundreds of Russian Security Cameras, Many Affiliated with Russian Government Ministries
Hacktivists from the Anonymous Collective successfully tapped the security camera feeds of hundreds of retail businesses, restaurants, schools, and government installations across Russia. They setup a website to share the leaked camera feeds — all to discover some where critical security offices. Anonymous also defaced security camera displays with the message:
Putin is killing children
352 Ukrainian civilians dead
Russia lied to 200rf.com
Slava Ukraini! Hacked by Anonymous
8 March 2022 – 18:34 UTC
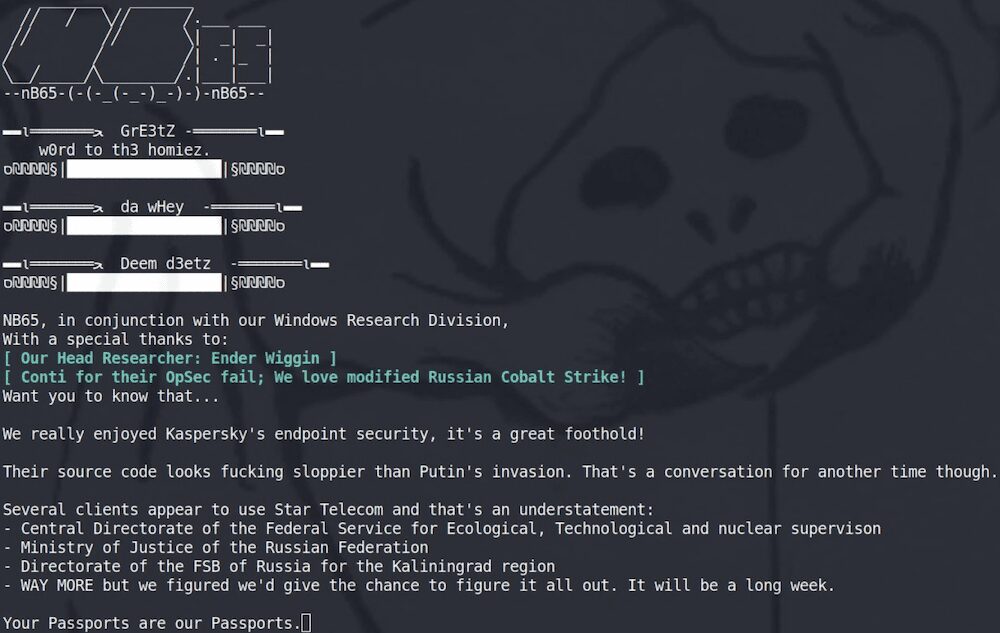
nb65 Group Claims to Have Acquired Kaspersky’s Source Code
After keeping quiet for several days, the group sent out mysterious posts across social media claiming to have accessed Kaspersky source code and found “interesting relationships” in this code.
They also claimed it was “sloppier than Putin’s invasion.”
7 March 2022 – 17:31 UTC
22nd Member of Notorious TrickBot Gang Doxxed
The pro-Ukrainian affiliate of the Trickbot cybercriminal empire has leaked the personal identity of 22 key members of the gang along with private chats between group members. Since the 4th of March, DarkOwl has seen the following aliases mentioned: baget, strix, fire, liam, mushroom, manuel, verto, weldon, zulas, naned, angelo, basil, hector, frog, core, rocco, allen, cypher, flip, dar, and gabr.

7 March 2022 – 13:01 UTC
Digital Cobra Gang Claims 49 “A-Groups” Led by Conti and Cobra Are Attacking America Cyberspace
The Pro-Russian group entered the campaign shortly after Anonymous started #opRussia (28 Feb) with the statement:
“DIGITAL COBRA GANG DCG has officially declared cyber war on hackers who attacking Russia as well and to protect justice”
They’ve given little indication of success, other than inflated claims they have acquired over 92Tb data from US’s military personnel files but no proof has been published.
Earlier today, they posted that members of Conti were helping and 49 “A-team” groups were hacking Amera.
(9 March 2022) – US AWS and Azure cloud platforms have experienced higher than normal traffic on the network but no major disruptions.
7 March 2022 – 06:44 UTC
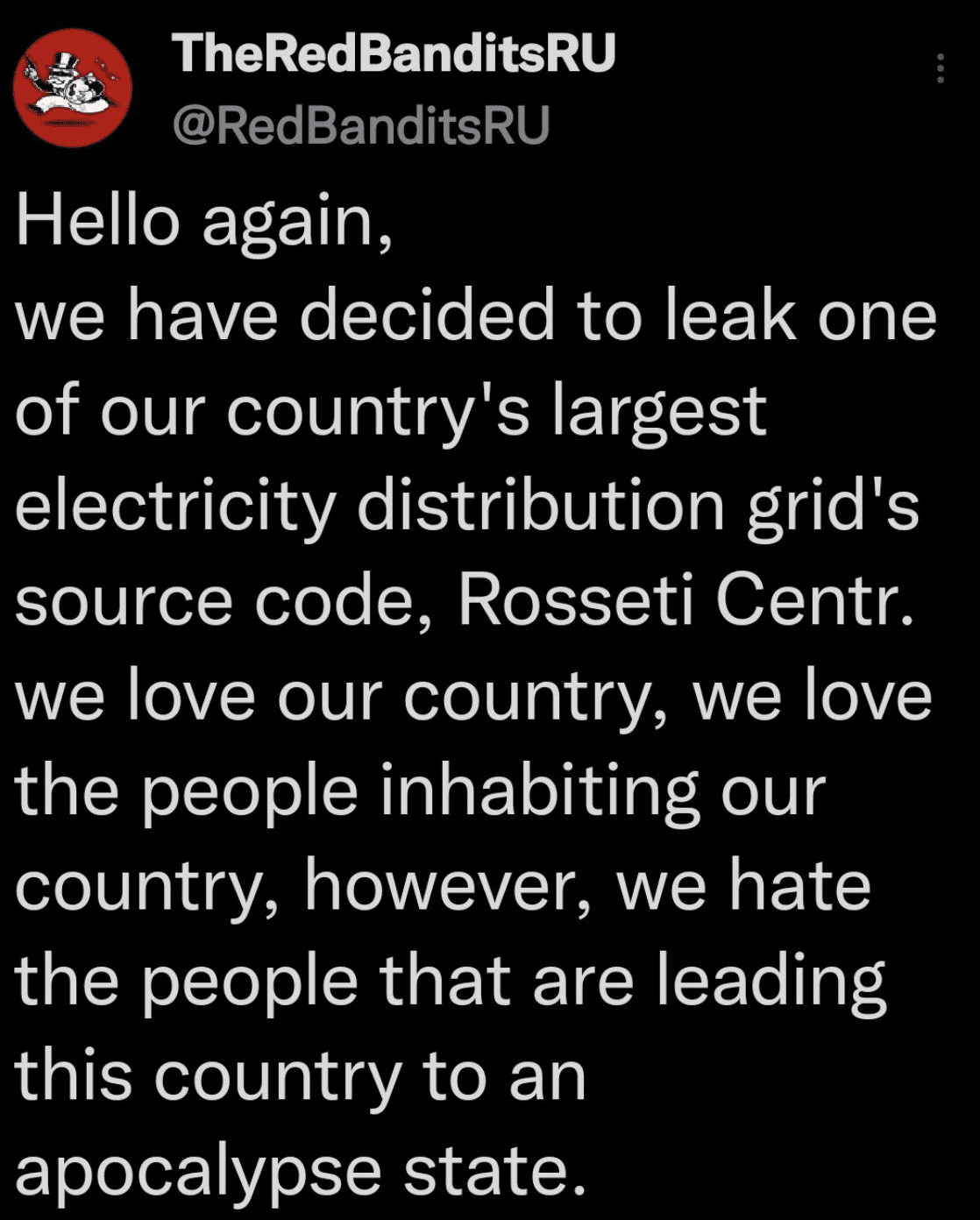
RedBanditsRU Leaks Russian Electrical Grid Source Code Data
The pro-Russian group, originally assembled to counter-hack Anonymous and cyber actors targeting Russian organizations, posted today that they are leaking the source code Rosseti Centre’s [mrsk-1[.]ru] electrical grid networking infrastructure. Rosseti Centre provides reliable electricity for more than 13 million people in the subjects of the Central Federal District of the Russian Federation.
The group is sharing this information because they believe Putin and his supporters are “leading this country to an apocalypse state.”
DarkOwl warns security researchers opening these archives should always use isolated sandbox environments in the event there is malware and viruses included in the leak.
7 March 2022 – 04:55 UTC
AgainstTheWest (ATW) Returns to the Fight and Drops Multiple Leaks of Russian Corporate Data
In the last 24 hours, ATW dropped URLs for at least 7 leaks corresponding to various Russian technical companies and organizations, reportedly breached by the cybercriminal group. ATW’s participation in the campaign has been controversial as they have had multiple dramatic departures and returns to the campaign and reports of “health issues” of some of the team’s members.
Security researchers reviewing the information from dataleaks last week calls into question the veracity of the information ATW is sharing. Checkpoint released analysis stating that after, “checking their claims deeper reveals that for many of the claims there are no solid proofs apart of very generic screenshots that are allegedly from the breached organizations.”
(Update 7 March 2022 – 18:36 UTC) The group also posted to their Telegram channel that they had successfully breached a Russian cybersecurity company that has been “hording” US-based government data, exposure of multiple SonarQube instances and requested someone get in touch with them immediately. It’s unclear if this is legitimate or just further ego inflation.

6 March 2022
Free Civilian Tor Service Leaks Entire DIIA Contents
Recently, the administrator of Free Civilian shared a post on their Tor service containing the entire Ukraine’s DIIA database of users. They stated the buyer of the database consented to the release, with the understanding some records were deleted. The downloads consist of 60+ archives containing gigabytes of data. The download links have been unstable since DarkOwl discovered them.
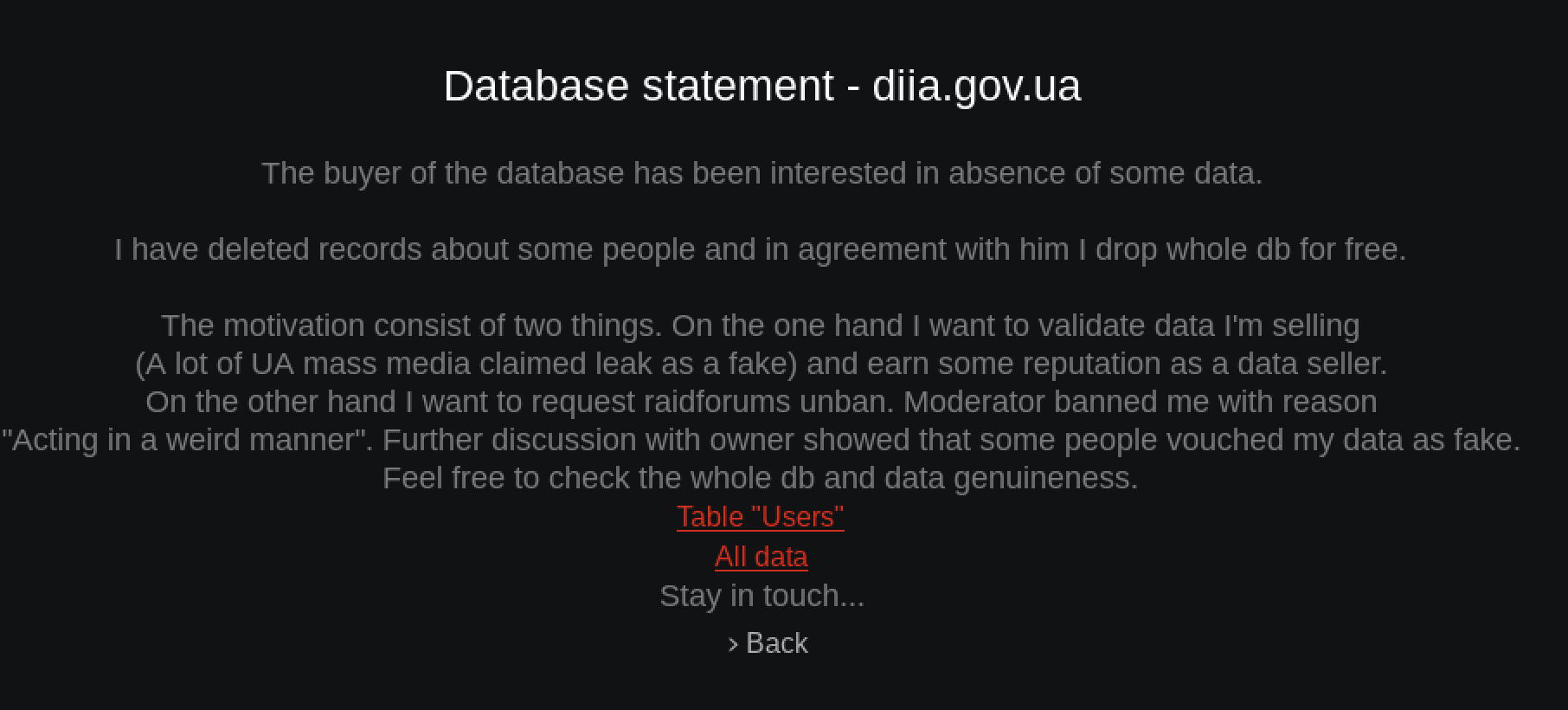
The administrator also expressed desire to have the ban on their “Vaticano” Raid Forums account lifted, claiming this leak proved the legitimacy of the information they shared back in January.
Recently, screenshots of an indictment for the alleged seizure of Raid Forums on VeriSign has been in circulation, after users spoke of rifts between pro-Ukrainian users and Russian hackers, potential FBI seizures, and the alleged hijacking the alias of former admin Omnipotent on Darknet World. Prominent users from the forum have setup RF2 and advised any old working Raidforums links are likely phishing logins for the FBI.

6 March 2022 – 18:43 UTC
Anonymous Continues Information Warfare Against Russian Media; Video Services Wink and ivi Stream Anti-War Messaging
After Putin’s overt authoritarian take on media sharing the realities of the war in Ukraine, Anonymous managed to hack Russian video services Wink and ivi to stream pro-Ukrainian messages and video of the conflict.
This weekend, Putin’s parliament passed a “fake-news” law imposing prison sentences for media using the words “war” or “invasion” prompting numerous western outlets to pull their journalists and suspend operation.

6 March 2022 – 15:39 UTC
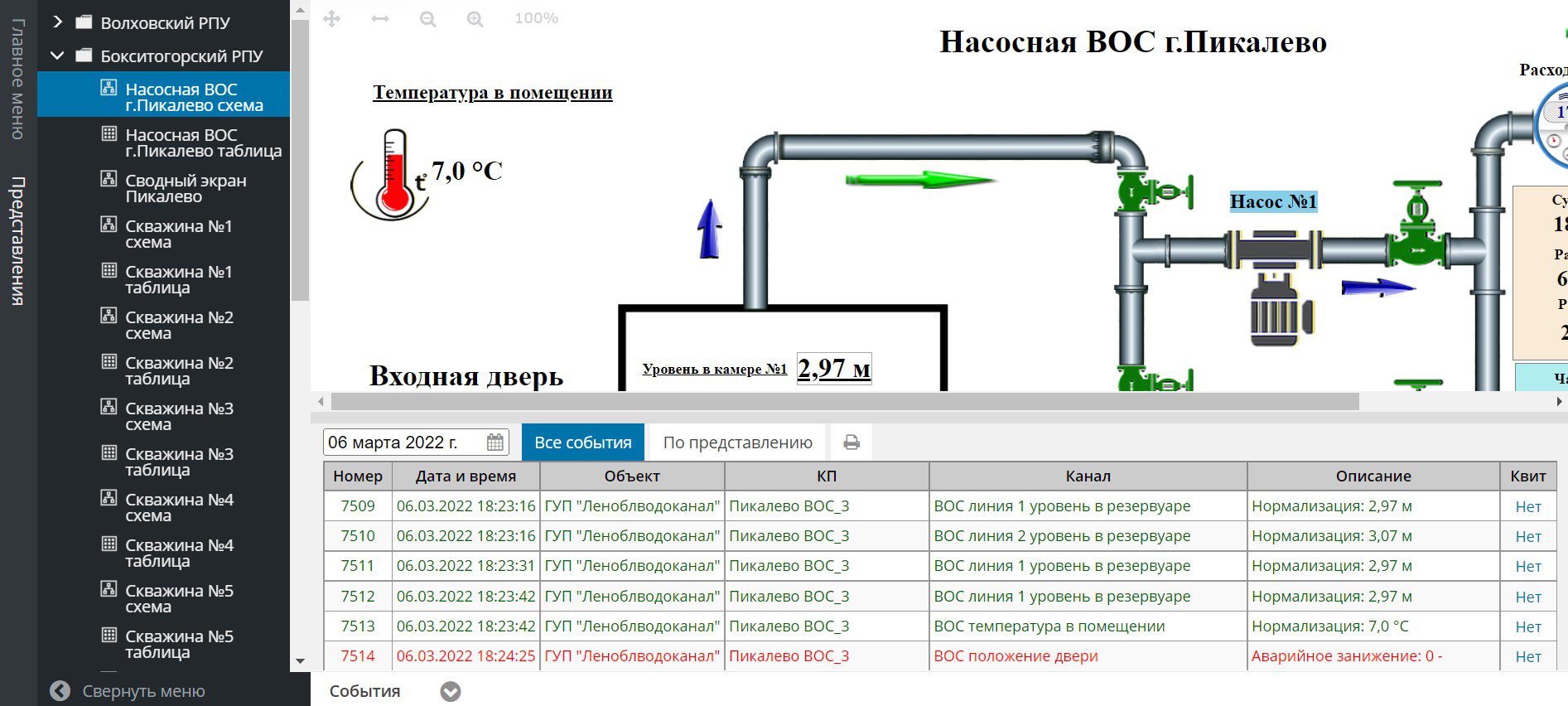
AnonGhost Enters Campaign and Claims SCADA Attacks Against Multiple Russian Infrastructure Targets
This weekend, AnonGhost entered Anonymous’ #opRussia campaign with a vengence, and claims today they have hacked multiple Russian infrastructure control systems via SCADA attacks and “shut it down.”
They list the following targets:
- Волховский РПУ> Volkhov RPU
- Бокситогорский РПУ> Boksitogorsk RPU
- Лужский РПУ> Luga RPU
- Сланцевский РПУ> Slantsevsky RPU
- Тихвинский РПУ> Tikhvinsky RPU
- Выборгское РПУ> Vyborg RPU
This is after they leaked data from 9 Russian commercial servers hours earlier.
- azovkomeks[.]ru
- vserver24[.]ru
- dvpt[.]ru
- ach[.]gov[.]ru
- itmo[.]ru
- vpmt[.]ru
- pvlt[.]ru
- hwcompany[.]ru
- corbina[.]ru
DarkOwl is in the process of pulling in this data to review and assess the contents of all of the databases.
The AnonGhost group is reportedly one of the more senior anonymous hacktivist teams in the underground, with reporting of the group going back to the early 2010s. According to open-source reporting, AnonGhost was led by Mauritania Attacker. In an online interview with a hacker’s blog in 2013, Mauritania Attacker claimed to be a 25 year old male from Mauritania who started hacking at a young age by joining TeaMp0isoN and ZCompany Hacking Crew (ZHC), two hacking groups known for their attacks of high-profile targets such as NATO, NASA, the UN, and Facebook. (Source)
For those who remember Stuxnet, SCADA type attacks are controversial as there is a fine line between disruption and destruction. Services knocked offline but able to be restored is disruptive and inconvient, causing delays in operation and psychological concern over the safety of such services. However, disruptions that lead to destructive events, e.g. hard disks wiped and unrecoverable, de-railed trains, power plant overheating resulting in explosions, & satellites falling out of the sky are considered serious and may be interpreted as an act of war and result in severe retaliation.
Yesterday, Putin declared western sanctions an act of war and uttered similar threats about hacking satellites earlier this week.
6 March 2022 – 14:52 UTC
GhostSec Returns with Leaks from Russia’s Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) and Department of Information (DOI) FTP Server Data
Hours ago, an archive consisting of several gigabyte emerged from GhostSec reportedly containing information from Russia’s nuclear research and disinformation activities. GhostSec has been silent for most the last week, perhaps busy with this activity.
According to their website (jinr.ru), the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research is an international intergovernmental organization established through the Convention signed on 26 March 1956 by eleven founding States and registered with the United Nations on 1 February 1957.
As of time of writing, the public facing website is online.
6 March 2022 – 12:34 UTC
Anonymous Dumps Leak of 139 Million Russian Email Addresses
An archive of over 139 Million email addresses, broken up into 15 separate files with mail_ru at the beginning of each file, lists the email addresses for presumed account holders for mail_ru services. VK (VKontakte) assimilated mail.ru email services into its internet services conglomerate in the fall of 2021.
The files included two additional HTML files with ominous warnings – possibly shared on the servers from which these leaks were obtained.

[image translation]
Russian soldiers!
If you think that you are going to an exercise, in fact you are being sent to Ukraine to DIE.
DarkOwl has not determined the veracity of this data, nor confirmed how these emails were obtained; some combolists of this nature are created as an aggregation of other leaked data.
As of time of writing, mail.ru’s public facing website is still online and operational.
5 March 2022 – 20:41 UTC
Anonymous Targets Russian FSB; Letter Appears from Possible FSB Whistleblower
The Federal Security Service (FSB) of the Russian Federation [Федеральная служба безопасности (ФСБ)] is the principal security and intelligence agency of Russia and the main successor agency to the Soviet Union’s KGB.
Earlier today, Anonymous hacktivists targeted the FSB (at the direction of the IT Army Ukraine) and managed to take the external facing website offline. Rumors on social media and chatrooms suggested Anonymous managed to “breach” the FSB’s server.
Shortly after the announcement of the website’s offline status (e.g. #TangoDown) a deep web paste emerged containing a list of 62 subdomains for the fsb.ru domain. This could be for additional targeting and exploitation.

The stability and alliances of members of the FSB are in question by threat intelligence and security researchers across the community. Last night, an alleged FSB whistle-blower letter surfaced (via the founder of http://gulagu.net) that damned Russia’s military performance in Ukraine and predicted a disaster for the RU in the next weeks and months. An English translation of the letter has appeared in the deep web (excerpt below).
To be honest, the Pandora’s box is open – a real global horror will begin by the summer – global famine is inevitable (Russia and Ukraine were the main suppliers of grain in the world, this year’s harvest will be smaller, and logistical problems will bring the catastrophe to a peak point). I can’t tell you what guided those at the top when deciding on the operation, but now they are methodically lowering all the dogs on us (the Service).
We are scolded for analytics – this is very in my profile, so I will explain what is wrong. Recently, we have been increasingly pressed to customize reports to the requirements of management – I once touched on this topic. All these political consultants, politicians and their retinue, influence teams – all this created chaos. Strong. Most importantly, no one knew that there would be such a war, they hid it from everyone.
And here’s an example for you: you are asked (conditionally) to calculate the possibility of human rights protection in different conditions, including the attack of prisons by meteorites. You specify about meteorites, they tell you – this is so, reinsurance for calculations, nothing like this will happen. You understand that the report will be just for show, but you need to write in a victorious style so that there are no questions, they say, why do you have so many problems, did you really work badly. In general, a report is being written that when a meteorite falls, we have everything to eliminate the consequences, we are great, everything is fine.
And you concentrate on tasks that are real – we don’t have enough strength anyway. And then suddenly they really throw meteorites and expect that everything will be according to your analytics, which was written from the bulldozer.
That is why we have a total piz_ets – I don’t even want to pick another word.
5 March 2022 – 16:37 UTC
Anonymous Claims to Breach Yandex (Russia’s Mail and Search Service); Leaks Account Credentials
DarkOwl discovered two leaks shared through the Anonymous hacktivist collective network consisting of over 5.2 Million user accounts’ email addresses and password combinations. We are in the process of analyzing this data leak to determine the veracity of its contents. 1.1 Million Yandex accounts were previously dumped in 2014. Many hackers are using #opRussia to opportunistically claim clout for breaches that did not occur, when in reality they are circulating old previously dumped data and/or verifying accounts by credential stuffing.
5 March 2022 – 15:23 UTC
Paypal Suspends Service in Russia
Paypal announced on LinkedIn they would be halting its operations in Russia; a statement released days after suspending signing up new users on the payment platform on Tuesday. Dan Schulman, CEO wrote:
We remain steadfast in our commitment to bring our unique capabilities and resources to bear to support humanitarian relief to those suffering in Ukraine who desperately need assistance. We will also continue to care for each other as a global employee community during this difficult and consequential time.
On Wednesday, 3 March, the IT Army of Ukraine launched a petition calling for all supporters to sign a petition on change.org:
[TRANSLATION]
While Ukraine protects its people and places, and Russia faces the radical consequences of its war crimes, the most popular payment service via PayPal is still available to the aggressor. This means that it also helps finance the bloody war against Ukraine through PayPal.
We are absolutely sure that modern technologies are a powerful response to tanks, grads and missiles. We call on the company to block its services in Russia via PayPal and launch them in Ukraine, as well as provide an opportunity to raise funds to restore justice and peace in our country and the world.
5 March 2022 – 15:03 UTC
Anonymous Leaks Private RocketChat Conversations from Russian Government Officials
Anonymous is targeting Russia by any means possible and managed to collect private chats between Russian officials on the messaging service, rocket.chat. After review, these chats are different from the ones dropped by @contileaks last week.
The chat includes the network ID, username, and “real name” of 14 members of the chat group. The domain associated with the leak corresponds to the official website of the Russian government and the Governor of the Moscow region.
5 March 2022 – 06:04 UTC
squad303 Sets Up SMS Messaging System to Text Random Russian Citizen Phone Numbers
With the lack of Russian media coverage of the invasion of Ukraine and the intentional misinformation spread by Putin’s disinformation agencies, a pro-Ukraine hacktivist collective, known as squad303 setup an SMS messaging system for citizens around the globe to use to randomly text Russian citizens a scripted message about the nature of world events.
The squad303 team also setup an API for more advanced users.
Update: As of 8AM UTC, 6 March 2022, the service had been used to send over 2 Million texts Russian mobile phone numbers.
The team also reports of suffering from heavy DDoS attacks from pro-Russian cyber actors.

5 March 2022 – 02:34 UTC
Anonymous Hackers Claim to Have Accessed Communication Data for a Russian Military Satellite
After nb65’s reported success accessing Roscosmos earlier this week, it appears that members of the Anonymous collective under the campaign #opRussia have ventured into breaching the communications of Russian military satellite for data collection. The satellite – designated COSMOS 2492 (aka glonass132) is likely active in geospatial intelligence collection over Ukraine for Russia. (note: the original indication of the connection occurred 4 March 2022 @ 09:35 by Anonymous collective member, @shadow_xor.)
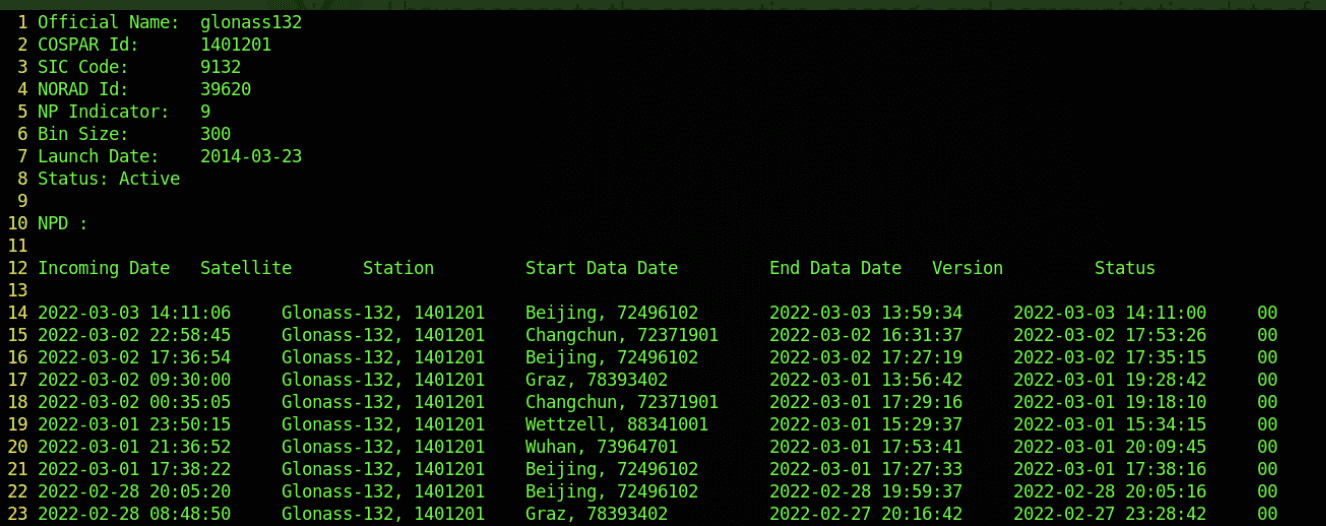
DarkOwl also uncovered a leak shared by LulzSec member @shadow_xor titled, “Leak_RUSAT_shadow_xor.zip” which contains significant geopositioning data since the satellite’s launch in 2014. The hacker stated they could not change the coordinates of the satellite, but did capture orbital, passage, and communications data.
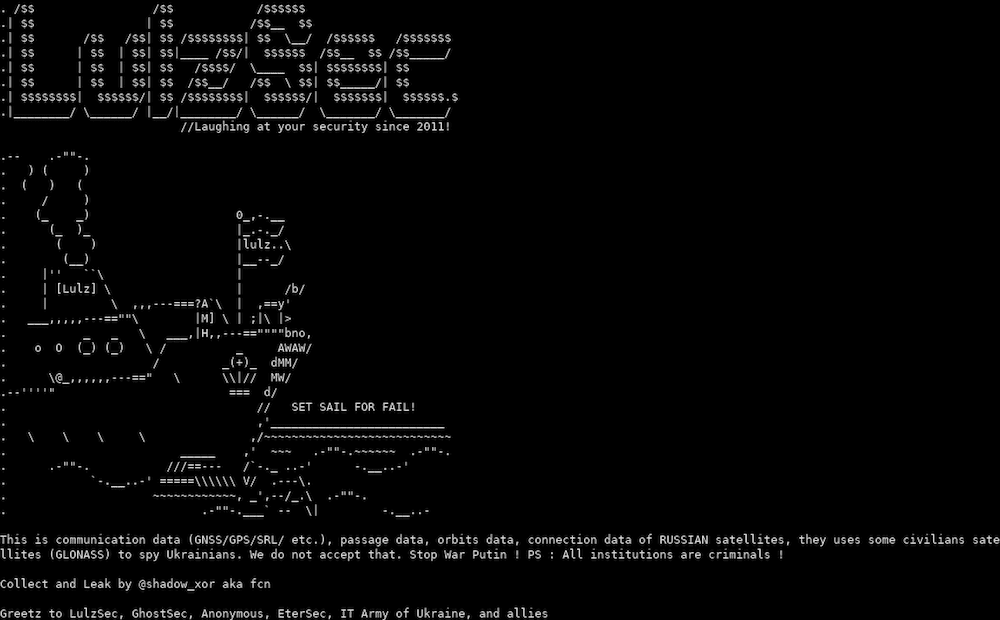
Our original reporting on this suggested the hackers were Russian-based, but further analysis only indicated that a number of Russian-based hackers supported the attack on COSMOS 2492.
4 March 2022 – 18:16 UTC
Putin Officially Bans Facebook in Russia
In order to combat the information operations campaign against them online, Putin ordered for ISPs to block Facebook servers and websites across Russia. Security researchers also note an uptick in Russian trolls on social media with bot accounts promoting Putin’s military operations in Ukraine.
Putin’s parliament also passed a law imposing prison terms of up to 15 years for individuals spreading intentionally “fake news” about the military. The terms “invasion” and “war” are no longer allowed in press and media coverage.
Several foreign and Western media outlets, including BBC, CNN, and Bloomberg, have temporarily suspended reporting on the war from Russia.
4 March 2022 – 09:44 UTC
NB65 Teases Information Security Community with Riddles on their Activities
NB65 – the pro-Ukrainian group who claimed responsibility for accessing and shutting down Russia’s spy satellites via SCADA vulnerabilities – teased the information security community that they been quiet cause they were parsing and analyzing numerous vulnerabilities in Russian cyber targets.
If we seem quiet, it’s because we have an olympic sized swimming pool worth of data and vulnerabilities. But here’s some fun that you can participate in…
DarkOwl discovered a post matching the target hidden in the riddle and the content suggests the group has access to RUNNET: Russia’s UNiversity Network.
4 March 2022
IT Army of Ukraine Calls for Volunteers to Support the Internet Forces of Ukraine
Ukraine’s Ministry of Digital Transformation steps up its information warfare against Putin’s propaganda by forming the Internet Forces of Ukraine (ITU). Forming a separate Telegram channel at the start of the month, the channel is dedicated to posting instructions and guidance for citizens around the world that want to aid Ukraine and lack an IT/cybersecurity background.
Друзі, наш ворог, окрім наявної війни у наших містах та селах, веде також інформаційну війну. Не вірте фейкам, не вірте брехні пропаганди путіна – ніякої капітуляції України НЕ БУДЕ!!! У нас потужна армія, ми сильні духом і нас підтримує весь світ! Тому, не ведіться на провокації і вірте в Україну. Поширюйте це серед рідних та близьких у соціальних мережах, щоб вони також не велись на нісенітниці кремля. Ми разом і ми переможемо!!🇺🇦
Friends, our enemy, in addition to the existing war in our cities and villages, is also waging an information war. Do not believe fakes, do not believe the lies of Putin’s propaganda – there will be no capitulation of Ukraine!!! We have a powerful army, we are strong in spirit and we are supported by the whole world! Therefore, do not be fooled by provocations and believe in Ukraine. Spread this to your family and friends on social networks, so that they also do not fall for the Kremlin’s nonsense. We are together and we will win!! 🇺🇦
4 March 2022 – 01:46 UTC
Trickbot Gang Members Doxxed and Links to FSB Confirmed
At 15:00 UTC, before DarkOwl could even finish analyzing the ContiLeaks, a Ukrainian-aligned underground account leaked details of key members of the infamous TrickBot gang. Over the course of the day at a cadence of every 2 hours, dossiers for the individuals appeared on social media. Private chats between members of the gang were included with each of the leaks. 7 male members and their aliases identified: baget, fire, strix, mushroom, manuel, verto, and liam. Twitter has since suspended the account.


3 March 2022 – 20:54 UTC
Russian-Aligned Hackers Target Anonymous Hacktivists in Canada
A pro-Russian cyber group using the name Digital Cobras, claims to have been targeting #opRussia hackers from the Anonymous collective across the US, UK, Greece, and Canada. Earlier today, they posted several names of individuals along with pictures of some of the alleged members of Anonymous.
They also claimed to have “hacked Anonymous’ servers” and downloaded over 260gb of their files and tools. They also claimed to have full access of the administration of Tor Project, including their crypto accounts.
Anonymous does not possess servers or centrally locate their information or tools as it is an organic decentralized collective of hacktivists around the world. Similarly, the Tor Project is run by a network of volunteers.
It is very likely this group is designed to spread disinformation and FUD.

3 March 2022
Size of Zeronet Anonymous Network Increases Since Invasion
In the week since the Putin launched an invasion against the Ukrainian people, DarkOwl has noticed an increase of 385 Zeronet domains in the last week and a near 20% increase in the network’s activity. Zeronet has been historically most heavily used by Chinese threat actors. The trend in “new domain” activity appears to have started on or about February 27th, within hours after the IT Army of Ukraine rallied the underground.
The Tor Project has reported significant increases in the number of unique addresses on Tor on the same day.
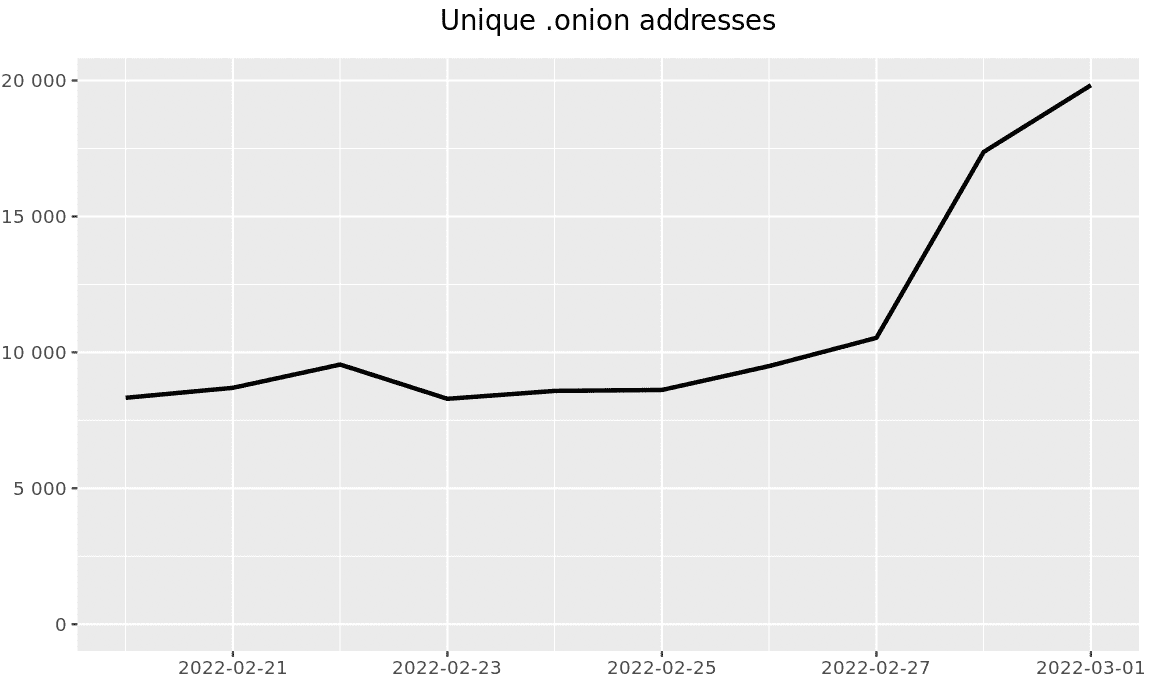
3 March 2022 – 17:10 UTC
Anonymous Leaks Database Containing Bank Account Holders Information
bkdr – member of the Anonymous hacktivist collective – released an Excel spreadsheet containing the personal information of over 8,700 business bank account holders in Russia. Full names, passport, DoBs, account standing, etc are included in the file.
3 March 2022 – 15:40 UTC
Pro-Russian Cyber Team, Killnet Claims To Hack Vodafone Services in Ukraine
Killnet, a Pro-Russian organized threat actor has claimed they were successful in attacking Vodafone’s telecommunications services across Ukraine. The group shared links to the vodafone.ua website (as offline) and network graphs proving the website suffered an outage.
The group also claims to have attacked “Anonymous” networks directly, prompting criticism as the Anonymous hacktivist has no central severs or repositories.
[Google Translate]
Cellular communication services under the Vodafone trademark on the territory of Ukraine are provided by the partner of Vodafone Group plc, PRO “VF Ukraine”
⚠ OUR ATTACK WAS REPELLED [REFLECTED] AFTER 4 HOURS.
3 March 2022 – 05:22 UTC
Anonymous Breaches Private Server in Roscosmos and Defaces Website
v0g3lSec – member of the Anonymous hacktivist collective – claims to have infiltrated private servers at the Russian Space Agency, Roscosmos and exfiltrated files from their Luna-Glob moon exploration missions. The archive consists of over 700 MBs. Many of the files are drawings, executables, and technical documents dating back to 2011. A scientific review of the content would be needed to assess the value of the information collected.
In addition the website for the Space Research Institute (IKI) Russian Academy of Sciences (RAN) was also defaced by the same group.
3 March 2022 – 01:11 UTC
Anonymous Leaks Data from Rosatom, Russia’s State Atomic Energy Corporation
According to DarkOwl’s preliminary review of the 74 files, the leak appears to be a mixture of budget data, conference materials, powerpoint presentations, and technical files dating back to 2013. There is random mixture of information included that it is unclear whether this was obtained directly from a breach of the corporation’s servers, an employee at the organization, or collected via OSINT and compiled for use in #opRussia.
“There is no place for dictators in this world. You can’t touch the innocent, Putin. No secret is safe. State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom has been hacked!”
2 March 2022 – 19:55 UTC
ATW Quits Campaign – Cites Conflict with Anonymous, Attribution, and Twitter Suspension
Drama in the group started yesterday with AgainstTheWest claiming Anonymous was taking credit for their successes in the cyber war against Russia. They briefly turned their attention to China announcing several new victims, including the Chinese Science, Technology and Industry for National Defence organization. After their suspension from Twitter earlier today, they announced retirement claiming they had no means for communicating with the public. (Analysts note rebrand to BlueHornet occurred shortly after their announcement)
2 March 2022 – 19:09 UTC
Conti Leak Source Code, Panel, Builder, Decrypter Appear on Darknet Forum
Less than 48 hours after a pro-Ukrainian leaked the infrastructure of the CONTI gang’s operation, including botnet IP addresses and source code executables, users begin circulating the ransomware gang’s critical data across popular darknet forums and discussion boards.
2 March 2022 – 16:35 UTC
Leak Documents Surface Proving War Against Ukraine was Approved on 18 January
Anonymous hackers released photographs of captured documents from Russian troops titled, “WORKING MAP”, and authored by the commander of Russia’s Bomb Battery of the Black Sea Fleet. The maps and documents affirm to the public that the invasion of Ukraine was approved on January 18th with intention to seize the country sometime between 20 February and 06 March 2022. Liveuamap, under intermittent DDoS since this started, confirmed the data.
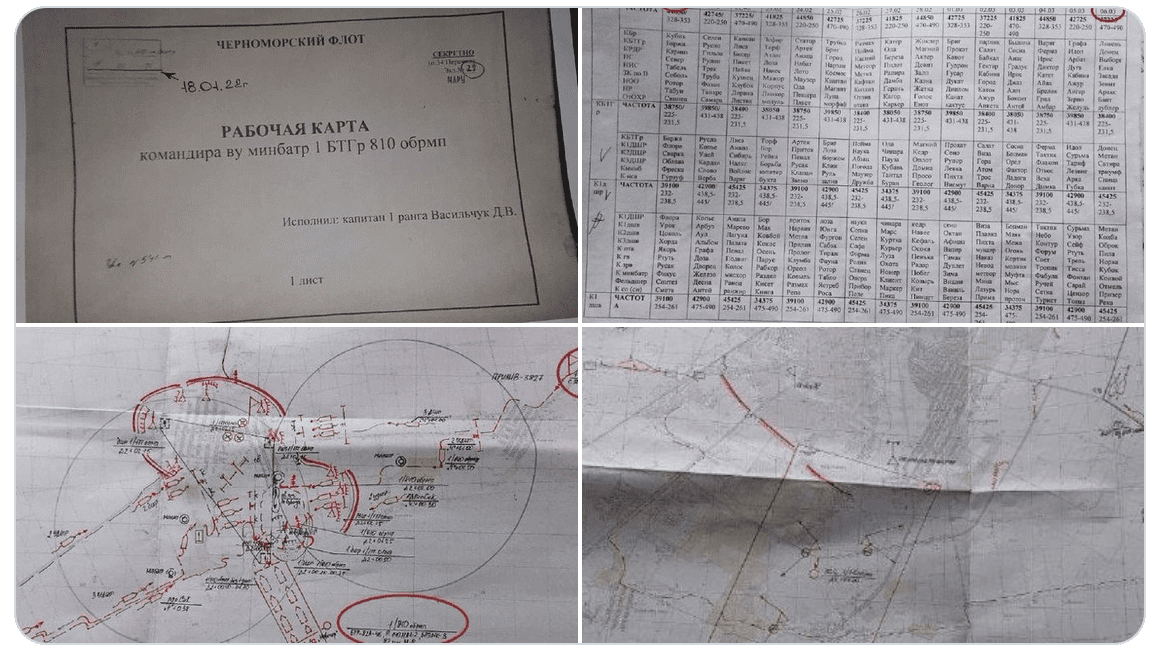
2 March 2022 – 13:52 UTC
XSS Admin Reports XMPP Jabber Service Ransomed and Heavy DDoS Attacks
A darknet forum popular with the Russian-speaking community has been experiencing technical issues, suffering from Jabber service outages and heavy DDoS attacks. The forum is well known in the darknet for malware discussions and coordination of attacks. The admin shared a post that the jabber service was hit with ransomware and the contents of the chats wiped from the services. They nonchalently suggested users register and continue using the service.
[Translated]
The server didn’t work yesterday. Because of ransom (which, by the way, is prohibited here) we were listed in a spamhouse. Instead of reporting the violation, the “brilliant” spamhouse immediately leafed through us. In principle, for many years I got used to their “adequacy”. I’m not surprised at anything. We have more than 21,000 users, and no one is able to check everyone. To do this, in fact, they came up with feedback contacts (xmpp, e-mail), they are listed everywhere.
Why, I wonder, they don’t block gmail.com ? So many, so to speak, violators of law and order use it, and nothing, for some reason they are not immediately listed.
In parallel with this, a powerful DDoS attack was conducted on us.
Our XMPP project is not commercial, completely free and subsidized. I’ve never understood the point of attacking toads.
At the moment, the functionality has been restored.
An unpleasant moment. Backups according to the law of meanness turned out to be broken. The last one alive was a week ago. Suddenly someone has lost contacts or a toad has disappeared, re-register.
2 March 2022 – 10:33 UTC
Leak Appears with Russian Air Force Officer’s Information
Anonymous leaked another database containing the personal information for over 300,000 of Russia’s military personnel and civilian citizens. The archive, titled “Translated Base Database” contains 35 separate database files containing personal details of the individuals. Information includes: full name, date of birth, age, passport number, address, occupation, etc.
1 March 2022 – 20:46 UTC
Russian Criminal Gang TheRedBanditsRU Recruits on Social Media – Offers Payments for Affiliates
The RedBandits openly recruit “affiliates for certain jobs” stating they did not want white hats, but that they want to “speak to exploit Devloplers, Spammers (phishing skills, vishing etc), Pentesters. We’re building an army!” They incentivize skilled hackers to join their cause for monetary gain, claiming partners would be paid well and to apply directly via qTox.
Earlier today, the group claimed that they did not agree with Putin as a leader nor of his invasion of Ukraine, but will protect him as a citizen of Russia.
“War is good for no one, come, take my hand, make money help your family”
1 March 2022 – 12:57 UTC
STORMOUS Ransomware Group Aligns With Russia
The STORMOUS ransomware group, which has been targeting international victims with their ransomware strain for months, claimed their alliance with the Russian government and threatens greater attacks against Ukraine.
The STORMOUS team has officially announced its support for the Russian governments. And if any party in different parts of the world decides to organize a cyber-attack or cyber-attacks against Russia, we will be in the right direction and will make all our efforts to abandon the supplication of the West, especially the infrastructure. Perhaps the hacking operation that our team carried out for the government of Ukraine and a Ukrainian airline was just a simple operation but what is coming will be bigger.
1 March 2022 – 09:26 UTC
Ukrainian Paper Leaks Personal Data for 120,000 Russian Military Personnel
In an effort to target the Russian soldiers invading Ukraine, the Centre for Defence Strategies in Ukraine has acquired the names and personal data of 120,000 servicemen who are fighting in Ukraine. Ukrainian newspaper, Ukrayinska Pravda has leaked the details of the soldiers which could be one of the biggest information warfare campaigns using doxing mid-military conflict, ever seen.
The doxxed soldiers are likely to face increased engagement on social media and direct phishing attacks.
1 Mar 2022 – 00:38 UTC
NB65 Takes on Russia’s Satellite Technology
nB65 claims that they successfully accessed Russia’s Roscosmos Space Agency and deleted the WS02, ‘rotated’ the credentials and shut down the server. They did not provide any leaks with the social media announcement.
The Russian Space Agency sure does love their satellite imaging. Better yet they sure do love their Vehicle Monitoring System.
Network Battalion isn’t going to give you the IP, that would be too easy, now wouldn’t it? Have a nice Monday fixing your spying tech. Glory to Ukraine.
28 February 2022 – 23:54 UTC
ATW Targets Russia’s Electrical Grid
AgainstTheWest Leaks Information from Russia’s PromEngineering corporation. Archives of corporate emails between employees, clients, vendors, as well as blueprints and engineering documentation for power stations around Russia are included in the leak.

28 February 2022 – 22:00 UTC
CONTI’s Entire Infrastructure Leaked
Does this signal the end of CONTI’s reign as leading RaaS?
Ukrainian aligned affiliate decides to destroy CONTI ransomware gang’s operation by exfiltrating and sharing 141 additional JSON data files of private Jabber chats from 2020, details of their server architecture, their sendmail phishing campaign data information, command and control botnet architecture, and ransomware executables (password protected). Analysis confirms that the gang uses BazarLoader backdoor for installing persistent malware on infected machines.
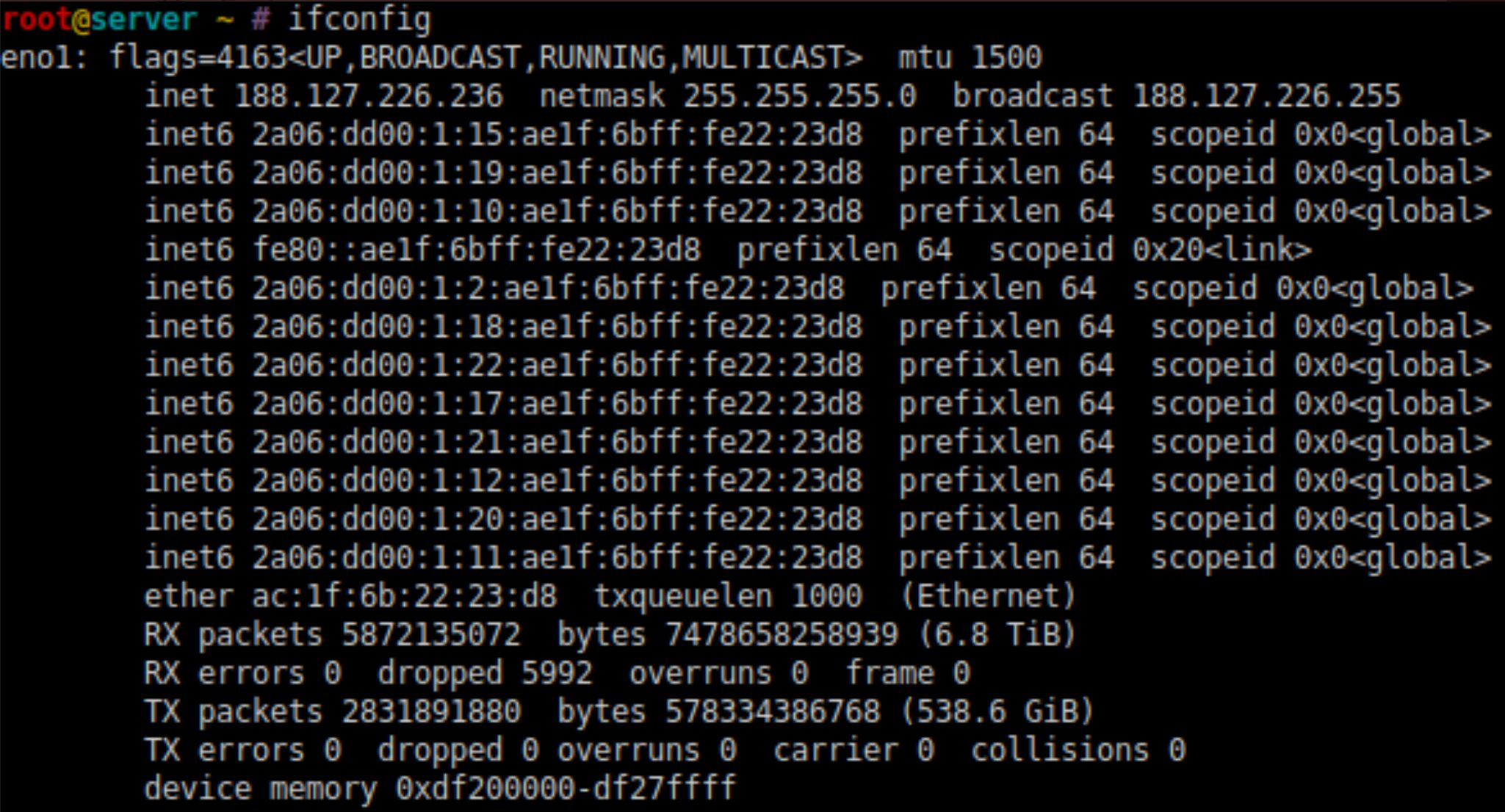
DarkOwl analysts also noted from leaked Jabber messages that RaaS affiliates were persistent at determining how to evade AV/EDR protection systems like Sophos and Carbon Black. Stating that they had setup sales calls and demos with Carbon Black and Sophos AV providers’ sales teams using proxy companies to gain more information, test the product and attempt to find specifics of the product’s AV/EDR bypass mechanisms.

This reminds us all the importance of vetting and verifying all commercial in-bounds for requests for demos and sales information, especially when it might present an opportunity to learn critical corporate intelligence.
The affiliate leaking the details wrote how this war against their people and Ukraine was breaking their heart.
My comments are coming from the bottom of my heart which is breaking over my dear Ukraine and my people. Looking of what is happening to it breaks my heart and sometimes my heart wants to scream.
28 February 2022 – 21:41 UTC
STORMOUS Ransomware Hits Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Ukraine
The Pro-Russian STORMOUS ransomware gang claims to have attacked Ukraine’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, mfa.gov.ua using their custom ransomware. The group posts victims’ information on their Telegram channel, posting in both English and Arabic. The group stated the Ukraine government network “fragile” and called for DDoS attacks them.
Their network is fragile – their various data has been stolen and distributed according to their phone numbers, email, accounts and national card numbers with an internal network hacked and access to most essential files. This is with placing denial attacks on their main site !
28 February 2022 – 18:00 UTC
China’s Huawei Steps in to Assist Russia with ISP Network Instability
According to Chinese deep web forums, Huawei is reportedly building a mobile broadband in Russia to help with internet outages. As of 26 February, at least 50,000 technical experts will be trained in networking and securty in Russia’s R&D centers.

28 February 2022 – 12:00 UTC
Russian Gas Station Pumps Hacked
Video of disabled electric vehicle (EV) charging stations in Russia surface, displaying error status and the following warning:
”Putin is a dick”, “Glory to Ukraine”, ”Glory to our heroes”,” death to our enemies”
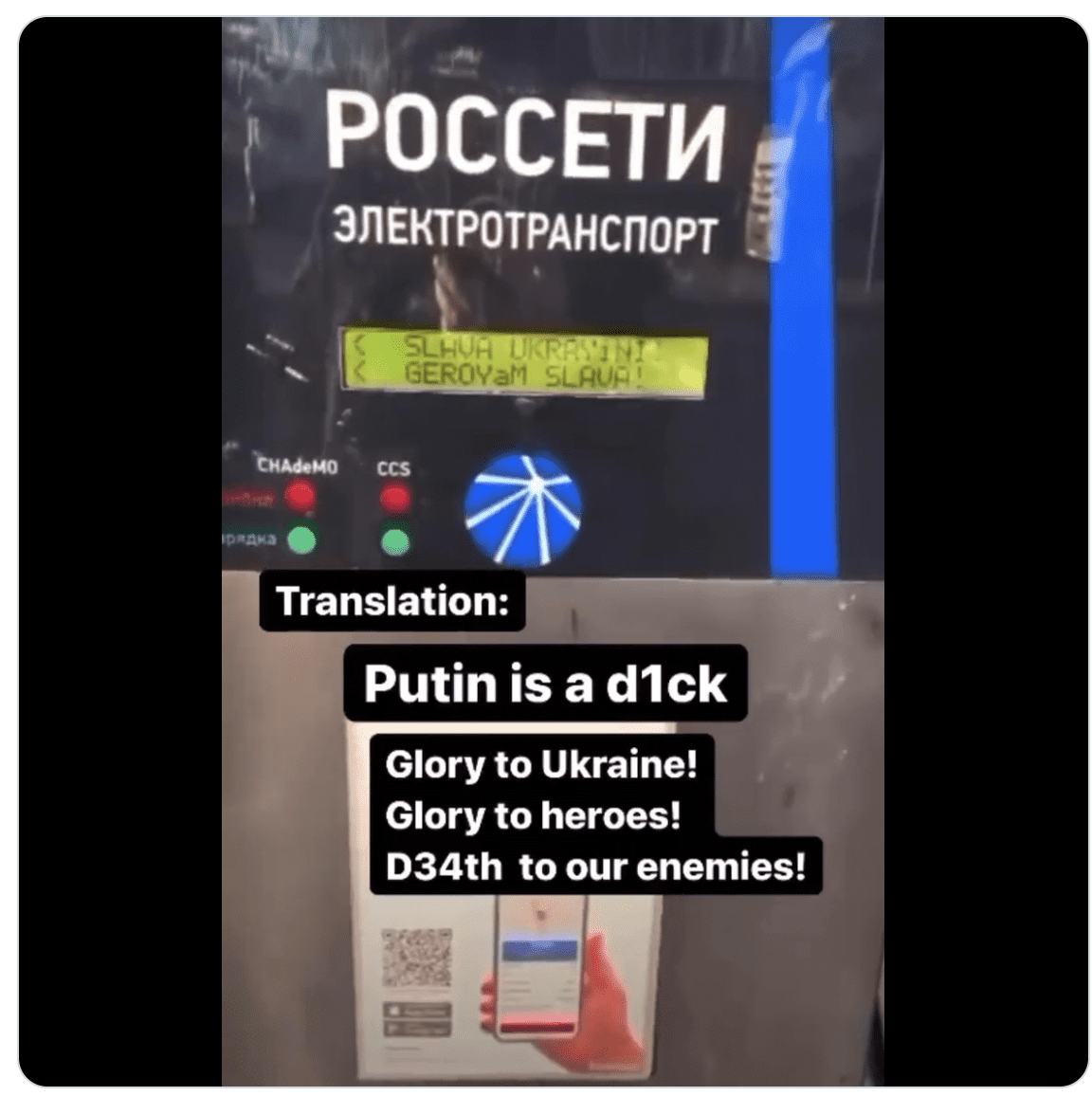
27 February 2022 – 23:06 UTC
Anonymous for Ukraine Leaks Customer Data from Sberbank Russia
While Anonymous leaked the files, the credit for the hack goes to Hacktivist group, Georgia Hackers Society. The two text files (bygng.txt & bankmatbygng.txt) appear to be personal data from the financial institution with the bankmat file containing 4,568 records.
27 February 2022 – 21:00 UTC
CONTI RaaS Suffers for Professing Their Allegiance to the Russian Federation
DarkOwl just discovered 393 JSON files containing private Jabber chats from the ransomware group since January 2021 leaked online. Many of CONTI’s affiliates were displeased with the group’s alliance with Russia.
27 February 2022 – 19:00 UTC
ATW Claims to Take Down CoomingProject Ransomware Group
AgainstTheWest assesses “CoomingProject are actually one of the dumbest “threat” groups online.” AgainstTheWest statement on Twitter:
“RIP CoomingProject. All data on them is being passed to relevant authorities in France.”
27 February 2022 – 16:54 UTC
Cyberpartisans Take Belarusian Railway’s Data-Processing Network Offline
The hacktivist group of cyber specialists located in Belarus managed to force the railway switches to manual control mode, to significantly slow down the movement of trains. The webservers for the railway’s domains (pass.rw.by, portal.rw.by, rw.by) are also offline.
The rail services are being essentially held hostage until Russian troops leave Belarus and there is peace in Ukraine.
27 February 2022 – 11:00 UTC
AgainstTheWest Ransomware Gang Enters the Campaign
AgainstTheWest (ATW) claims to have attacked Russia’s Department of Digital Development and Communications of the Administration of the Pskov Region with their own custom “wiper” malware. All data has been reportedly saved and deleted.
27 February 2022 – 09:00 UTC
Anonymous Attacks Russian Critical Infrastructure
Tvingo Telecom offers fiber-optic networking, internet and satellite services. Tvingo Telecom is a major provider to Russian clients.
27 February 2022 – 00:00 UTC
GhostSec Leaks More Data and Claims Attacks Against Belarusian Cybercriminals, GhostWriter
GhostSec is active in the Anonymous cyber war against Russia and released a sample of databases stolen from additional government and municipality sites across Russia (economy.gov.ru and sudak.rk.gov.ru).
They state on their Telegram channel they have been conducting attacks against “Russian hackers” and the “hacker group GhostWriter” (a.k.a. UNC1151).
26 February 2022 – 18:00 UTC
IT ARMY of Ukraine Now Active on Telegram
A Telegram Channel titled “IT ARMY of Ukraine” appeared earlier today to help coordinate cyber activities against Russia. The channel has already accumulated over 96K followers. Posts are shared in Ukrainian and English containing target server IP addresses and media for mass distribution on social media.
Videos of what events are really happening across Ukraine have appeared on intercepted Russian State Television channels.
В найближчу годину буде одне із найголовніших завдань!
26 February 2022 – 16:00 UTC
Anonymous Hackers Interrupt Russian State Television
Multiple reports across underground chatrooms suggest Russian television was allegedly briefly interrupted to play Ukrainian music and display national images. (Source)
Ukraine’s telecommunications’ agency also announced that Russia’s media regulator’s site was down as well.
26 February 2022 – 09:00 UTC
Russia Restricts Facebook and Twitter to Control Information
Open source internet monitoring reporting organizations discovered Twitter has been blocked by multiple ISPs across Russia. Ukraine’s government is regularly posting on social media to show the Russian people they are still fighting in the invasion. Cybercriminals and hacktivist campaigns also disrupt Russia’s information operations by calling out disinformation bots and taking critical communications sites offline. Twitter has reportedly blocked account registrations from IPs originating in the Russian Federation.
Russia’s state-controlled television station, RT, is still offline.
26 February 2022 – 01:00 UTC
Hackers Leak Data from Belarusian Weapons Manufacturer Tetraedr on the Darknet
Anonymous Liberland and the Pwn-Bär Hack Team announce the start of #OpCyberBullyPutin and leak a two-part archive (200GB total) of confidential employee correspondences from prominent defense contractor and radar manufacturer, Tetraedr in Belarus. The first part is the most recent 1,000 emails from each employee inbox, in .EML format. The second part is a complete archive of each inbox in .PST format.
The hacktivists stated they successfully attacked the company through an unpatched ProxyLogon security vulnerability.
25 February 2022 – 23:30 UTC
Russian Military Radio Frequencies Hijacked
Ukrainian radio frequency (RF) hackers intercepted Russian military numbers stations UVB-76, frequency 4625KHz, and trolled Russia communications by playing Swedish pop group Caramella Girls’ Caramelldansen on top of the radio waves.
The group also successfully intercepted frequencies utilized by Russian strategic bomber planes.
25 February 2022
CoomingProject Ransomware Group Announces Support for Russia
Another ransomware gang sides with Russia officially declaring war against anyone conducting cyber attacks against the Russian government on their Telegram channel.
“Hello everyone this is a message we will help the Russian government if cyber attacks and conduct against Russia”
25 February 2022 – 21:00 UTC
Russia’s Gasprom Energy Corporation Knocked Offline
Headquartered in St. Petersburg, Gasprom (ПАО “Газпром”) is the largest natural gas transmission company in Eastern Russia. The company is mostly owned by the Russian government even though the shares are traded publicly.
The Anonymous hacktivist collective, operating their campaign against Russia via the hashtag #OpRussia, has claimed responsibility.
25 February 2022 – 20:00 UTC
Anonymous Hackers Leak Database for Russia’s Ministry of Defense (MoD)
Russia’s gov.ru and mil.ru website server authentication data, including hundreds of government email addresses and credentials, surface on transient deep web paste sites and Telegram channels. Another leak consisting of 60,000 Russian government email addresses is also now in circulation.
GhostSec, also participating in Anonymous’s cyberwar against Russia, #OpRussia, claimed all subdomains for Russia’s military webservers were offline hours earlier as of 11:00 UTC.
Over around 100+ subdomains for the russian military were hosted on this IP (you may check DNSdumpster for validation) now all downed. In Support of the people in Ukraine WE STAND BY YOU!
25 February 2022
CONTI’s decision to side with Russia has dire consequences for the RaaS Gang
The ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) gang CONTI (a.k.a. CONTI News) has officially sided with the Russian Federation against “Western warmongers” in the conflict.
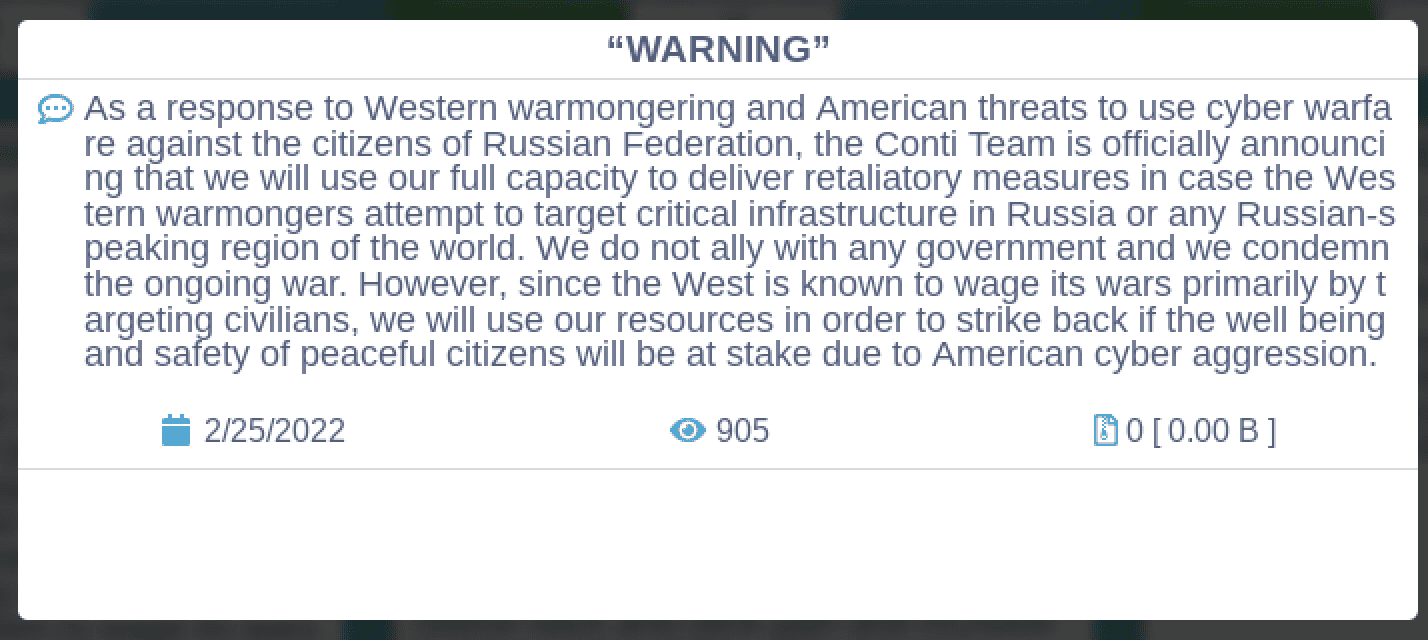
Many of their affiliate partners are reportedly in disagreement – siding with Ukraine – which became evident once certain private chats were leaked on their internal affiliate platform on social media. It’s uncertain how these political divisions will impact the effectiveness of the ransomware gang’s campaigns. Conti revised their WARNING statement claiming they do “not ally with any government and we condemn the ongoing war.”
25 February 2022 – 16:30 UTC
Hundreds of Russian IP Addresses Appear on Deep Web for Targeting
Over 600 IP addresses correlating to key Russian web services emerge on transient paste sites and underground hacker forums. (Source DarkOwl Vision)
25 February 2022 – 05:00 UTC
Anonymous Threatens to Take Russian Industrial Control Systems Hostage
The hacker group known as Anonymous stepped up its participation in defending Ukrainians through its cyber war with Russia. In an ominous video posted to Twitter, the group called for UN to establish a “neutral security belt” between NATO and Russia to ease tensions. They elevated their influence by threatening to “take hostage industrial control systems” against Russia. Expect Us. We do not forgive. We do not forget.
“If tensions continue to worsen in Ukraine, then we can take hostage… industrial control systems.” Expect us. Operation #Russia Engaged
24 February 2022 – 19:00 UTC
Free Civilian Tor Service Announces 54 New Ukrainian Government Database Leaks
The administrator of the Free Civilian Tor Service – who DarkOwl analysts believe is the Raid Forums threat actor, Vaticano – updated their database leaks service, stating they had confidential data for dozens of Ukrainian government services. DarkOwl analyzed these databases closely and confirmed the threat actor likely exfiltrated the data in December 2021. (Source)
24 February 2022 – 17:00 UTC
Russia’s FSB Warns of Potential Attacks against Critical Infrastructure as a result of Ukraine Operations
The National Coordination Center for Computer Incidents (NCSCI) released an official statement warning citizens of Russia of imminent cyber attacks and for the country to brace for the disruption of important digital information resources and services in response to the on-going special military operation in Ukraine.
“Attacks can be aimed at disrupting the functioning of important information resources and services, causing reputational damage, including for political purposes” – NCSCI
24 February 2022 – 05:00 UTC
Cryptocurrency Markets Crash in Wake of Invasion
Bitcoin cryptocurrency fell below $35,000 USD for the first time since January in reaction to the Russian troops crossing over the Ukraine border. Ethereum fell more than 12% in the last 24 hours.
According to open-source reporting, the collective cryptocurrency market has plummeted over $150 billion dollars in value since the tensions began.
beginning of post